Meta’s New AI Superintelligence Lab Signals a Bold Shift in the Global AGI Race

In a bold move that underscores its long-term ambitions in the artificial intelligence (AI) race, Meta Platforms, Inc. — the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp — has announced the creation of a dedicated lab aimed at developing what it terms ‘superintelligence’. This initiative marks one of the most significant shifts in Meta’s AI strategy to date and positions the company in direct competition with other technology giants such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Anthropic, and Microsoft.
The concept of superintelligence — an AI system whose capabilities far surpass those of the most gifted human minds across virtually all domains — has long occupied a near-mythical status within both academic and industry circles. Now, with Meta’s latest commitment, the pursuit of such a transformative technology is moving from theory to deliberate corporate strategy. The announcement reflects not only Meta’s technological ambitions but also its broader vision of shaping the next era of computing and human-computer interaction.
Meta’s AI journey has evolved dramatically over the past decade. Its Fundamental AI Research (FAIR) group, launched in 2013, established Meta as a serious player in foundational AI research. Subsequent innovations, including the development of the LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) series and its leadership in open-source AI frameworks such as PyTorch, have further cemented the company’s influence in the field. However, the establishment of this new superintelligence lab signals an even more aggressive and expansive phase.
The timing of this initiative is highly strategic. The global AI landscape is currently witnessing an unprecedented acceleration, with large language models (LLMs), multimodal AI systems, and AI agents pushing the boundaries of what machines can do. Meta is now entering this arena with an explicit focus on building systems that can demonstrate autonomous reasoning, advanced planning, and sophisticated decision-making at scales beyond current capabilities. According to Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg, the company aims to achieve a general-purpose AI that is not only highly capable but also safe, ethical, and broadly beneficial.
Beyond its technical aspirations, Meta’s move reflects deep competitive pressures within the tech ecosystem. Rivals like OpenAI and Google DeepMind are investing heavily in the development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), with OpenAI’s GPT models and DeepMind’s Gemini platform setting new performance benchmarks. By launching its superintelligence lab, Meta is signaling that it intends to be at the forefront of this race — and perhaps to shape the contours of AI governance and public discourse along the way.
The implications of this initiative are profound. Success in developing superintelligence could redefine Meta’s core products, enable entirely new categories of AI-powered experiences, and catalyze breakthroughs in fields ranging from healthcare to scientific discovery. Conversely, it also raises complex ethical, social, and regulatory questions, given the immense power such systems could wield.
This blog post will explore Meta’s superintelligence initiative in depth. It will examine the lab’s goals and structure, analyze the strategic motivations driving Meta’s pursuit of advanced AI, and assess the technical, ethical, and governance challenges involved. Finally, it will consider how this move might reshape the competitive dynamics of the global AI landscape — and what it means for the future of intelligent systems.
Inside Meta’s New Superintelligence Lab
Meta’s new superintelligence lab represents a pivotal evolution in the company’s AI research strategy. Conceived as a bold and forward-looking initiative, this dedicated lab is tasked with achieving breakthroughs that transcend the current capabilities of large language models and multimodal AI systems. While Meta has not disclosed every operational detail, a wealth of information from corporate statements, public filings, and industry sources provides a comprehensive picture of the lab’s structure, goals, and positioning.
A Strategic Expansion Beyond FAIR
Meta’s original AI research powerhouse — Fundamental AI Research (FAIR) — has been a cornerstone of the company’s success in AI since its inception in 2013. FAIR’s contributions include advancements in computer vision, natural language processing, generative AI, and reinforcement learning, as well as the development of open-source tools like PyTorch. However, FAIR was designed primarily as an academic-style research lab. The new superintelligence lab will complement and extend FAIR’s efforts with a more applied and product-oriented focus.
According to internal sources and public comments by Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg and Chief AI Scientist Yann LeCun, the new lab will operate semi-autonomously within Meta’s broader AI organization. It will have its own leadership team, budget, and dedicated technical staff, while maintaining close collaboration with FAIR, Reality Labs, and Meta’s product divisions.
The lab’s mission is explicit: to develop a general-purpose AI system that achieves superhuman intelligence in a broad array of cognitive domains. This includes not only advanced language and reasoning skills but also autonomous learning, creativity, and adaptive problem-solving.
Leadership and Talent
Leadership for the superintelligence lab is expected to include a combination of Meta’s top AI scientists and newly recruited talent. While Mark Zuckerberg remains the executive sponsor, day-to-day leadership is likely to be distributed among senior FAIR researchers and external experts.
Yann LeCun, one of the world’s foremost AI researchers and a vocal advocate for open AI systems, is expected to play a key advisory role. Meta has also been aggressively recruiting top AI talent from universities, rival companies, and the open-source community. The lab’s staffing targets reportedly include hundreds of engineers and researchers over the next two years.
Key areas of expertise being sought include:
- Large-scale deep learning
- Reinforcement learning and planning
- Neuroscience-inspired AI architectures
- AI safety and alignment
- Scalable AI infrastructure and distributed computing
Infrastructure and Compute
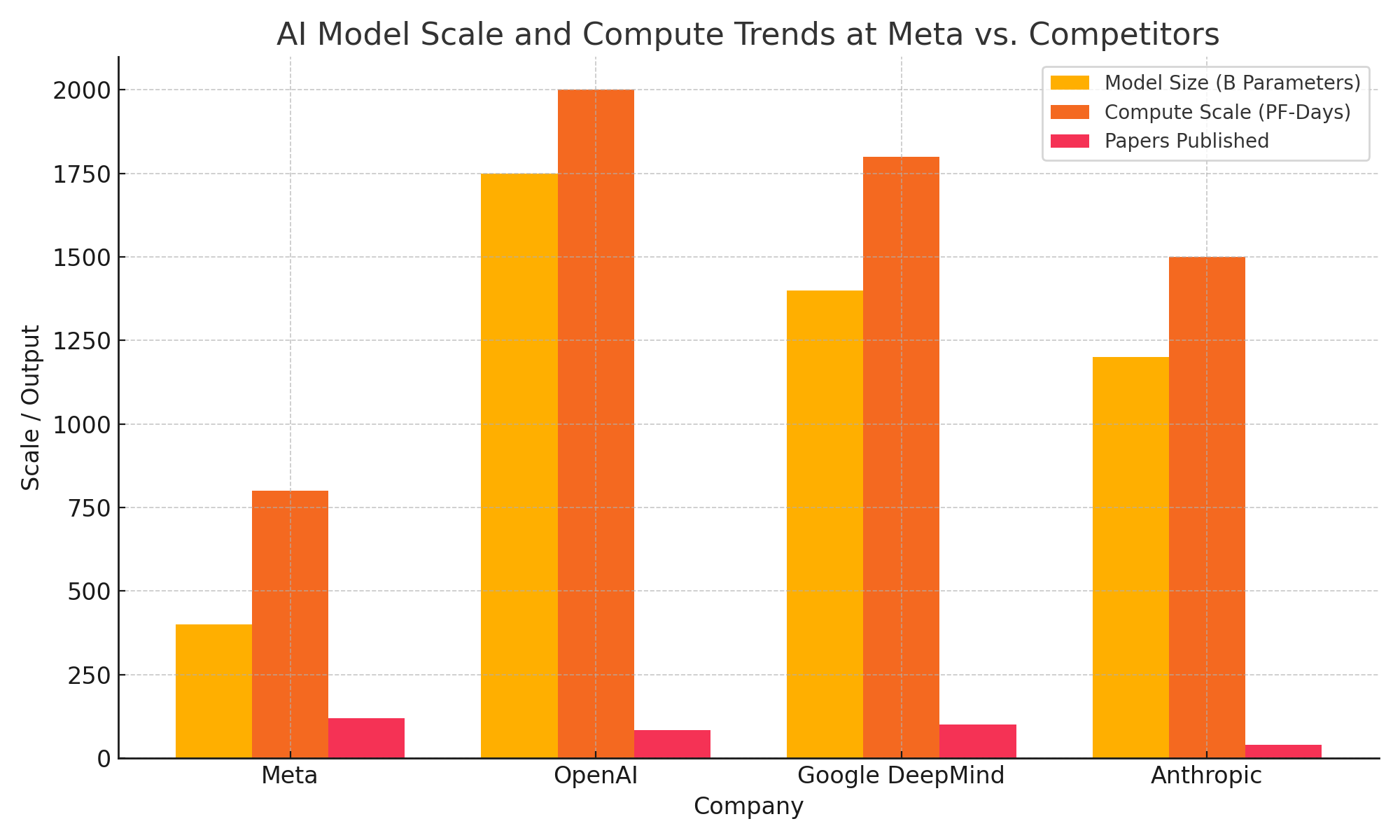
Building superintelligence requires an unprecedented scale of computational resources. Meta is committing significant capital to this effort. The company has already ordered tens of thousands of NVIDIA H100 GPUs, with plans to deploy these chips across massive AI superclusters. Meta’s custom AI inference and training chips — internally known as MTIA (Meta Training and Inference Accelerator) — will also play a central role.
Meta aims to deploy one of the world’s largest AI compute infrastructures by 2026, capable of supporting model training runs at scales approaching or surpassing those of GPT-5 and Gemini Ultra. The company is building dedicated data center capacity to support this effort, including new facilities optimized for high-density AI compute.
Moreover, Meta is investing in novel software frameworks to facilitate distributed training across vast GPU clusters. The emphasis is on achieving not only scale but also efficiency and flexibility, enabling experimentation with diverse AI architectures.
Research Focus Areas
The lab’s research agenda is designed to target the core challenges of developing superintelligence:
- Autonomous reasoning: Moving beyond pattern recognition toward systems that can plan, reason, and adapt autonomously in complex environments.
- Memory and long-term context: Developing AI models with persistent, dynamic memory that allows them to learn and apply knowledge across extended timescales.
- Grounded intelligence: Building systems that understand and interact with the physical world and multimodal sensory inputs (vision, sound, touch).
- Creativity and innovation: Fostering AI systems capable of genuine creative synthesis, from scientific discovery to art and design.
- Safety and alignment: Ensuring that superintelligent systems behave in ways that are consistent with human values and societal goals.
Meta is particularly interested in neuroscience-inspired approaches, as championed by LeCun, which may depart from today’s transformer-based architectures. Research directions include energy-based models, hierarchical predictive learning, and neuro-symbolic systems.
Open Research and Ecosystem Integration
In line with Meta’s stated philosophy of promoting open innovation, the superintelligence lab is expected to publish much of its work in the public domain. The company has pledged to continue releasing key model weights, research papers, and software tools under permissive open-source licenses.
This approach is intended to:
- Foster collaboration with the global AI research community.
- Drive standards and best practices for AI development.
- Build trust and transparency around Meta’s AI efforts.
- Differentiate Meta’s ecosystem from more closed models pursued by some competitors.
At the same time, Meta will retain strategic control over certain models and capabilities where commercial or safety considerations warrant.
Initial Milestones and Roadmap
While timelines for achieving true superintelligence remain speculative, Meta has outlined an aggressive near-term roadmap:
- By late 2025: Release next-generation LLaMA models with enhanced reasoning and planning abilities.
- By 2026: Demonstrate prototype AI agents capable of autonomous learning and goal-directed behavior in simulated and real-world tasks.
- Beyond 2026: Achieve scalable, general-purpose AI systems approaching Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) benchmarks across multiple domains.
These milestones are ambitious and fraught with uncertainty. Nonetheless, Meta’s willingness to make such commitments publicly underscores its confidence and strategic resolve.
Strategic Motivation — Why Meta Wants to Build Superintelligence
Meta’s pursuit of superintelligence is not merely an academic exercise; it is a highly strategic move designed to align with the company’s long-term vision and competitive positioning. The decision to invest heavily in developing a general-purpose AI system stems from a confluence of factors — technological, commercial, and geopolitical — that are reshaping the landscape of global innovation. Understanding these motivations is critical to grasping why Meta is willing to commit vast resources to this ambitious endeavor.
AI as a Core Business Driver
Meta’s evolution over the past decade reflects a shift from being primarily a social media company to positioning itself as a technology platform company driven by AI and immersive experiences. Today, artificial intelligence powers virtually every aspect of Meta’s operations — from content recommendations on Facebook and Instagram to language translation, content moderation, and advertising optimization.
Building superintelligence is the logical next step in this trajectory. Mark Zuckerberg has publicly stated that he envisions general-purpose AI agents becoming integral to the user experience across Meta’s family of apps and devices. These agents would:
- Provide personalized assistance.
- Enable advanced content creation.
- Facilitate natural language interactions.
- Support complex decision-making for both consumers and businesses.
By developing superintelligence in-house, Meta aims to control the foundational technology that will drive the next wave of product innovation, thereby reducing its dependence on external partners and ensuring differentiation in an increasingly crowded AI landscape.
Enabling the Metaverse Vision
Another powerful motivator behind Meta’s superintelligence initiative is its long-standing commitment to building the Metaverse — a fully immersive, persistent virtual world where users can interact, work, and play. Realizing this vision requires far more than advanced graphics and hardware; it demands AI systems capable of understanding context, generating rich content, and facilitating dynamic social interactions.
Superintelligent AI could serve as the cognitive backbone of the Metaverse by enabling:
- Realistic non-player characters (NPCs) with adaptive personalities.
- Intelligent virtual assistants that help users navigate complex environments.
- Generative tools for creating virtual worlds, objects, and avatars.
- Cross-language communication and real-time translation.
- Emotional intelligence to foster more authentic social interactions.
By embedding superintelligence into the Metaverse, Meta aims to create experiences that are not only immersive but also highly personalized and responsive — key to driving user engagement and retention.
Competing in the AI Arms Race
The global race to develop AGI and superintelligence is intensifying. Companies like OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Anthropic, and Microsoft are investing billions in pursuit of AI systems that can match or exceed human cognitive abilities. Meta cannot afford to lag behind in this race, as control over superintelligent AI will confer substantial strategic advantages.
These advantages include:
- Technological leadership that attracts top talent and partnerships.
- Control over platform standards and APIs for AI-driven applications.
- First-mover advantage in deploying AI agents and assistants.
- Influence over regulatory frameworks and industry norms.
- Long-term value creation through transformative new products and services.
By establishing its own superintelligence lab, Meta seeks to shape the direction of AI development rather than merely reacting to external breakthroughs. The goal is to ensure that Meta remains at the forefront of the AI revolution, with capabilities that rival or surpass those of its competitors.
The Open-Source Advantage
A distinctive aspect of Meta’s AI strategy is its commitment to open-source development. Unlike some competitors who tightly guard their most advanced models, Meta has consistently released its LLaMA models, PyTorch frameworks, and other tools to the broader AI community.
This open-source philosophy serves several strategic purposes:
- Ecosystem building: By fostering a large community of developers and researchers around Meta’s tools, the company increases its influence in shaping the future of AI.
- Talent attraction: Open-source initiatives help Meta attract top AI talent who value the opportunity to contribute to widely used projects.
- Trust and transparency: In a field often criticized for opacity, open-source practices enhance Meta’s credibility and public trust.
- Regulatory positioning: By demonstrating a commitment to openness and collaboration, Meta may be better positioned to engage constructively with regulators.
Superintelligence development will continue this approach, with Meta pledging to publish research papers and release key models where appropriate, while balancing safety and commercial considerations.
Strategic Risks and Rewards
The pursuit of superintelligence is not without significant risks. Developing AI systems of such capability introduces challenges related to:
- Safety and alignment: Ensuring that superintelligent AI behaves in ways that align with human values.
- Security: Preventing misuse of powerful models by malicious actors.
- Public trust: Addressing societal concerns about the impact of superintelligence on employment, privacy, and autonomy.
- Regulatory compliance: Navigating a rapidly evolving landscape of AI regulations across different jurisdictions.
Yet the potential rewards are equally compelling:
- Revenue growth: AI-powered products and services could unlock massive new revenue streams.
- Platform resilience: Superintelligence would strengthen Meta’s competitive moat against both established tech giants and emerging startups.
- Societal impact: Breakthroughs in AI could drive progress in healthcare, education, scientific discovery, and more.
- Corporate legacy: Success in this domain would cement Meta’s status as a global technology leader for decades to come.
In essence, Meta’s superintelligence lab represents a calculated bet that the transformative potential of AGI outweighs the associated risks — and that Meta has the vision, talent, and resources to lead this historic endeavor.
Technical and Ethical Challenges on the Road to Superintelligence
While Meta’s ambition to develop superintelligence is clear and strategically compelling, the path to achieving this vision is fraught with formidable technical and ethical challenges. Building an AI system that surpasses human intelligence across a broad range of cognitive domains requires not only scaling existing technologies but also inventing entirely new paradigms of machine learning and cognition. Simultaneously, Meta must navigate the complex moral and societal implications of creating such powerful systems.
In this section, we examine the key scientific, engineering, and governance hurdles that Meta — and indeed the entire AI research community — must address to ensure that the pursuit of superintelligence results in safe, beneficial, and trustworthy outcomes.
Scientific and Engineering Hurdles
Data and Model Scaling
One of the most immediate technical challenges involves scaling models to the levels required for superintelligence. Today’s state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4 and Gemini Ultra, already require vast amounts of data and compute resources. Achieving superintelligence will likely necessitate orders-of-magnitude increases in both.
However, this approach faces diminishing returns:
- Data saturation: The pool of high-quality, diverse training data is finite. Meta and others must find ways to leverage synthetic data and self-supervised learning to overcome these limitations.
- Compute efficiency: Training larger models becomes exponentially more expensive and energy-intensive. Innovations in model architectures, training algorithms, and hardware acceleration are essential to maintain progress.
Robustness and Generalization
Current AI systems excel at pattern recognition but struggle with robust reasoning and generalization beyond their training data. Superintelligence will require models that can:
- Abstract and transfer knowledge across domains.
- Exhibit common-sense reasoning and causal understanding.
- Operate reliably in novel and dynamic environments.
Achieving these capabilities demands fundamental advances in machine learning theory and architecture design. Meta is exploring neuroscience-inspired approaches (such as hierarchical predictive learning) and hybrid systems that combine symbolic reasoning with deep learning.
Memory and Continual Learning
Another critical limitation of current AI models is their lack of persistent memory and ability to learn continuously. Superintelligent systems must:
- Maintain and update long-term memory structures.
- Integrate new knowledge without catastrophic forgetting.
- Adapt to changing environments and user needs in real time.
This requires rethinking core aspects of model design, including storage architectures, training methodologies, and learning paradigms.
Autonomy and Agency
Superintelligence implies not just intelligence but agency — the ability to set and pursue goals autonomously. Building AI agents capable of:
- Strategic planning
- Multi-step reasoning
- Adaptive goal selection
remains a grand challenge.
Meta must ensure that such capabilities are developed with strong alignment mechanisms to prevent unintended behaviors or goal misalignment with human values.
AI Safety and Alignment
As AI systems become more capable, ensuring their safety and alignment with human values becomes paramount. Key concerns include:
- Specification gaming: The tendency of AI to exploit loopholes in poorly defined objectives.
- Value misalignment: Difficulty in precisely encoding complex human values and norms into machine systems.
- Unintended side effects: Emergent behaviors that may be harmful or destabilizing.
- Instrumental convergence: The risk that AI systems may pursue sub-goals (such as resource acquisition or self-preservation) that conflict with human interests.
Meta must invest heavily in AI safety research, developing both technical solutions (e.g., interpretability, corrigibility, robustness) and governance frameworks. Notably, Yann LeCun has advocated for AI systems that are grounded in physical and social reality, reducing the risk of harmful abstraction or goal drift.
Criticism of Meta’s Open-Source Strategy
Meta’s commitment to open-sourcing powerful AI models has attracted both praise and criticism. On one hand, open research fosters collaboration, transparency, and rapid innovation. On the other, it raises concerns about the proliferation of dual-use technologies that could be misused for:
- Disinformation and propaganda
- Cyberattacks and malware generation
- Automated surveillance
- Advanced fraud and manipulation
Balancing openness with responsibility is a delicate task. Meta must implement robust release criteria, engage with the broader research and policy community, and develop usage guidelines and monitoring mechanisms to mitigate misuse risks.
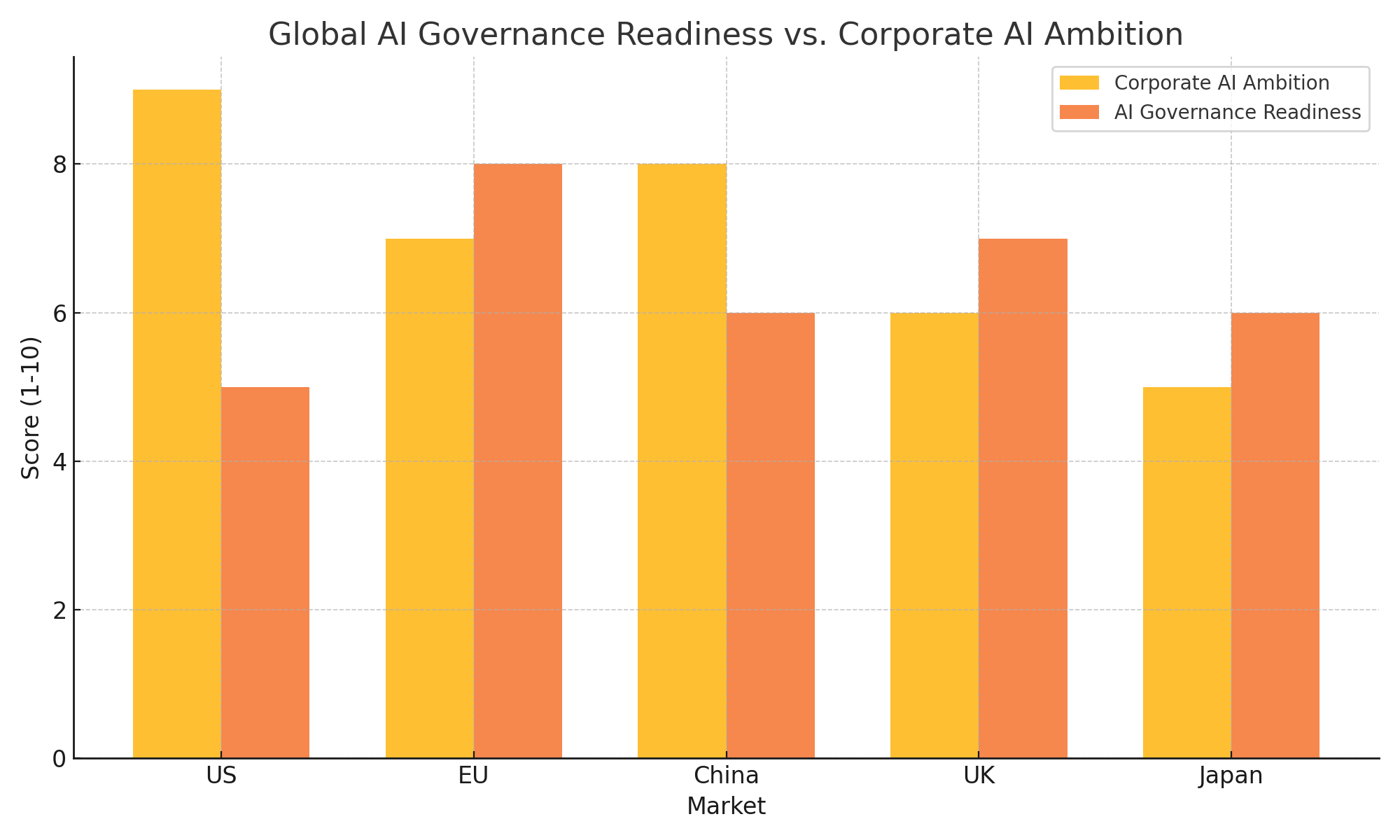
Regulatory Landscape and Governance
The global regulatory environment for AI is evolving rapidly. The European Union’s AI Act, the U.S. AI Executive Order, and various international initiatives reflect growing governmental interest in overseeing advanced AI development. Key regulatory priorities include:
- Transparency and explainability of AI systems.
- Robustness and accuracy testing.
- Privacy protections for training data.
- Accountability frameworks for AI-driven decisions.
- Safety and security standards for high-capability models.
Meta must proactively engage with regulators and policymakers to shape reasonable and effective AI governance. Failure to do so could result in restrictive regulations that stifle innovation or damage public trust.
Public Trust and Societal Impact
Finally, Meta must contend with broader societal concerns about the impact of superintelligence on:
- Employment and economic disruption.
- Social cohesion and democratic processes.
- Human agency and autonomy.
- Cultural and ethical values.
Building public trust requires more than technical safeguards. Meta must foster open dialogue, transparency, and inclusive governance to ensure that superintelligence serves the collective good.
How Meta’s Superintelligence Push Could Reshape the AI Landscape
Meta’s decision to invest heavily in building superintelligence is set to reverberate across the global AI ecosystem. Should the company succeed, the implications would extend far beyond its own product portfolio — influencing the direction of AI research, reshaping competitive dynamics, and catalyzing new waves of innovation. At the same time, Meta’s approach raises critical questions about the future governance of AI, public trust, and the societal role of superintelligent systems.
In this section, we explore how Meta’s superintelligence initiative could reshape the AI landscape and what this means for technology companies, researchers, policymakers, and society at large.
Impact on the Open-Source AI Community
One of the most immediate impacts of Meta’s strategy will be felt within the open-source AI community. By continuing to publish model architectures, weights, and research findings, Meta will help democratize access to cutting-edge AI capabilities. This could accelerate innovation across a wide range of sectors, from startups and academic research to non-profit and governmental applications.
Key potential benefits include:
- Lower barriers to entry: Smaller organizations and researchers can build upon Meta’s work without the need for massive proprietary compute resources.
- Faster iteration: Open models allow for rapid experimentation and adaptation to new use cases.
- Cross-pollination: Meta’s open-source releases will likely inspire new hybrid approaches and architectures from the broader community.
However, this approach also comes with trade-offs. As discussed in Section 3, open access to powerful models increases the risk of misuse. Meta will need to develop and promote robust community standards, responsible use guidelines, and monitoring mechanisms to mitigate these risks while preserving the benefits of open innovation.
Implications for Enterprise AI Adoption
Meta’s superintelligence lab is likely to drive a new wave of enterprise AI adoption. Businesses increasingly seek AI solutions that can support complex reasoning, creativity, and autonomous decision-making — capabilities that current models only partially deliver. If Meta succeeds in developing general-purpose superintelligent systems, enterprise customers could gain access to:
- Highly capable AI agents for customer service, knowledge management, and business process automation.
- Advanced data analysis and insight generation tools.
- AI-driven creativity for marketing, design, and content creation.
- Adaptive systems that continuously learn and improve over time.
Meta’s open-source philosophy may further enhance enterprise adoption by enabling companies to customize and control AI models in-house, rather than relying solely on proprietary cloud APIs. This flexibility is particularly attractive to organizations concerned about data privacy, regulatory compliance, and vendor lock-in.
However, enterprise adoption will depend heavily on Meta’s ability to:
- Demonstrate the robustness and reliability of its models.
- Provide enterprise-grade support and tooling.
- Address ethical and legal concerns surrounding the use of superintelligent AI.
Competitive Pressure on Rivals
Meta’s superintelligence push will undoubtedly intensify competition among leading AI companies. Rivals such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind, Anthropic, and Microsoft will be forced to respond, potentially accelerating the pace of innovation across the industry.
Possible competitive responses include:
- Increased openness: Other firms may adopt more open-source strategies to maintain relevance and community goodwill.
- Strategic partnerships: Expect deeper collaborations between AI labs and cloud providers, hardware manufacturers, and industry verticals.
- Talent wars: The demand for top AI researchers and engineers will continue to escalate, driving up compensation and fueling aggressive recruitment efforts.
- Differentiation strategies: Companies may pursue specialized forms of intelligence (e.g., domain-specific AGI, constitutional AI) to carve out unique market positions.
This competitive dynamic carries both opportunities and risks. On one hand, it could lead to rapid technological progress and a wealth of new applications. On the other, it raises concerns about rushed development, insufficient safety testing, and fragmentation of governance efforts.
Potential for New AI Agents and Applications
Superintelligence would enable the creation of entirely new categories of AI agents and applications that go far beyond today’s capabilities. Possible innovations include:
- Personal AI companions with deep emotional intelligence and lifelong memory.
- Scientific discovery agents capable of generating and testing new hypotheses at scale.
- Autonomous economic agents that can negotiate, transact, and optimize resource allocation in complex systems.
- AI-mediated governance systems that support more transparent and participatory decision-making in organizations and governments.
These applications could drive profound changes in how individuals interact with technology, how businesses operate, and how societies function. However, they also raise challenging questions about control, accountability, and the evolving role of human agency.
Acceleration and Disruption of the Metaverse and Social Platforms
For Meta specifically, superintelligence could be the catalyst that transforms its Metaverse vision from aspiration to reality. As discussed in Section 2, superintelligent AI would enable:
- Richer, more adaptive virtual environments.
- Seamless multimodal interaction (speech, gesture, gaze).
- Persistent, intelligent NPCs and virtual assistants.
- Personalized content generation and world-building.
Similarly, Meta’s core social platforms could be radically enhanced with AI-driven features such as:
- Context-aware content recommendations.
- Automated community moderation with deeper semantic understanding.
- Dynamic user experiences tailored to individual preferences and needs.
- Advanced tools for creators and influencers.
However, these capabilities also heighten concerns about privacy, manipulation, and algorithmic control — issues that Meta must address proactively to maintain user trust and regulatory compliance.
Shifts in Public Discourse Around AGI
Finally, Meta’s superintelligence initiative is likely to influence public discourse around AGI and its societal implications. As one of the world’s most visible and scrutinized tech companies, Meta’s actions and communications will help shape how policymakers, media, and the public perceive:
- The feasibility and timeline of AGI.
- The risks and benefits of superintelligent systems.
- The appropriate frameworks for governance and oversight.
- The ethical responsibilities of AI developers.
Meta must approach this role with transparency, humility, and a commitment to broad stakeholder engagement. Failure to do so could exacerbate public fears and erode the legitimacy of the AI field as a whole.
Conclusion
Meta’s decision to launch a dedicated superintelligence lab marks a profound inflection point not only in the company’s history but also in the broader evolution of artificial intelligence. With this move, Meta is signaling its intent to become a global leader in the pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) — and ultimately, superintelligence — a goal that has long been the province of science fiction but is now becoming an active area of corporate investment and scientific inquiry.
The journey ahead will be both challenging and transformative. From a technical standpoint, building superintelligence demands breakthroughs across multiple fronts: model scalability, robustness, memory, reasoning, and autonomy. Meta’s commitment to open-source innovation and its vast compute resources give it a unique position to tackle these challenges, though significant scientific and engineering hurdles remain.
Equally important are the ethical, governance, and societal dimensions of this work. As Meta’s capabilities grow, so too does its responsibility to ensure that the systems it creates are safe, aligned with human values, and beneficial to society at large. The company’s open-source philosophy, if implemented thoughtfully, offers an opportunity to democratize access to advanced AI — but it also requires vigilant oversight to prevent misuse.
Strategically, Meta’s superintelligence initiative is poised to reshape the competitive dynamics of the AI industry. It will drive new waves of innovation, push rivals to accelerate their own efforts, and likely influence the regulatory landscape for years to come. For Meta itself, success in this domain could enable the realization of its Metaverse vision, redefine the capabilities of its social platforms, and open vast new opportunities in enterprise AI.
Yet the path is not without risk. The rapid pursuit of superintelligence carries potential dangers — both technical and societal — that must be managed with care. Meta must engage proactively with regulators, the research community, and the public to foster trust and ensure that its AI developments serve the common good.
As the global AI race intensifies, Meta’s bold move underscores a broader truth: the future of intelligence — artificial or otherwise — will be shaped not only by those who possess the most advanced algorithms or the largest compute clusters, but by those who wield these tools with wisdom, responsibility, and a deep commitment to human flourishing.
The world will be watching Meta’s superintelligence lab closely in the coming years. Its progress, setbacks, and decisions will help define the trajectory of AI for the next generation. For now, one thing is clear: the age of superintelligent systems is no longer a distant dream — it is an active and unfolding chapter in the story of human technological advancement.
References
- https://about.fb.com/news
- https://ai.facebook.com/blog
- https://pytorch.org
- https://openai.com
- https://deepmind.com
- https://www.anthropic.com
- https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/data-center/h100
- https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52021PC0206
- https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases
- https://www.weforum.org/agenda/archive/artificial-intelligence
