Why AI Chatbots Are Rapidly Becoming the Public’s New Favorite News Source

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming nearly every facet of modern life, and the way we consume news is no exception. In recent years, AI-powered chatbots have emerged as an increasingly prominent source of news and information for audiences worldwide. From the integration of AI tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Anthropic Claude, to newer platforms such as Perplexity AI, these conversational agents are rapidly reshaping public habits around accessing, engaging with, and evaluating news content.
This trend is unfolding against a backdrop of shifting consumer behavior. Traditional news media, already grappling with declining print readership and diminishing advertising revenues, now faces another disruptive force: AI chatbots that can instantly summarize, personalize, and deliver news updates in real time. Meanwhile, search engines and social media platforms are evolving to embed AI-driven interactions directly into their ecosystems, offering users the ability to inquire about breaking developments, contextualize complex stories, and follow live updates — all through conversational interfaces.
The acceleration of AI-driven news dissemination raises important questions about trust, credibility, and journalistic integrity. While AI chatbots promise unprecedented convenience and accessibility, they also introduce challenges, including risks of misinformation, hallucination, lack of source transparency, and potential biases. Public trust in AI-generated news content remains in flux, with significant differences across demographic and regional lines. Moreover, the technology’s rapid deployment is sparking debates among media organizations, regulators, and technology companies regarding fair use, revenue sharing, and content licensing.
In this blog post, we will explore the evolving role of AI chatbots as a news source, examining the technological underpinnings, consumer trends, industry impacts, and the broader implications for the future of journalism. We will analyze how chatbots deliver news, compare key players in the space, review emerging trust dynamics, and assess how traditional media is adapting to this AI-powered landscape. Through data-driven insights, charts, and expert perspectives, this post aims to provide a comprehensive view of how conversational AI is gaining ground in one of society’s most critical domains: the public’s access to information.
The Changing Landscape of News Consumption
The landscape of news consumption has undergone a seismic shift over the past decade, as digital technologies continue to reshape how people access, interpret, and engage with current events. Traditional media outlets—once the primary gatekeepers of information—now operate in an environment characterized by audience fragmentation, declining trust, and an unprecedented proliferation of digital alternatives. This disruption has accelerated with the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly AI-powered chatbots, which are rapidly gaining popularity as a convenient and personalized source of news.
A critical factor driving this transformation is the ongoing decline in traditional news consumption. Print media has been on a steady downward trajectory for years, with newspaper circulation and advertising revenues plummeting in most regions. Television news, while still widely watched by older audiences, is also experiencing erosion, particularly among younger demographics who increasingly rely on digital platforms for information. Even digital-native news outlets face mounting challenges, as audiences gravitate toward social media, short-form video, and AI-driven services that promise faster, more engaging, and often more interactive experiences.
The rise of AI chatbots fits squarely within this broader context. These tools cater to a new generation of news consumers—primarily younger, mobile-first users—who prioritize immediacy, personalization, and accessibility. Rather than visiting multiple websites or scrolling through lengthy articles, users can now ask AI chatbots direct questions about current events, request concise summaries, or receive curated news briefings on topics of interest. This conversational interface represents a paradigm shift from the traditional broadcast model of journalism to an interactive, on-demand model that puts user agency front and center.
Several factors contribute to the appeal of AI chatbots as news sources. Speed and convenience are paramount: chatbots can provide instant answers to user queries, drawing on vast datasets and real-time updates. Personalization is another key driver, as AI models learn user preferences over time and tailor news delivery accordingly. Moreover, chatbots can break down complex topics into digestible formats, making information more accessible to audiences who may find traditional reporting dense or intimidating. In multilingual contexts, AI-powered translation capabilities further broaden access, enabling users to engage with news from global sources in their native language.
Importantly, this shift is not occurring in isolation. It is part of a broader realignment of the media ecosystem, in which search engines, social media platforms, and AI applications increasingly compete for attention and influence. Major technology companies are integrating AI chatbots into their core offerings, from search results pages to messaging apps, further blurring the lines between news distribution, search, and conversation. As a result, news consumption is becoming more ambient and conversational, with users encountering news content not only through dedicated outlets but through a diverse array of digital touchpoints.
At the same time, this changing landscape raises significant questions about the quality and integrity of the information being consumed. AI chatbots, while powerful, are not infallible. Issues such as misinformation, hallucination, and source attribution remain challenges that the industry must address. Moreover, the shift toward AI-driven news consumption has implications for the economic sustainability of traditional journalism, as audiences and advertising revenues migrate toward new platforms.
To illustrate the magnitude of this transformation, consider the following chart, which highlights recent trends in news consumption across different media channels:
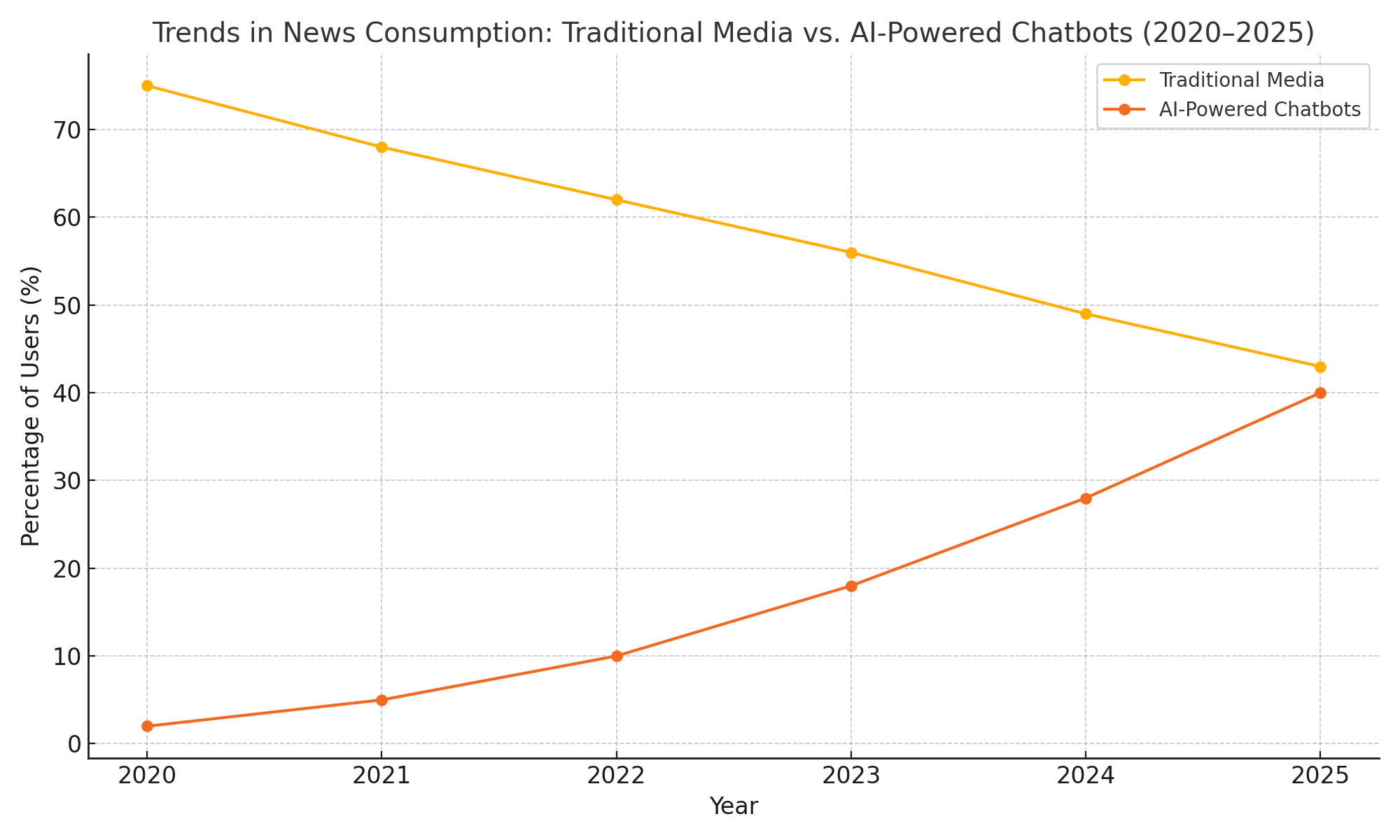
In sum, the rise of AI chatbots as news sources marks a pivotal development in the evolving media landscape. It reflects changing audience expectations, technological innovation, and a reconfiguration of the pathways through which information flows in society. As we proceed, we will delve deeper into how these AI chatbots operate, the opportunities and challenges they present, and their long-term implications for journalism and public discourse.
How AI Chatbots Deliver News
The rapid rise of AI chatbots as an emerging news source is underpinned by a sophisticated blend of natural language processing (NLP), large language models (LLMs), real-time data integration, and adaptive user interfaces. Understanding how these tools deliver news offers valuable insight into their growing appeal and potential challenges. This section provides a detailed look at the technical and functional mechanisms through which AI chatbots operate, as well as the user experience they create in the evolving news ecosystem.
At their core, AI chatbots leverage LLMs—such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and Meta AI’s LLaMA—trained on vast corpora of text from books, websites, and structured datasets. These models possess the capacity to understand and generate human-like language, enabling fluid, conversational interactions with users. However, when applied to news delivery, their performance depends on additional systems that address the limitations of static training data. News is dynamic by nature; thus, AI models must either access real-time information or be continuously updated to remain current.
Several technical approaches are used to ensure chatbots provide up-to-date news content. One widely adopted method involves integrating browsing or retrieval capabilities into the chatbot architecture. For instance, OpenAI’s ChatGPT with browsing capability can conduct live searches, extract relevant information from authoritative news sources, and synthesize responses in real time. Similarly, Google Gemini is designed to pull data from Google’s search index, news feeds, and knowledge graph, providing summaries and updates with contextual depth.
Another approach leverages partnerships with news organizations and dedicated APIs. Platforms such as Perplexity AI aggregate news from curated databases and licensed sources, ensuring higher reliability and proper citation of material. By connecting chatbots to trusted news providers, these integrations enhance both the timeliness and credibility of the information presented. In some cases, AI chatbots also utilize RSS feeds, real-time alerts, and news wire services as part of their input streams.
The user experience of consuming news through AI chatbots differs significantly from traditional formats. Instead of passively receiving headlines or navigating through articles, users engage with chatbots through prompt-based interactions. They may inquire about a particular event, request a summary of recent developments in a region, or seek background information on complex geopolitical issues. The AI responds with concise, context-aware text, often enriched with citations and links for further reading.
Personalization is a defining feature of this mode of news delivery. AI chatbots learn user preferences through interaction history, tailoring content recommendations and framing responses in ways that resonate with individual interests. For example, a user who frequently asks about technology startups may receive proactive updates or suggested queries on emerging trends in that sector. Moreover, AI chatbots can summarize articles at varying levels of detail—offering brief overviews, in-depth explanations, or even multi-part conversations that explore different aspects of a topic.
Integration with platforms and devices further enhances accessibility. AI chatbots are now embedded into search engines (as with Microsoft’s Copilot), mobile operating systems (such as Gemini on Android), messaging apps (including Meta’s WhatsApp and Messenger), and standalone chatbot apps. This ubiquity allows users to engage with news in the context of their daily digital routines, reducing friction and increasing frequency of interaction.
Despite these advances, challenges remain. Accuracy and timeliness are critical in news contexts, yet LLMs are prone to generating hallucinations—plausible but incorrect statements. To mitigate this, leading platforms have introduced features such as source citation, confidence scores, and user feedback loops. Additionally, content moderation systems filter out misinformation and flag potential biases. Companies are also working to improve transparency by disclosing when AI-generated content is used and clarifying the provenance of information.
Ethical considerations extend beyond accuracy. The editorial process in traditional journalism involves human judgment, editorial standards, and accountability mechanisms—elements that are not inherently present in AI-driven news delivery. Without clear disclosure, users may conflate chatbot responses with verified journalism, potentially eroding trust or amplifying unverified narratives. Regulatory frameworks in several regions are beginning to address these concerns, seeking to ensure that AI-based news delivery adheres to standards of transparency, accuracy, and fairness.
To provide a clearer view of the current landscape, the following table compares the news features of several leading AI chatbots:
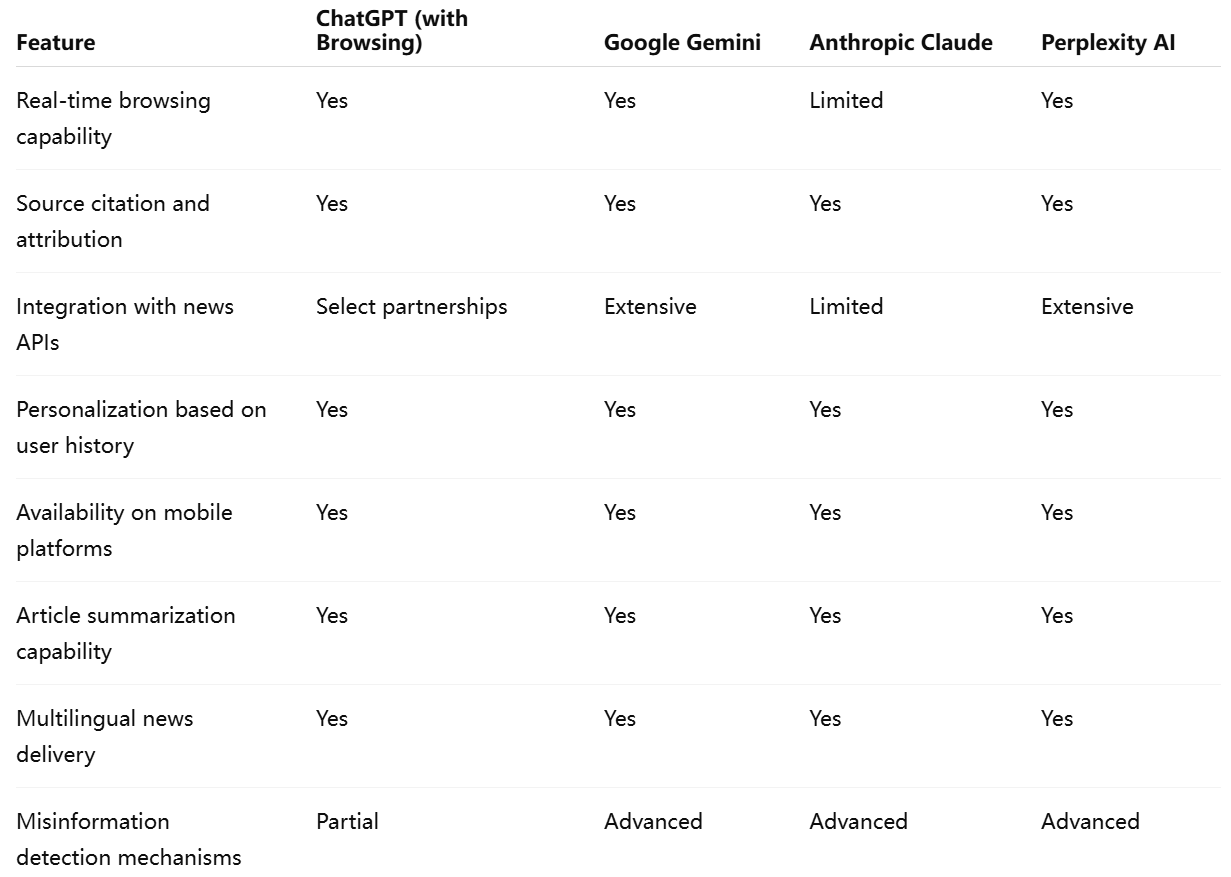
In conclusion, AI chatbots deliver news through an intricate interplay of advanced language models, real-time data integration, and highly personalized user interfaces. While they offer clear advantages in speed, convenience, and accessibility, their emergence also introduces complex challenges related to accuracy, transparency, and editorial responsibility. As these tools continue to evolve, striking the right balance between innovation and integrity will be essential to their long-term success as trusted news sources.
Trust, Credibility, and Public Perception
As AI chatbots increasingly enter the news ecosystem, public trust and perceptions of credibility are critical factors shaping their adoption. While users are drawn to the convenience and personalization that AI-powered news delivery offers, concerns persist about the accuracy, transparency, and editorial integrity of the content presented by these systems. In this section, we examine how public trust is evolving, explore the credibility challenges faced by AI chatbots, and analyze how companies are working to address these concerns.
One of the most salient issues in this evolving landscape is the challenge of accuracy. Large language models (LLMs), even when connected to real-time data feeds, are prone to generating hallucinations—statements that appear factually plausible but are incorrect or unsupported by evidence. In the context of news, where accuracy is paramount, even minor factual errors can undermine public confidence in AI-generated content. Early adopters of AI chatbots for news consumption have reported mixed experiences in this regard: while many appreciate the immediacy and breadth of coverage, instances of erroneous or outdated information have tempered trust.
Compounding this issue is the question of source transparency. Traditional journalism operates under established norms of attribution and editorial oversight. In contrast, AI-generated news responses often aggregate content from multiple sources, sometimes without clear citation or disclosure of origin. Although platforms like ChatGPT with browsing, Google Gemini, and Perplexity AI are increasingly integrating citation features, users frequently remain unsure of the underlying provenance of the information they receive. Without transparent sourcing, it becomes difficult for users to independently verify the accuracy of chatbot-delivered news or to assess potential biases.
The issue of bias further complicates trust dynamics. LLMs reflect the biases present in their training data, which can influence the tone, framing, and selection of news topics. Moreover, as AI chatbots personalize responses based on user interactions, there is a risk of reinforcing echo chambers or delivering content that aligns with user preferences rather than journalistic objectivity. These tendencies raise ethical questions about the role of AI in shaping public discourse and the extent to which such systems may inadvertently contribute to polarization.
Despite these challenges, surveys indicate a nuanced and evolving public perception of AI chatbots as news sources. Trust in AI-generated news varies significantly across demographic and geographic lines. Younger audiences, particularly those in the 18–34 age group, tend to exhibit higher levels of openness to chatbot-delivered news, viewing these tools as a natural extension of their digital-first information habits. Conversely, older users often express greater skepticism, citing concerns about accuracy, transparency, and the perceived absence of human editorial judgment.
Regional differences also play a role. In markets with high levels of trust in traditional media, such as parts of Western Europe, adoption of AI chatbots for news has been more cautious. In contrast, regions where public trust in legacy media is lower—such as the United States and parts of Asia—have seen more rapid uptake of AI-driven news services, often mediated through platforms like messaging apps and social media integrations.
To illustrate these trends, consider the following chart, which summarizes current survey data on public trust in AI chatbots as news sources across different age groups and regions:
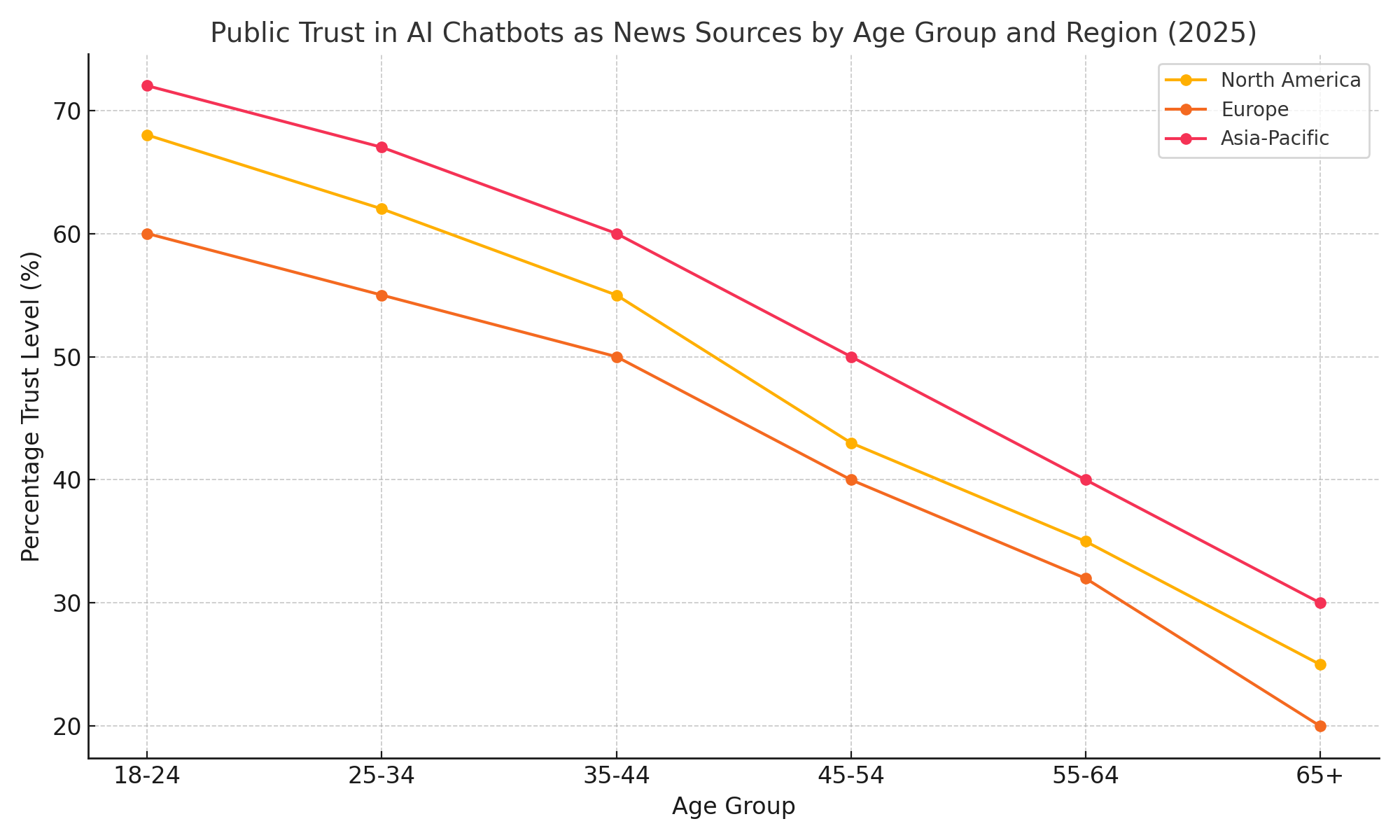
In response to these trust challenges, leading AI companies are taking proactive steps to enhance credibility. Several key strategies are emerging:
- Citation and Attribution — Chatbots increasingly cite sources for news content, linking to original articles and providing users with pathways for independent verification.
- Updated Browsing and Retrieval Models — Continuous improvements in browsing capabilities ensure that chatbots draw on the most current and reliable information, reducing the risk of outdated or inaccurate responses.
- User Feedback Mechanisms — Platforms encourage users to flag errors or questionable content, creating feedback loops that inform model tuning and future updates.
- Content Transparency — Clear disclosure of AI involvement in content creation is being adopted to ensure users understand when they are engaging with AI-generated responses.
- Editorial Partnerships — Some AI platforms are pursuing partnerships with reputable news organizations, integrating licensed content to improve accuracy and reinforce editorial standards.
While these measures represent meaningful progress, it is clear that building and sustaining public trust will be an ongoing process. The evolving capabilities of AI chatbots must be matched by robust transparency, accountability, and ethical frameworks that align with journalistic principles.
In sum, public trust and credibility remain central concerns in the rise of AI chatbots as news sources. As these technologies continue to mature, the ability of platforms to address issues of accuracy, bias, and transparency will play a decisive role in shaping their long-term viability and public acceptance.
Industry Impacts and the Future of Journalism
The rise of AI chatbots as a significant source of news is not only transforming user behavior but also reshaping the competitive landscape for journalism and media. As conversational AI technologies proliferate across digital platforms, traditional publishers, news aggregators, and broadcasters face mounting pressures to adapt. The ripple effects extend beyond audience engagement to affect advertising models, subscription revenues, content licensing, and even the ethical frameworks that govern modern journalism.
One of the most immediate industry impacts is the phenomenon of traffic cannibalization. AI chatbots, by delivering concise, conversational summaries of news content, increasingly serve as endpoints for user queries. Where users might previously have clicked through to publisher websites, they now obtain the essential information directly within AI interfaces. This dynamic is particularly pronounced in cases where chatbots provide answers without prominently linking to the original sources, thereby reducing referral traffic to news publishers. As a consequence, many publishers report declining site visits, particularly for commoditized news topics where AI summaries suffice to meet user needs.
This shift has profound implications for the economics of journalism. Many news organizations rely heavily on web traffic to generate advertising revenue or to funnel users into subscription paywalls. As AI chatbots interpose themselves between audiences and news outlets, the traditional monetization pathways are disrupted. Smaller publishers and local newsrooms, which are especially dependent on organic search traffic, face heightened risks of revenue erosion in this new ecosystem.
The competitive field is also evolving. AI chatbots are positioning themselves alongside — and in some cases ahead of — search engines, news aggregators, and curated feeds. Platforms such as Perplexity AI offer a hybrid model that combines conversational querying with curated citations, appealing to users who seek both efficiency and transparency. Meanwhile, search giants like Google and Microsoft are integrating AI chatbot functionalities into search experiences, fundamentally altering how users discover and consume news. This raises strategic questions for traditional aggregators and social media platforms, which must now compete with increasingly sophisticated conversational agents.
In response, news organizations are pursuing a range of adaptive strategies. One approach involves partnerships with AI companies to license content and ensure proper attribution. Major publishers such as The Associated Press, Reuters, and Axel Springer have inked deals with AI firms, exchanging structured news feeds for licensing fees or revenue shares. These partnerships aim to create more sustainable models for AI-powered news delivery while reinforcing editorial standards.
Simultaneously, AI-assisted journalism is gaining momentum within newsrooms themselves. Journalists are adopting AI tools to automate routine reporting tasks, analyze large datasets, and generate first drafts for articles. Rather than replacing human reporters, these tools augment editorial capabilities, freeing up resources for investigative and analytical work. The integration of AI into newsroom workflows underscores the technology’s potential to support, rather than solely disrupt, the journalistic process.
Regulatory frameworks are beginning to emerge to address the complex legal and ethical dimensions of AI-driven news. In Europe, discussions around the EU’s AI Act and Digital Services Act have highlighted concerns about content provenance, intellectual property rights, and misinformation risks. Similar debates are unfolding in the United States and Asia, where regulators are grappling with how to balance innovation with protections for journalism and the public sphere. These evolving policies will play a critical role in shaping the future interplay between AI technologies and the media industry.
Looking ahead, several potential scenarios emerge for the future of journalism in an AI-powered landscape:
- Coexistence and Integration — Newsrooms adopt AI tools to enhance reporting and delivery, while AI chatbots become key distribution channels for trusted content.
- Consolidation of Platforms — A handful of dominant AI platforms mediate most news consumption, compelling publishers to negotiate partnerships to maintain visibility and revenues.
- Disruption and Disintermediation — Unchecked AI-driven news delivery undermines traditional journalism’s economic base, leading to further newsroom closures and a degraded public information ecosystem.
- Regulatory Intervention — Strong regulatory frameworks enforce transparency, licensing, and attribution requirements, ensuring a more balanced and sustainable media environment.
In all scenarios, the central challenge will be to preserve the core values of journalism—accuracy, accountability, and public service—amid rapid technological change. As AI chatbots continue to evolve, their long-term impact on journalism will depend on how effectively stakeholders across the media, technology, and regulatory sectors can navigate this complex and dynamic transition.
Evolving User Expectations and the Path to Responsible AI News
As AI chatbots continue to gain prominence in the news ecosystem, user expectations are evolving at an equally rapid pace. Beyond speed and convenience, modern news consumers are beginning to demand greater transparency, contextual depth, and ethical accountability from AI-driven services. In parallel, there is a growing recognition—both within technology companies and among regulators—that the path to responsible AI-powered news delivery must be shaped by intentional design choices and collaborative governance.
One of the clearest trends is the increasing demand for contextual awareness. Users no longer seek isolated facts but expect AI chatbots to provide meaningful context, highlight differing viewpoints, and reference source credibility. This marks a departure from early AI news summarization, which often favored brevity over nuance. In response, leading platforms are enhancing their models to offer multi-perspective narratives, surface primary sources, and explicitly indicate when information is incomplete or contested.
Alongside contextual depth, ethical transparency has become a key expectation. Surveys show that users want to know when content is AI-generated, what sources inform chatbot responses, and how potential biases are mitigated. The deployment of clear disclosure mechanisms—such as visible AI usage labels and source citations—is becoming a de facto requirement for building and sustaining user trust.
Equally important is the expectation that AI chatbots should actively guard against misinformation and disinformation. Given the proliferation of false narratives online, users increasingly look to trusted AI platforms as a bulwark against manipulation. This places significant responsibility on technology companies to continuously improve content verification systems, engage in proactive moderation, and collaborate with reputable news organizations and fact-checking networks.
From a governance perspective, industry leaders are moving toward greater transparency and accountability. Initiatives such as OpenAI’s model documentation, Google’s AI Principles, and Anthropic’s “Constitutional AI” approach reflect a growing commitment to responsible innovation. However, these voluntary efforts must be complemented by regulatory frameworks that enshrine standards of accuracy, fairness, and public interest.
Regulators are beginning to respond with policies designed to promote AI transparency, licensing, and editorial accountability. Proposed legislation in the European Union and similar initiatives in the United States and Asia aim to ensure that AI chatbots do not operate in a legal or ethical vacuum. Effective regulation will require ongoing dialogue between policymakers, technology providers, news organizations, and civil society.
Ultimately, the path to responsible AI news hinges on balancing innovation with integrity. AI chatbots hold immense potential to democratize access to information, broaden public engagement, and enhance media literacy. But realizing this potential depends on addressing the fundamental challenges of trust, credibility, and ethical responsibility.
As user expectations evolve, so too must the AI news experience. The future of journalism in an AI-driven world will be shaped not merely by technical capabilities, but by the values and principles embedded in these systems—and by the collective will of stakeholders to ensure that the public good remains at the heart of news delivery.
Conclusion
The emergence of AI chatbots as a mainstream source of news represents one of the most significant shifts in the modern media landscape. Fueled by advances in large language models, real-time data integration, and conversational interfaces, these technologies are redefining how information is accessed, consumed, and shared. As platforms like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity AI, and Anthropic Claude gain traction, they are fundamentally altering the dynamics of news delivery — making it more immediate, personalized, and interactive.
This transformation is unfolding amid broader changes in audience behavior. Users increasingly favor convenience, speed, and relevance, gravitating toward AI chatbots that can provide concise summaries and tailored insights on demand. Younger, mobile-first generations are particularly receptive to these tools, while traditional modes of news consumption continue to decline.
Yet, this evolution also brings complex challenges. Issues of accuracy, transparency, bias, and source attribution remain pressing concerns. Public trust in AI-generated news varies widely, shaped by demographic, cultural, and regional factors. As AI chatbots become more deeply embedded in the digital ecosystem, the imperative to uphold journalistic standards and safeguard the public’s right to trustworthy information grows ever more urgent.
The impact on the journalism industry is equally profound. From traffic cannibalization to shifts in monetization, AI chatbots are forcing publishers to rethink longstanding business models. At the same time, AI presents opportunities for innovation—both in content delivery and in newsroom operations. The rise of AI-assisted journalism demonstrates how human and machine collaboration can enhance editorial capacity, provided that ethical frameworks and professional standards are rigorously maintained.
Looking to the future, the relationship between AI chatbots and journalism will continue to evolve. Whether this results in coexistence, further disruption, or a new synthesis will depend on the actions of multiple stakeholders: technology companies, news organizations, regulators, and the public itself. Transparency, accountability, and collaboration will be essential to navigating this new frontier and ensuring that AI enhances rather than undermines the vital role of journalism in democratic societies.
In conclusion, as AI chatbots gain ground as news sources, they present both unprecedented opportunities and formidable challenges. Their long-term success — and their impact on the future of journalism — will be determined not only by technological advances but by the collective commitment to uphold the principles of truth, integrity, and the public good in an increasingly AI-driven world.
References
- https://www.reuters.com/technology/chatgpt-now-surfs-web-brings-latest-news
- https://blog.google/technology/ai/google-gemini-ai-explained
- https://perplexity.ai/about
- https://www.anthropic.com/index/claude
- https://openai.com/chatgpt
- https://www.niemanlab.org/2024/ai-tools-reshaping-newsrooms
- https://pressgazette.co.uk/media-business/ai-chatbots-impact-on-news-publishers
- https://www.ft.com/content/ai-news-consumption-trends
- https://www.poynter.org/ethics-trust/ai-generated-news-content
- https://www.theverge.com/2024/ai-news-chatbots-trust
