OpenAI, Cisco, and Oracle Collaborate on Stargate UAE Data Center

In a significant stride toward shaping the global AI infrastructure landscape, OpenAI has announced a strategic collaboration with Cisco and Oracle to develop an advanced artificial intelligence data center in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). This ambitious initiative marks OpenAI’s first major international expansion of its infrastructure, reinforcing the company’s commitment to decentralizing AI capabilities and tapping into global innovation ecosystems. Set in Abu Dhabi, the facility will be part of the expansive "Stargate" network—a visionary project dedicated to building some of the most powerful AI supercomputing environments on Earth.
This collaborative venture is more than just a technological deployment—it represents a convergence of geopolitical ambition, economic transformation, and cutting-edge scientific development. The UAE, under its long-term national strategy for AI and digital transformation, has made clear its intention to be a global epicenter for artificial intelligence research and innovation. With an emphasis on clean energy, sovereign compute, and economic diversification, the project has been positioned as a cornerstone of the country's next-generation digital infrastructure.
OpenAI's participation signifies its increasing role not just as a technology provider but as a key architect of AI ecosystems beyond U.S. borders. The organization, renowned for developing foundational models like GPT-4 and the multimodal GPT-4o, brings both technical prowess and strategic vision to the table. Cisco, as a leader in networking and cybersecurity, will ensure the stability, efficiency, and security of data center operations. Oracle, on the other hand, is poised to deliver its AI-optimized cloud infrastructure, thereby enabling seamless orchestration and scaling of massive AI workloads.
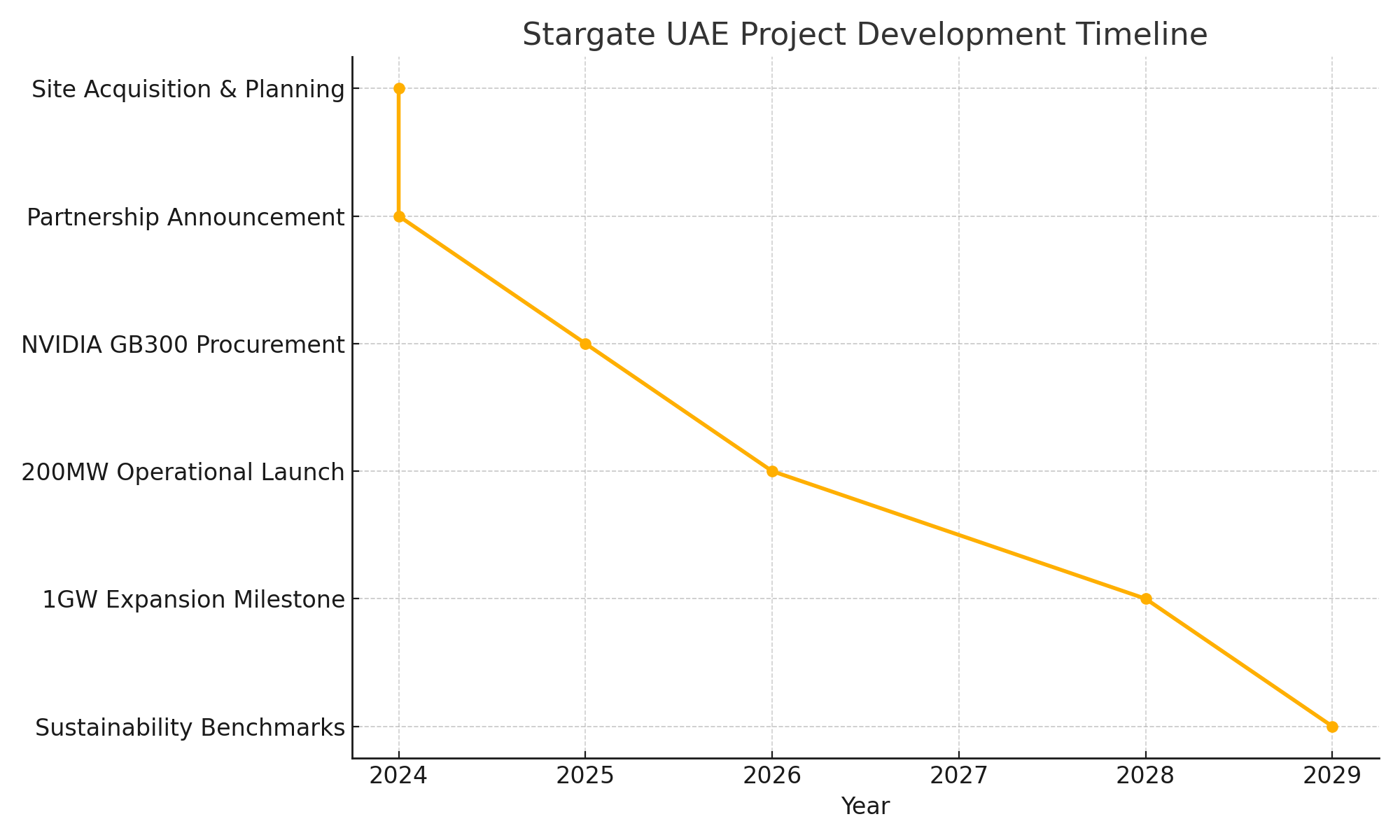
At the heart of the project is a 1-gigawatt data center—a facility that will initially provide 200 megawatts of computing power by 2026. This infrastructure will reportedly be powered by NVIDIA’s cutting-edge GB300 Grace Blackwell superchips, expected to number around 100,000, allowing for unprecedented performance in training and deploying large-scale generative models. The facility’s design also incorporates state-of-the-art sustainability features, including the use of solar, nuclear, and natural gas power to ensure reduced environmental impact.
The strategic collaboration also includes G42, a leading UAE-based AI firm, which has been instrumental in advancing AI initiatives in the region and will oversee construction and on-ground execution. This alliance of leading American and Emirati players is emblematic of a new global AI order—one that is increasingly multipolar and focused on international partnerships rather than centralized innovation.
Moreover, the Stargate UAE project carries deep economic implications. It is expected to catalyze the local job market by attracting top-tier AI talent, foster the growth of ancillary digital industries, and create new educational and training opportunities. With the UAE's already forward-thinking regulatory environment and infrastructure readiness, this project could serve as a prototype for future international AI collaborations.
This blog post will explore the details of the UAE data center project in depth, examining the roles and technologies each partner brings to the initiative, the anticipated economic and strategic benefits, and its broader implications on the global AI landscape. Through detailed analysis, supported by charts and tables, we aim to provide a comprehensive view of how this project could redefine the future of AI deployment across borders.
In the following sections, we will delve into the technical specifications of the project, examine the strategic motivations behind each stakeholder’s involvement, and place the initiative in the context of global AI infrastructure trends. We will also analyze the economic impact of this monumental endeavor and what it signals for the future of AI power dynamics in the Middle East and beyond.
The UAE has long positioned itself as a hub for innovation, and this partnership with OpenAI, Cisco, and Oracle underscores that commitment. As the global AI arms race intensifies, the Middle East—through infrastructure projects like Stargate UAE—may well emerge as one of its central battlefields. This blog will unpack how and why.
Project Scope and Technical Specifications
The joint development of the Stargate UAE data center by OpenAI, Cisco, and Oracle represents a formidable convergence of cutting-edge hardware, resilient cloud infrastructure, and sovereign digital architecture. With its location strategically set in Abu Dhabi, this ambitious project is slated to be among the largest and most advanced artificial intelligence facilities in the world, designed to meet the growing global demand for high-performance computing dedicated to generative AI.
Infrastructure Design and Development Phases
The project’s foundational phase outlines a scalable model that begins with an operational capacity of 200 megawatts by the year 2026, with long-term ambitions to scale up to a staggering 1 gigawatt. To contextualize, this level of power provisioning far exceeds that of typical hyperscale data centers and places the Stargate UAE facility among the top tier of global computing hubs.
The architecture of the center is being engineered with modular expansion in mind. The phased rollout ensures minimal disruption to service delivery while incrementally introducing greater compute and storage capacity. This enables real-time adaptation to evolving AI demands and global compute requirements, particularly as foundational models continue to scale exponentially in complexity and size.
Compute Power: NVIDIA GB300 Grace Blackwell Integration
A key technical highlight of the Stargate UAE facility is its use of NVIDIA’s state-of-the-art Grace Blackwell GB300 GPUs. These processors are designed explicitly for high-throughput AI training and inference at hyperscale levels. The center will deploy approximately 100,000 GB300 chips, a configuration that positions it as one of the most compute-dense AI supercomputing installations globally.
The Grace Blackwell platform merges CPU and GPU architectures into a cohesive system, thereby reducing data bottlenecks and drastically improving energy efficiency. This innovation is essential for running large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 and future multimodal models that integrate text, vision, speech, and reinforcement learning. Such compute capacity also empowers the development and deployment of regional AI models, including those fine-tuned for Arabic language and Middle Eastern contexts.
Cloud Infrastructure and Orchestration by Oracle
Oracle plays a pivotal role in providing the underlying cloud framework upon which OpenAI’s workloads will operate. Oracle’s Generation 2 Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers high-speed networking, autonomous data management, and ultra-low latency—features critical for training AI models with billions or even trillions of parameters.
Moreover, OCI is integrated with Kubernetes-based orchestration layers, allowing dynamic scaling of compute clusters, efficient management of containerized AI services, and granular observability. The infrastructure is tailored for massive-scale parallel processing, which is instrumental in training foundation models efficiently.
Oracle’s expertise also extends to disaster recovery, failover systems, and multi-tenancy, thereby ensuring that OpenAI’s deployments maintain high availability and compliance with global data residency norms. This is particularly significant in the UAE context, where data sovereignty and regulatory adherence are essential pillars of digital strategy.
Advanced Networking, Security, and Monitoring by Cisco
Cisco’s contributions are central to the project’s ability to guarantee uninterrupted, secure, and observable AI operations. As the backbone of the network infrastructure, Cisco is deploying its latest innovations in data center switching, firewalls, zero-trust architecture, and AI-enhanced observability tools.
The Stargate UAE data center will utilize Cisco Nexus switches with silicon photonics for high-bandwidth, low-latency data transport between compute nodes. In parallel, the implementation of Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense and Identity Services Engine (ISE) ensures zero-trust access control at every layer of the stack—from physical access points to virtualized services.
Furthermore, Cisco's observability suite leverages AI-driven analytics to proactively identify system anomalies, optimize energy use, and predict potential failures. This predictive approach aligns with the project's emphasis on reliability, sustainability, and long-term cost efficiency.
Energy Architecture: Toward Sustainable AI Compute
Powering such a massive facility comes with inherent sustainability challenges, particularly in a region known for its arid climate and high energy demands. The Stargate UAE project confronts this head-on by adopting a diversified energy approach that leverages nuclear, solar, and natural gas sources. The aim is to offset the environmental cost of compute with a clean energy footprint that aligns with the UAE’s sustainability commitments under Vision 2031.
Cooling, one of the most energy-intensive operations in data centers, will be handled through a combination of seawater cooling systems and AI-optimized thermal management algorithms. These systems are designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures while minimizing water and energy consumption.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Sovereignty
A foundational component of the Stargate UAE strategy is ensuring full compliance with Emirati data localization laws and international privacy standards. The facility is engineered to host sovereign AI systems that do not require transnational data transfers for training or inference.
In effect, this ensures that datasets relevant to Middle Eastern cultures, governance, and economies can be processed within the UAE, reducing reliance on foreign infrastructure while enhancing national digital autonomy. This is a particularly compelling value proposition for regional governments, universities, and private enterprises seeking to deploy LLMs without exposing sensitive data to external jurisdictions.
Strategic Partnerships and Economic Implications
The Stargate UAE initiative is not solely a technical marvel; it is also a calculated geopolitical and economic maneuver orchestrated through a nexus of high-profile partnerships. This section explores the strategic relationships among OpenAI, Cisco, Oracle, G42, and supporting stakeholders such as SoftBank and NVIDIA. It also analyzes the broader economic implications for the UAE and the wider Middle East as it positions itself at the forefront of the artificial intelligence revolution.
OpenAI’s Expanding Global Footprint
OpenAI’s participation in the Stargate UAE data center is a marked shift from its historically U.S.-centric infrastructure strategy. By collaborating with partners in the Middle East, OpenAI is extending its influence into regions that are not just economically dynamic but are also rapidly adopting sovereign AI frameworks. This expansion aligns with OpenAI’s strategic imperative to decentralize access to high-performance computing and ensure global inclusivity in the development and deployment of generative AI.
Moreover, OpenAI’s involvement in the UAE—a region known for both its investment prowess and strategic autonomy—signifies a deliberate pivot to infrastructure diplomacy. By anchoring part of its AI training and inference capabilities in Abu Dhabi, OpenAI ensures proximity to regional data, cultural contexts, and localized AI innovation, thus enhancing the contextual relevance of its models in non-Western environments.
Cisco and Oracle: Enterprise-Grade AI Enablement
Cisco and Oracle serve not only as technology providers but also as critical enablers of enterprise-scale AI readiness. Cisco, with its robust portfolio of zero-trust security, observability, and data center networking, plays a foundational role in establishing a secure and scalable operational environment. Its participation enhances the credibility of the project and ensures compliance with global cybersecurity standards, which are paramount given the geopolitical sensitivities surrounding data centers.
Oracle’s cloud infrastructure, meanwhile, underpins the operational stack with enterprise-grade resiliency, data governance, and vertical-specific optimizations. The partnership is further strengthened by Oracle’s recent collaborations with OpenAI to run its models on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), a move that ensures seamless integration across global deployments. This arrangement positions Oracle as not merely a vendor but a key orchestrator of next-generation AI workloads.
G42: The Emirati Catalyst
The participation of G42, a leading Emirati AI company backed by Abu Dhabi’s Mubadala Investment Company, is central to the project’s strategic localization. G42 is responsible for constructing the data center, navigating regulatory environments, and ensuring alignment with the UAE’s digital vision. The company has previously worked with OpenAI on multiple initiatives and is a critical intermediary in translating global AI innovations into regionally adapted services.
The collaboration also underscores a growing pattern of technologically sovereign partnerships between U.S.-based AI firms and Middle Eastern tech conglomerates. These alliances are being designed to address both national security concerns and the need for local AI capabilities. For the UAE, which has prioritized AI as a pillar of its economic diversification strategy, this partnership further solidifies its global relevance in the field of digital transformation.
Financial Contributions and Stakeholder Roles
The Stargate UAE project is made possible through a multi-layered funding and technology ecosystem. SoftBank, the Japanese investment powerhouse, is reportedly contributing financial capital to support the facility’s build-out. NVIDIA, whose GB300 chips are central to the data center’s compute strategy, plays a dual role as both supplier and stakeholder. These contributions underscore the global nature of the partnership and the breadth of institutional commitment behind the initiative.
This ecosystem approach reduces dependency on a single entity and distributes strategic risk across multiple actors, thereby enhancing the project’s resilience and longevity. It also creates a layered structure of accountability and shared interest, which is critical for large-scale infrastructure deployments.

This collaborative matrix is not merely about pooling resources; it represents a carefully constructed alignment of strategic interests, ranging from technological dominance to geopolitical influence.
Economic Implications for the UAE
The economic implications of the Stargate UAE data center are manifold. First, it is expected to generate thousands of high-skilled jobs in the areas of data science, cybersecurity, data center operations, and AI ethics. These roles are critical for building local expertise and reducing the region’s reliance on imported talent.
Second, the project will act as a magnet for ancillary businesses such as chip manufacturing support, AI research institutions, and clean energy vendors. Over time, this ecosystem effect is likely to catalyze the emergence of a robust digital economy centered around Abu Dhabi and, by extension, the wider GCC region.
Third, the partnership sets a precedent for regulatory innovation. The UAE is already home to progressive frameworks around data protection and AI governance, and the Stargate initiative is expected to stimulate further policy advancements. This regulatory clarity is particularly attractive for global companies looking to establish AI operations in jurisdictions that balance innovation with legal certainty.
Fourth, the increased demand for AI capabilities will inevitably spill over into sectors such as healthcare, education, finance, and logistics. As enterprises and public agencies adopt OpenAI-powered solutions via Oracle’s infrastructure, the benefits of the project will permeate deep into the socio-economic fabric of the UAE.
Geopolitical Significance
On the geopolitical front, the Stargate UAE project is emblematic of a new era in international technology alliances. It reflects the UAE’s rising status as a trusted partner in the global AI order—capable of managing sensitive data and hosting world-class infrastructure. For the U.S., this project demonstrates the power of soft tech diplomacy, enabling American firms to extend their global reach through strategic partnerships without direct government intervention.
Moreover, it allows for a multipolar AI development model, where countries outside the traditional U.S.-China AI axis can play a pivotal role in shaping the future. In a landscape marked by concerns over data sovereignty, digital colonialism, and AI ethics, Stargate UAE offers a compelling blueprint for ethically aligned, globally distributed AI infrastructure.
In summary, the strategic partnerships driving the Stargate UAE initiative reflect a blend of technological ambition, economic foresight, and geopolitical nuance. With stakeholders ranging from Silicon Valley giants to Middle Eastern investment firms, the project is not merely about data and chips—it is about shaping the future of digital sovereignty and global innovation.
Global Context and Future Prospects
The Stargate UAE initiative, though regionally situated, is undeniably global in its ambition and implications. As nations and corporations intensify the race to build sovereign AI infrastructure, the collaboration between OpenAI, Cisco, Oracle, and the UAE marks a turning point in the distribution and architecture of artificial intelligence compute capabilities. This section places the Stargate UAE project in the context of international trends, compares it with other large-scale AI infrastructure initiatives, and explores its influence on future policy, technological evolution, and the balance of global AI power.
The Global AI Infrastructure Race
In recent years, the artificial intelligence landscape has undergone a rapid metamorphosis—from centralized compute deployments in Silicon Valley to distributed, multi-jurisdictional infrastructure projects spanning continents. The surge in demand for foundational models, multimodal AI systems, and real-time inference services has prompted leading organizations to rethink traditional cloud paradigms. These shifts are driven by several key factors:
- Latency and Proximity: AI applications are increasingly being deployed in real-time use cases such as autonomous driving, healthcare diagnostics, and finance. These applications require data centers close to the point of use to minimize latency.
- Sovereignty and Compliance: Governments are instituting strict data localization laws, compelling AI firms to train and host models within specific geopolitical boundaries to ensure regulatory compliance and national security.
- Energy and Sustainability: As AI infrastructure becomes more energy-intensive, there is growing demand for regions with access to renewable or low-cost energy sources to offset environmental impact and ensure operational efficiency.
- Geopolitical Realignment: The growing tension between major powers, particularly the United States and China, has created a need for “non-aligned” or “neutral” AI zones. These zones allow global firms to expand without entanglement in techno-nationalist conflicts.
Within this context, the Stargate UAE project is highly significant. It not only addresses all the above concerns but also establishes the UAE as a sovereign, neutral zone that is technologically sophisticated, diplomatically stable, and energetically self-sufficient.
Comparison with Other Stargate and Hyperscale Projects
The Stargate network, conceived by OpenAI’s broader ecosystem, is designed to be a distributed network of hyper-efficient data centers tailored for advanced AI workloads. In addition to the UAE facility, multiple sites are either planned or under development, including in the United States and Southeast Asia.
The flagship site, Stargate Abilene (Texas), is reported to be among the largest AI computing hubs in North America, featuring tens of thousands of NVIDIA H100 and GB200 chips. While it benefits from favorable U.S. regulatory and innovation environments, it is constrained by higher energy costs and mounting scrutiny over AI ethics and data monopolization.
In contrast, the UAE center offers a more agile and sovereign model. It is optimized not only for performance but also for geopolitical flexibility and environmental compliance. Furthermore, the UAE’s political will and state-backed investment allow for faster project execution, as evidenced by the 2026 target for achieving 200MW operational capacity.
Additionally, hyperscale initiatives by Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure in regions such as India, Brazil, and Germany reveal a similar trend: data centers are becoming national assets. The difference, however, lies in the collaborative governance model that defines Stargate UAE—where multiple stakeholders co-design and co-govern the infrastructure. This federated governance structure is likely to influence future infrastructure planning across both developed and emerging markets.
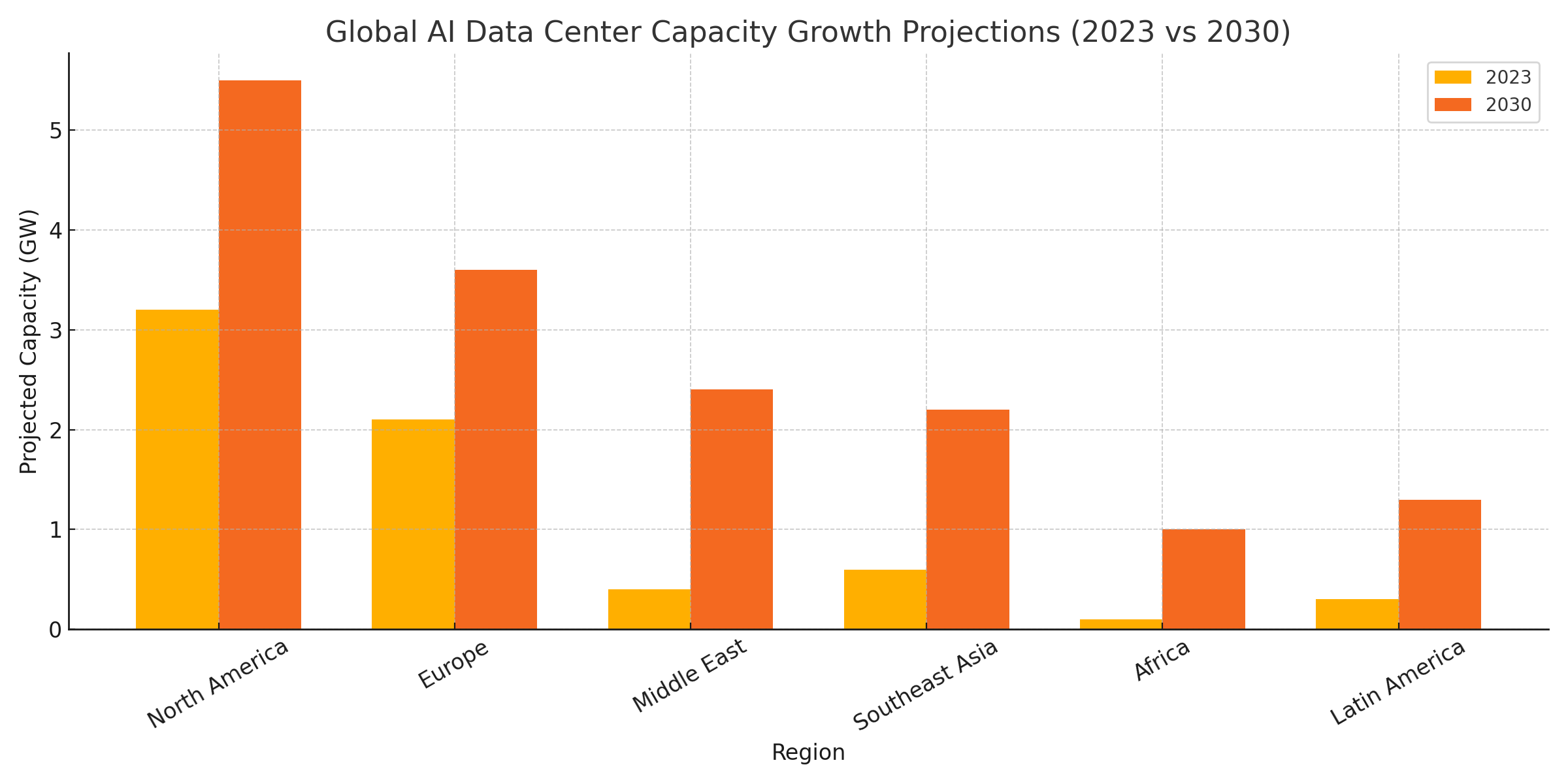
This visualization underscores the redistribution of compute power away from traditional strongholds like the U.S. and China toward more strategically neutral and technologically adaptive regions.
Setting a Precedent for Sovereign AI Frameworks
One of the most important long-term prospects of the Stargate UAE initiative is its potential to influence global norms around sovereign AI. As large language models (LLMs) become embedded in national infrastructure—from digital identity to predictive governance—the question of who controls these models becomes paramount.
Stargate UAE sets a precedent for “hosted sovereignty,” whereby local governments retain jurisdictional authority over data and model outputs while leveraging foreign AI expertise and hardware. This is especially important in multi-lingual, culturally diverse societies like those of the GCC, where Western-trained models often lack contextual accuracy or relevance.
This model could be replicated in other parts of the world, such as Africa, Eastern Europe, and Southeast Asia, where there is strong demand for AI services but limited indigenous capacity to build large-scale infrastructure independently. Stargate UAE demonstrates that with the right public-private alignment, even mid-sized economies can establish world-class AI hubs without compromising on sovereignty or ethics.
Prospects for Talent, Education, and Innovation
The emergence of such a data center also signals profound implications for education and talent cultivation. The facility is expected to work closely with universities, vocational institutes, and think tanks to develop AI curricula tailored to regional needs. This ensures a pipeline of qualified professionals capable of maintaining, innovating, and responsibly deploying advanced AI technologies.
Furthermore, it creates opportunities for homegrown startups to access high-performance compute at subsidized rates, encouraging innovation ecosystems around natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and autonomous robotics tuned to local use cases—from Arabic speech recognition to desert climate forecasting.
With sovereign AI infrastructure in place, regional governments will be better positioned to launch AI-based e-governance initiatives, while private enterprises can train proprietary models without depending on foreign cloud monopolies. In effect, Stargate UAE lowers the barriers to participation in the global AI economy.
Influence on Global AI Policy and Standards
Finally, the project has significant ramifications for global AI policy. The collaborative nature of Stargate UAE—featuring U.S., Emirati, Japanese, and multinational partners—offers a counter-model to both the centralized (e.g., U.S. Big Tech) and state-dominated (e.g., China’s AI governance) paradigms.
It reinforces the argument for multi-stakeholder governance frameworks that respect both international innovation standards and national autonomy. As international regulatory bodies like the OECD, ITU, and UNESCO work toward universal AI governance principles, projects like Stargate UAE will serve as real-world testbeds for balancing innovation, security, and ethics.
In conclusion, the Stargate UAE initiative is not merely a regional infrastructure investment; it is a geopolitical, economic, and technological signal. It symbolizes the future of AI as a globally distributed yet locally governed force—a future where high-performance compute is not the exclusive privilege of superpowers but an attainable goal for all nations willing to invest in aligned partnerships and visionary planning.
Pioneering the Future of AI in the UAE
The Stargate UAE initiative, a monumental collaboration between OpenAI, Cisco, Oracle, G42, and additional global stakeholders, signals not only the construction of a technologically advanced AI data center but also the birth of a transformative paradigm in global AI infrastructure. Through its scale, ambition, and design, the project reflects a broader trend in which artificial intelligence is increasingly becoming a geopolitical and economic cornerstone rather than merely a technological tool. The UAE, with its visionary policies and capacity to implement large-scale innovation, has decisively positioned itself at the frontier of this transformation.
At its core, the Stargate UAE project represents the materialization of a multipolar AI infrastructure strategy. By decentralizing compute power and enabling sovereign AI capabilities outside the confines of the traditional U.S.-China tech axis, this initiative paves the way for a more inclusive, diversified, and resilient global AI ecosystem. In contrast to legacy models where compute was primarily localized in a handful of metropolitan data centers in the Western world, this project introduces a new governance and architecture framework—one that is collaborative, federated, and geographically diversified.
For OpenAI, the decision to partner in building such a facility in Abu Dhabi reflects a strategic pivot. It underlines the importance of regional relevance in AI development, where future models must not only scale computationally but also culturally, linguistically, and ethically. The deployment of foundational models like GPT in sovereign environments ensures that locally significant data can be processed and leveraged without contravening privacy laws or cultural norms. This not only boosts trust but also improves the contextual quality of AI outputs.
Cisco and Oracle’s involvement further elevates the project’s importance. Cisco’s robust security and observability technologies will ensure the center operates under stringent safeguards, thus securing data integrity and system reliability in an increasingly adversarial cyber landscape. Oracle’s cloud orchestration and AI-specific infrastructure bring the requisite scalability and enterprise-grade performance needed to support LLM training, inference, and deployment at regional and international levels. The synergy between these stakeholders reflects a strategic alignment of commercial expertise and public utility.
From the UAE’s standpoint, this collaboration is a linchpin in the country’s overarching AI strategy, as outlined in its National Artificial Intelligence Strategy 2031. The initiative resonates with the Emirates’ ambition to be a global leader in AI governance, sustainability, and technological innovation. It complements other national efforts, including smart governance platforms, autonomous vehicle testing, and AI-driven healthcare innovations.
Economically, the project has a multiplier effect. Beyond the immediate creation of jobs and technology transfer, it has the potential to reconfigure the UAE’s labor market into one driven by digital and cognitive skills. Universities, vocational institutions, and research bodies are expected to align their curricula with the new wave of AI capabilities, ensuring the emergence of a homegrown ecosystem of data scientists, engineers, AI ethicists, and system architects. This talent pipeline is vital for the long-term sustainability of AI infrastructure in the region.
Additionally, the Stargate UAE facility will play a catalytic role in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) and fostering the growth of AI-focused startups. With local access to supercomputing power, smaller firms and academic institutions can train and fine-tune models without the prohibitive costs associated with leasing compute power from overseas hyperscalers. This democratization of access reduces the entry barriers for innovation and contributes to a thriving knowledge economy.
On a macro level, the project also sets a precedent in energy-conscious AI development. Data centers are typically among the most energy-consuming facilities in modern infrastructure. Stargate UAE’s tri-energy strategy—relying on nuclear, solar, and natural gas—demonstrates that energy sustainability and AI scalability are not mutually exclusive. Coupled with Cisco’s AI-augmented observability tools, the project will actively monitor and minimize energy waste, making it a showcase of responsible infrastructure planning.
The implications of this development stretch beyond borders. As AI becomes increasingly enmeshed in statecraft, economic development, and defense, the question of who owns and controls infrastructure becomes paramount. Stargate UAE provides a blueprint for “shared control”—a governance model wherein strategic infrastructure is neither monopolized by a single entity nor subject to extraterritorial regulation. It is governed through a constellation of partners whose mutual interests align toward ethical AI development, technological excellence, and geopolitical balance.
Moreover, this initiative enhances the UAE’s soft power. By becoming a convening point for global AI talent and thought leadership, Abu Dhabi reinforces its image not merely as an oil-rich economy, but as a digital capital of the future. It can host policy summits, ethical debates, and technical workshops that shape the discourse on how AI should be governed, scaled, and distributed. The country’s reputation as a neutral, forward-looking player in international affairs further amplifies the significance of the Stargate project on the world stage.
Looking ahead, the success of Stargate UAE could serve as a replicable model for other regions aspiring to become AI leaders. It proves that with the right mix of regulatory clarity, investment capital, infrastructure readiness, and strategic partnerships, it is possible to leapfrog into the future of AI. Whether in Africa, Southeast Asia, or Latin America, similar ecosystems can take inspiration from the UAE’s ability to translate policy vision into operational infrastructure.
For OpenAI and its partners, Stargate UAE marks the beginning of a new chapter—one that is not merely about scaling models but about scaling systems, societies, and opportunities. As AI continues to permeate every aspect of human endeavor, the infrastructure upon which it is built will define the contours of digital civilization. By anchoring part of this infrastructure in the Middle East, this initiative alters the gravitational center of global AI innovation.
In conclusion, the Stargate UAE data center is more than a technological installation; it is a geopolitical statement, an economic catalyst, and a philosophical prototype. It invites us to imagine a world where artificial intelligence is not just a tool of the privileged but a distributed capability—responsibly governed, ethically deployed, and equitably accessed. The UAE, through its alliance with OpenAI, Cisco, Oracle, and G42, has not only imagined this world—it has begun building it.
References
- OpenAI Official Website – https://openai.com
- Cisco Newsroom on AI & Cloud – https://newsroom.cisco.com
- Oracle AI and Cloud Infrastructure – https://www.oracle.com/cloud/ai/
- G42 Technology Group – https://www.g42.ai
- UAE Ministry of Artificial Intelligence – https://ai.gov.ae
- NVIDIA GB300 Chip Overview – https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/data-center/grace-blackwell/
- SoftBank Vision Fund – https://visionfund.com
- Abu Dhabi Investment Office – https://www.investinabudhabi.ae
- IDC Data Center Trends – https://www.idc.com
- World Economic Forum: AI Governance – https://www.weforum.org/centre-for-the-fourth-industrial-revolution/artificial-intelligence
