Google’s ‘AI Mode’: Redefining Search for the Generative Era

In a bold move signaling the next chapter in internet navigation, Google has unveiled what it calls a “total reimagining of search” by introducing a powerful new feature: AI Mode. This innovation represents a decisive leap into the future of information retrieval, redefining the user's relationship with the search engine. For over two decades, Google has stood as the world’s most trusted gateway to the web. From simple keyword-based results to the integration of artificial intelligence through models like BERT and MUM, each evolutionary phase has focused on improving relevance and speed. Now, with the advent of AI Mode, Google is fundamentally shifting the paradigm—from delivering search results to generating answers and insights.
The integration of generative AI into search is not a mere enhancement but a structural transformation. With the backing of Gemini, Google’s most advanced family of large language models, AI Mode offers a more intuitive, conversational, and multimodal experience. Instead of presenting users with a list of links in response to queries, AI Mode delivers AI-generated summaries, follow-up suggestions, and contextually aware insights—all while retaining links to authoritative sources. The goal is not just to answer what users ask, but to anticipate their needs and assist with complex, multi-step tasks like planning vacations, evaluating product options, or drafting emails.
This transformation comes at a critical moment for the broader technology ecosystem. The rise of generative AI applications such as ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, and Perplexity AI has disrupted conventional notions of search. With users increasingly expecting AI assistants to provide synthesized responses rather than raw lists of documents, the pressure on incumbents like Google has intensified. In response, the company has shifted its focus from merely indexing the world’s information to reasoning over it in real-time. In this sense, Google is not just competing—it is attempting to reclaim its leadership position by integrating deep learning and large context capabilities directly into its core product.
AI Mode represents the culmination of several years of experimentation and iterative enhancements. The journey began with the Search Generative Experience (SGE), a beta feature that allowed users to preview what AI-generated search summaries might look like. Drawing on feedback and usage data, Google has now matured this concept into a formalized feature within its main search interface. AI Mode will be opt-in initially, allowing users to choose when and how they engage with the new capabilities. This opt-in model is designed to accommodate varying preferences and privacy expectations, ensuring that users retain control over their experience.
The announcement of AI Mode also carries significant implications for industries that rely on Google Search as a key channel—particularly digital publishers, advertisers, SEO professionals, and e-commerce platforms. As the interface changes and AI-generated summaries become more prominent, traditional click-through pathways may diminish, prompting a reevaluation of content strategies and advertising models. Furthermore, questions around the reliability of AI-generated content, potential hallucinations, and information sourcing standards remain open and contentious. These issues will be explored in greater detail in subsequent sections of this blog.
In this post, we will analyze Google’s AI Mode from multiple perspectives: the technical foundations of the update, the strategic impact on search and digital marketing, and the competitive landscape in which this innovation is situated. We will also examine the broader implications for user behavior, content discovery, and the business of the internet itself.
To support our analysis, the blog includes two data-driven charts and one comparative table. These visualizations will provide insight into the timeline of Google’s AI development, forecasted shifts in user engagement metrics, and a side-by-side feature comparison between traditional Google Search and AI Mode. Together, they aim to equip readers—especially professionals working in SEO, digital strategy, product development, and AI policy—with the information needed to navigate this transformative moment.
As we begin, one thing is clear: Google is no longer just helping users find information. It is seeking to understand their intent, interpret their needs across modalities, and proactively assist in fulfilling complex tasks. This is not simply an upgrade to search; it is a redefinition of what search can be in the generative AI era.
From Search Engine to Answer Engine
The Evolution of Google’s Vision
Google’s transformation from a utilitarian index of hyperlinks into a multifaceted intelligence engine is one of the most defining stories in the history of the internet. Since its inception in 1998, Google Search has evolved in response to users' shifting expectations and technological breakthroughs. Yet the launch of “AI Mode” represents a pivotal moment—one that recasts Google not merely as a tool for retrieving documents but as an AI-powered assistant capable of reasoning, generating, and conversing in human-like ways. This transformation from a Search Engine to an Answer Engine has been driven by more than incremental improvements. It reflects a new philosophical and technical commitment to generative artificial intelligence.
A Brief History of Google Search Evolution
In the early years, Google’s dominance was rooted in its innovative PageRank algorithm, which prioritized web pages based on link popularity and relevance. Unlike its competitors, which largely relied on keyword matching, Google created a mathematical model of reputation, effectively sorting content by what other content found valuable. This allowed it to deliver more relevant results, creating a feedback loop of user satisfaction and rising traffic.
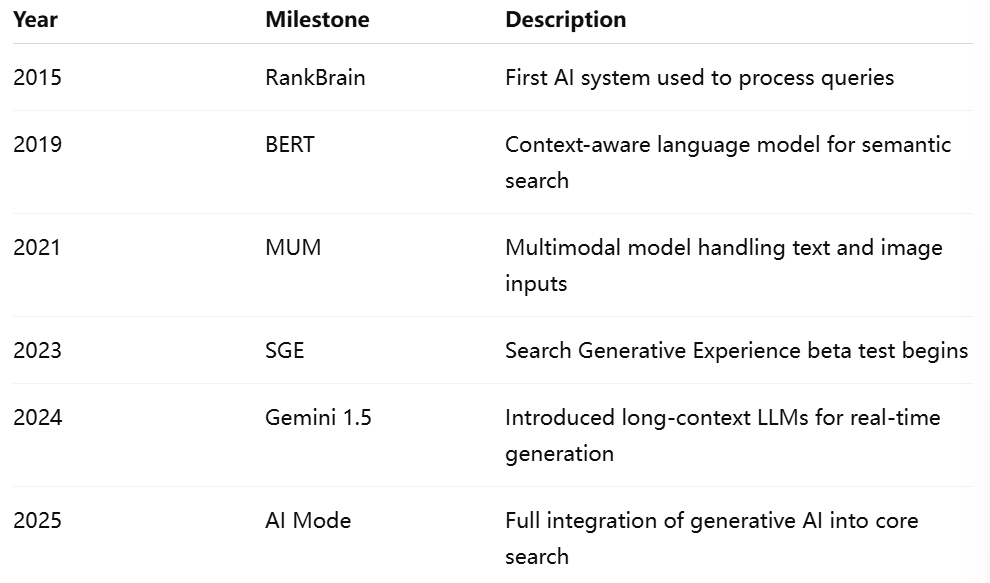
As the volume and complexity of online content grew, Google expanded its capabilities. The 2010s marked the integration of machine learning models to improve language understanding. The introduction of RankBrain in 2015 marked Google’s first serious foray into AI-enhanced search. RankBrain used vector space models to interpret queries in a way that could accommodate synonyms, misspellings, and vague language.
The next critical leap came with BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) in 2019. BERT represented a paradigm shift—it allowed Google to understand the full context of words in a sentence by examining words before and after a target term. This was no longer a keyword-based search but a semantic understanding of language, which made the search engine far more effective in parsing complex queries.
Following BERT, MUM (Multitask Unified Model) was announced in 2021, pushing the boundaries further. MUM could process both text and images and was capable of multitasking—such as understanding a query and generating relevant suggestions in a single step. With MUM, Google signaled a commitment to developing multimodal and multilingual AI that could understand deeper context across content types and languages.
Laying the Foundation: Search Generative Experience (SGE)
Before AI Mode was unveiled to the public, Google initiated a limited rollout of its Search Generative Experience (SGE). SGE, launched in mid-2023, provided a sandbox for Google to test AI-generated summaries directly within search results. By activating SGE in Search Labs, users could receive AI-generated snapshots that synthesized information from various sources into concise narratives.
The rollout of SGE was strategic and deliberate. It allowed Google to measure user interactions with AI-generated answers, test the latency of LLM integrations, evaluate the fidelity of responses, and understand engagement trends. More importantly, SGE helped Google shape an experience that respects publisher interests, ensures factual accuracy, and enables a balance between AI assistance and traditional link-based discovery.
SGE became a crucial stepping stone. It was neither fully conversational nor entirely static. Instead, it hinted at the possibilities of a “search that thinks”—a model that can proactively interpret the multi-layered intent behind user queries. The user feedback loop from SGE directly informed the design of AI Mode, particularly around personalization, multimodal input handling, and seamless follow-up interactions.
The Emergence of AI Mode – Core Features and Philosophy
With the public release of AI Mode, Google has codified the next evolution in its product vision. AI Mode is more than just an interface overlay; it is a dynamic integration of generative AI into the search engine's core logic. Powered by Gemini 1.5, a state-of-the-art large language model (LLM) with long context capabilities, AI Mode can handle nuanced queries, multi-step reasoning, and even real-time generation of multimedia outputs.
At its heart, AI Mode is built around three central innovations:
- Conversational Search Threads: Users can interact with the search engine in an ongoing, fluid dialogue. Rather than rephrasing or restarting queries, follow-ups are interpreted in the context of previous interactions. This allows for a richer, more efficient information retrieval experience.
- AI Overviews and Summaries: Upon entering a query, users receive an AI-generated snapshot summarizing key points from multiple sources. These overviews reduce the need to click through multiple links and are especially useful for research, comparisons, and decision-making tasks.
- Multimodal Query Processing: AI Mode introduces a shift toward flexible input types. Users can search using voice, text, or images—and receive answers in mixed modalities, including diagrams, lists, code snippets, or maps, depending on context.
This shift reflects a redefinition of the user-Google relationship: from searcher and index to collaborator and assistant.
Implications of the Vision Shift
The most significant consequence of this vision shift is a departure from the information retrieval model to a knowledge synthesis model. Google is no longer just surfacing what’s on the web—it is interpreting, aggregating, and presenting it as curated responses. This changes not only how users engage with search results, but also how they form knowledge.
Additionally, the reimagined search framework redefines authority and trust on the web. While hyperlinks remain visible, the AI-generated content acts as a filter, potentially reducing exposure for publishers who previously relied on traditional rankings. It also introduces a layer of algorithmic subjectivity—since the content summary is shaped by model training, weighting mechanisms, and confidence scores.
The promise, however, is equally profound. For users, especially those unfamiliar with navigating fragmented or technical content, AI Mode simplifies access. It assists in transforming questions into plans, ideas into drafts, and interests into action items—without requiring deep expertise in search syntax or boolean logic.
For Google, this evolution is both a defense and an offense. It addresses the existential threat posed by general-purpose AI assistants, while offering a compelling new user experience that keeps engagement within the Google ecosystem. The generative pivot is not optional; it is foundational to maintaining relevance in an era where users expect technology to do more than search—they expect it to understand.
In conclusion, Google’s journey from search engine to answer engine marks a monumental shift not only in its product offering but in the future of how we interact with digital information. This transformation, rooted in over a decade of AI investment and iterative advancements, signals a broader transition from querying data to collaborating with intelligence.
How ‘AI Mode’ Works
Architecture, Features, and Technical Insight
Google’s introduction of “AI Mode” in its search engine is not merely a cosmetic update—it is a fundamental reengineering of its architecture, algorithms, and user interface. At the heart of this innovation is the seamless integration of large language models (LLMs), real-time contextualization, and multimodal processing. This section explores the technical foundations of AI Mode, delving into how it operates, what makes it distinct, and how it reshapes the user experience.
The Backbone: Gemini 1.5 and Long-Context AI
The most critical component of AI Mode is its reliance on Gemini 1.5, Google's most advanced large language model as of 2025. Gemini represents a convergence of capabilities developed from earlier models such as PaLM, MUM, and Bard, but with several transformative features that specifically empower AI Mode:
- Extended Context Window: Gemini 1.5 supports multimodal context windows of up to 1 million tokens. This allows the model to interpret extended user queries, multi-turn interactions, and long documents with continuity and coherence.
- Unified Multimodal Input: Unlike earlier models that required distinct pipelines for text, image, and audio, Gemini integrates all input types into a single transformer-based architecture. This enables a fluid interplay between image uploads, voice commands, and typed queries.
- Real-Time Latency Optimization: AI Mode is engineered for low-latency deployment. This involves distillation techniques, hardware-accelerated inference (using TPUv5), and edge-cloud collaboration to ensure fast, responsive outputs.
Together, these capabilities allow AI Mode to provide human-like comprehension and structured summarization across varied query types—whether they involve comparing smartphones, planning an international trip, or seeking Python code for a specific task.
Core Features and UX Enhancements
AI Mode is designed around user-centricity, offering features that both enhance convenience and extend the scope of what users can accomplish with search. The key pillars of its functionality include:
AI Snapshots and Smart Summaries
Instead of showing a conventional list of blue links, AI Mode generates a compact AI Snapshot at the top of the search result. This snapshot synthesizes information from multiple sources, providing a concise and coherent answer. It is ideal for:
- Definitions and quick facts
- Pros and cons comparisons
- Contextual explanations (e.g., legal terms, health symptoms)
- How-to instructions
These summaries are attributed, with inline links to sources, promoting transparency and enabling deeper exploration.
Contextual Threads and Conversational Continuity
A defining characteristic of AI Mode is its threaded interaction model. Users can follow up on their original query without restating context. For example, a user might search, “Best mirrorless cameras under $1000,” and then ask “How do they compare to DSLRs?”—AI Mode understands that “they” refers to the cameras previously discussed.
This capability is powered by context preservation mechanisms that store and retrieve session history. It allows for nuanced dialogues, similar to those in advanced chatbots like ChatGPT or Gemini Advanced, but embedded directly into the search environment.
Multimodal Input and Output
AI Mode expands traditional text search by integrating voice, image, and video inputs. Users can upload a photo of a plant to identify it, speak a command to generate a vacation plan, or insert a video clip to retrieve frame-by-frame analyses. Outputs are also multimodal: maps, charts, timelines, and visual cards are presented when relevant.
This is facilitated through Gemini’s Vision and Audio encoders, which map non-text inputs into a common latent representation space. These embeddings are then processed by the language model in combination with textual prompts to generate comprehensive outputs.
Personalization and User Control
AI Mode features opt-in personalization, allowing users to sync their search experiences with calendar events, previous queries, or app usage (e.g., Gmail, Google Docs). If enabled, Gemini can generate reminders, schedules, summaries of inbox contents, or tailored suggestions.
Google ensures this process is privacy-conscious by embedding federated learning techniques and on-device inference, giving users more control over what data is used and when. Privacy dashboards, context toggles, and visibility into model decisions are built into the interface.
Under the Hood: Technical Pipeline Overview
To deliver a seamless experience, AI Mode follows a sophisticated technical pipeline:
- Query Understanding Layer: The user's input—be it text, voice, or image—is parsed by a natural language understanding (NLU) module. Tokenization, embedding, and classification determine intent, sentiment, and entity types.
- Contextual Retrieval Module: Google’s index serves not just as a list of websites but as a semantically enriched database. A retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework fetches relevant documents to provide grounding facts to the LLM.
- Response Generation Engine: Gemini 1.5 generates a structured response using beam search, top-k sampling, or temperature-controlled decoding. Depending on complexity, it may call APIs for maps, weather, or e-commerce data.
- Post-Processing & Attribution Layer: Before the response is shown, it passes through a set of filters that add citations, check factual consistency, and ensure policy compliance (e.g., avoiding misinformation in medical or political topics).
- Interface Rendering and Feedback Loop: The UI renders AI responses, provides collapsible snapshots, and offers interactive buttons for feedback (“is this helpful?”). This user feedback is looped back into training and model fine-tuning processes.
To illustrate the functional leap from traditional search to AI Mode, we present the following comparative table:

This table highlights not only functional differences but also philosophical ones: AI Mode prioritizes user engagement, synthesis, and control over traditional retrieval.
Challenges in Deployment and Optimization
Despite its sophistication, deploying AI Mode at a global scale introduces substantial engineering and ethical challenges:
- Scalability: Generating real-time responses for billions of daily queries strains computational resources. Google mitigates this through selective invocation of AI Mode based on query classification.
- Latency Management: While Gemini is fast, the generation of high-fidelity outputs can take longer than traditional search. Google’s hybrid caching systems and TPU acceleration are critical to narrowing this gap.
- Factual Reliability: Ensuring that AI summaries are both accurate and up-to-date requires tight coupling between LLMs and retrieval systems. Google's hybrid fact-checking and citation enforcement mechanisms are still evolving.
- Security and Abuse Prevention: Generative models are susceptible to prompt injection, adversarial queries, and malicious use. Google employs adversarial training, red-teaming, and moderation filters to uphold safety standards.
In conclusion, AI Mode is the result of a layered integration of language models, context memory, multimodal input processing, and ethical guardrails. It redefines the very infrastructure of search—from how queries are parsed to how results are synthesized and displayed. By embedding Gemini 1.5 into its core, Google is not only delivering smarter answers but reshaping how billions of users interact with knowledge in the digital age.
Strategic Implications for Search, SEO, and Advertising
The introduction of Google’s AI Mode marks a pivotal juncture for the internet economy, with profound implications for search engine optimization (SEO), advertising strategies, content discovery, and digital visibility. For two decades, the digital ecosystem has revolved around a keyword-based search model, with clear principles guiding visibility, engagement, and monetization. AI Mode, by replacing link-dense result pages with synthesized answers and contextual threads, necessitates a comprehensive rethinking of how information is surfaced and monetized. In this section, we explore the potential disruptions, opportunities, and strategic recalibrations that this transformation entails for various stakeholders across the digital spectrum.
Disruption of Traditional SEO Mechanics
Historically, SEO has relied on optimizing web content around specific keywords and phrases to improve visibility in organic search results. Strategies included refining metadata, increasing backlinks, ensuring mobile responsiveness, and creating high-quality content tailored to likely search intent. However, AI Mode alters the mechanics of visibility in two fundamental ways:
Shift from Results to Answers
With AI Mode placing AI-generated summaries at the top of the page, often occupying the most valuable screen real estate, users are less likely to scroll through the traditional “10 blue links.” This “answer-first” format compresses the discoverability funnel, meaning that even highly ranked organic listings may receive significantly reduced click-through rates (CTR). While sources may still be cited, they are embedded within the narrative of the AI’s summary—no longer in direct competition for attention.
Obfuscation of Ranking Signals
In AI Mode, the traditional ranking algorithm becomes less visible. While links may be sourced from high-authority domains, their placement in generated summaries does not follow the same PageRank-based hierarchy. Instead, relevance is determined by semantic proximity and contextual appropriateness, making it harder for SEO professionals to reverse-engineer effective tactics. Optimization now involves aligning content with LLM preferences, including clear structuring, factual accuracy, and language suited to machine parsing.
Emphasis on Structured and High-Fidelity Content
AI Mode favors content that is structured, well-labeled, and data-rich. Content with schema markup, bullet points, FAQs, tables, and summaries is more likely to be selected by the generative model for inclusion in responses. This puts additional pressure on publishers to not only write for humans but also for machine readability. Technical SEO becomes as important as content strategy in this environment.
The Evolving Nature of Search Intent
Google’s generative shift does not merely impact visibility; it transforms how user intent is interpreted and served. Traditional search engines responded to explicit queries—what the user typed. AI Mode, in contrast, operates on a conversational and inferential basis, often generating insights the user didn’t explicitly request but may find valuable.
Intent Expansion and Anticipation
Instead of waiting for the user to refine a query, AI Mode anticipates follow-up questions and offers them proactively. For instance, a query about “best tablets for students” might automatically include comparisons across price points, brands, and features, effectively front-loading what would have been multiple search interactions. This reduces total page visits and re-queries—changing how content is consumed and how publishers should strategize for audience engagement.
The New Information Funnel
In the traditional model, a user's path might span several pages and queries before a conversion action (e.g., a purchase or newsletter signup). AI Mode condenses this funnel by synthesizing much of the required information upfront. This compression benefits users but diminishes opportunities for publishers to nurture leads, promote brand voice, or differentiate through UI/UX.
Impact on Advertising Models and Revenue Streams
Google’s search advertising business, primarily driven by pay-per-click (PPC) ads and shopping placements, has been finely tuned for a keyword-first experience. AI Mode challenges the viability and visibility of these models in the following ways:
Reduced Surface Area for Ads
With AI Snapshots occupying the top portion of the interface and AI interactions extending the session through conversational follow-ups, the immediate visibility of ads is diminished. Sponsored content must now be intelligently woven into these AI-driven experiences, which requires new ad formats and relevance models.
Rise of Contextual AI Advertising
Google is actively developing AI-native ad placements—ads generated or enhanced by the same LLM infrastructure that powers AI Mode. For instance, during a conversation about planning a trip to Paris, a Google-generated travel guide may subtly include a sponsored hotel booking option, flagged clearly but integrated into the narrative flow. This approach mirrors in-feed advertising seen on platforms like TikTok or Instagram.
Higher Ad Personalization and AI Targeting
AI Mode enables granular personalization by integrating user signals across Google’s ecosystem—Gmail, YouTube, Maps, and Android. This data allows for context-aware targeting, where ads are shown not only based on the current query but the inferred stage in a decision-making journey. For advertisers, this could mean fewer impressions but higher conversion rates, provided that targeting and creative alignment are optimized.
To quantify the potential implications of AI Mode, the following chart presents projected changes in organic CTR across key content categories based on industry forecasts and early user studies.
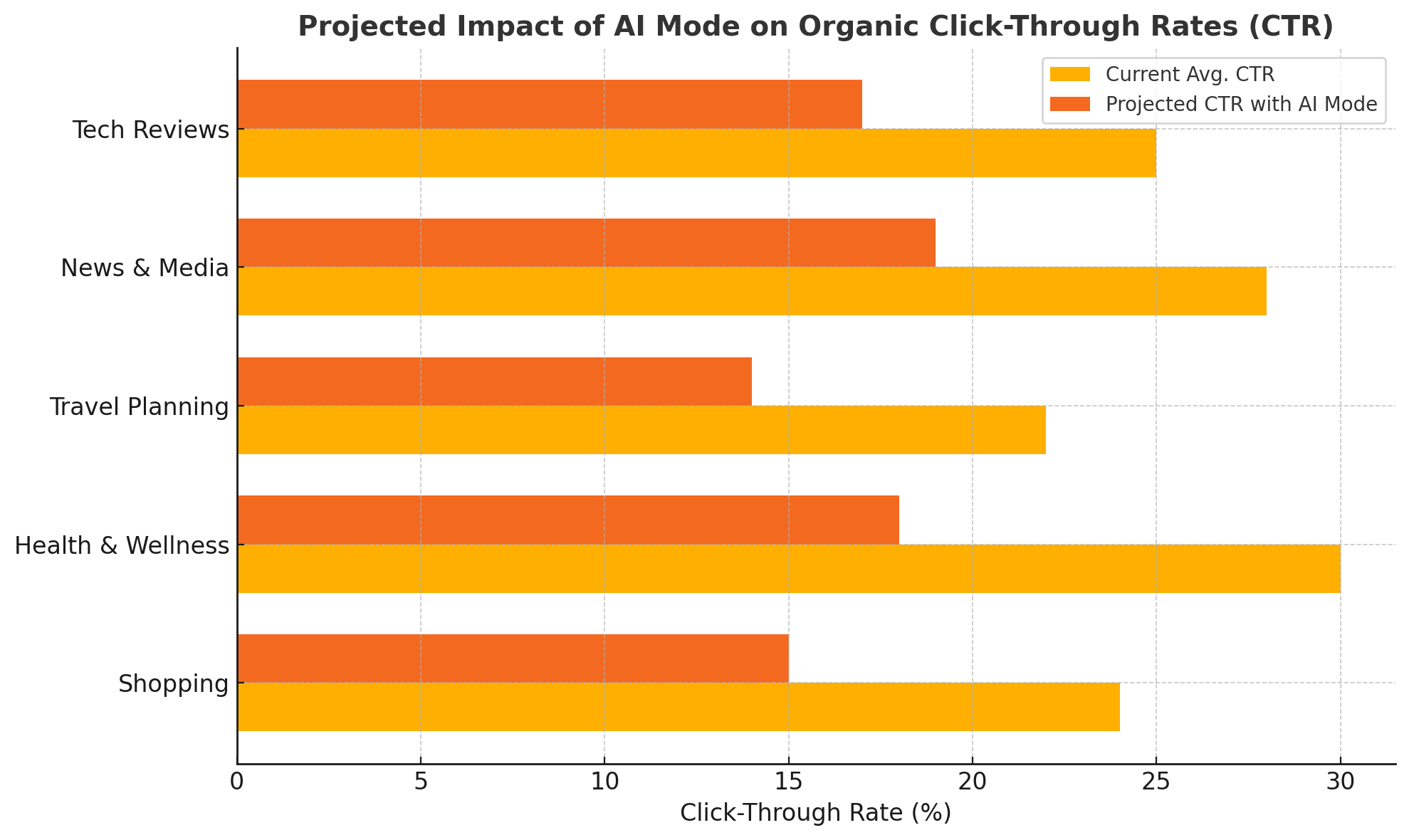
This forecast suggests that while AI Mode enhances user satisfaction and efficiency, it significantly cannibalizes traditional organic traffic, especially for content niches that previously dominated featured snippets and top-three listings.
Strategic Recommendations for Digital Stakeholders
In response to the paradigm shift introduced by AI Mode, various stakeholders must adapt strategically:
For SEO Professionals and Content Creators
- Optimize for machine-readable content: Use schema markup, JSON-LD, and semantic HTML to enhance content indexing.
- Prioritize topical authority: AI Mode selects sources with demonstrated expertise across a domain rather than isolated pages with high keyword density.
- Embrace multi-format content: Include diagrams, infographics, and video summaries to increase selection likelihood for multimodal answers.
For Advertisers and Marketers
- Reallocate budgets to AI-integrated ad products that blend with generative content.
- Craft ad creatives that align with conversational tone and anticipatory user behavior.
- Leverage Google’s AI insights to identify stage-specific intent and target accordingly.
For Publishers and Platforms
- Consider syndication deals with Google to ensure favorable citation in AI summaries.
- Develop zero-click engagement models such as widgets, embedded tools, or app redirects to retain value despite lower web traffic.
- Focus on building direct user relationships—newsletters, apps, and community platforms—beyond search dependence.
Ethical and Economic Tensions
Finally, it is worth noting the broader ethical and economic tensions introduced by this shift. Critics argue that AI Mode consolidates editorial control within the algorithm, effectively centralizing which voices are amplified. This could entrench power in the hands of those who control the underlying AI infrastructure and reduce the plurality of perspectives on the web.
Furthermore, the displacement of traditional traffic routes may undermine the ad-driven business models of independent publishers, eroding revenue at a time when journalism and educational content are already under pressure. Google has pledged to maintain transparency and support open web standards, but these challenges remain unresolved and require ongoing dialogue among developers, regulators, and civil society.
In summary, AI Mode is a profound reorientation of how digital information is discovered, consumed, and monetized. It introduces novel efficiencies and user-centric enhancements while simultaneously disrupting legacy frameworks that have defined online business strategies for years. As this new model gains traction, adaptation will not be optional but imperative for those seeking to remain competitive in a generative search environment.
The Competitive Landscape
Google vs OpenAI, Perplexity, Microsoft, and Others
The unveiling of Google’s AI Mode is not occurring in isolation—it is a strategic maneuver in a rapidly evolving race among global technology leaders to dominate the next frontier of search and information retrieval. As generative AI redefines how users engage with digital content, several key players are vying to build the most intuitive, intelligent, and authoritative AI-powered search assistant. Among them, OpenAI, Microsoft, and Perplexity AI represent formidable competitors, each with distinctive approaches and technological architectures.
In this section, we examine the competitive dynamics shaping the AI search landscape and evaluate how Google’s AI Mode stacks up in terms of functionality, adoption potential, and strategic positioning.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT with Search Integration
OpenAI, backed by Microsoft, has been at the forefront of generative AI innovation with its ChatGPT platform. The launch of ChatGPT Plugins, browsing capabilities, and most recently GPT-4o, has positioned OpenAI as a leading alternative to traditional search engines. Through real-time web access and the ability to retrieve and summarize documents live from the internet, ChatGPT is capable of acting as a search companion with conversational depth.
The fundamental difference lies in intent and interface. ChatGPT is designed for full-dialogue interaction, with users expected to pose queries, request elaboration, and receive human-like responses. It prioritizes clarity and coherence over brevity, often generating more detailed answers than AI Mode. However, it lacks Google’s native access to proprietary data sources such as YouTube, Gmail, Google Maps, and the extensive knowledge graph that underpins Google's AI ecosystem.
Moreover, OpenAI's approach to citations is evolving. Initially criticized for opacity, the company has introduced improved attribution and link-out features, especially in browsing mode. Still, it is dependent on partnerships with content providers and aggregators to ensure coverage, whereas Google benefits from direct indexing and ownership of the web’s largest information infrastructure.
Microsoft Copilot and Bing Search Integration
Microsoft’s integration of Copilot (formerly Bing Chat) into its ecosystem—including Windows, Edge, and Office—is a strategic attempt to rewire user behavior around generative search. Copilot is tightly woven into Microsoft products, offering inline summaries, document generation, and web answers powered by OpenAI’s models. Through its Bing Search backend and GPT-based front end, it offers a hybrid solution that echoes many of Google’s ambitions.
One advantage Microsoft has leveraged is deep integration into productivity software. While Google’s AI Mode dominates the public web search domain, Microsoft’s Copilot is rapidly becoming indispensable in work environments. It can assist with summarizing emails, drafting Word documents, and generating Excel formulas—all while referencing online data.
In terms of search engine usage, however, Bing continues to lag far behind Google in global market share. Despite the sophistication of Copilot, its reach remains limited compared to the billions of daily searches conducted through Google.
Still, Microsoft’s enterprise-first AI strategy gives it an edge in commercial settings, where trust, compliance, and data security are paramount. While AI Mode targets broad consumer adoption, Copilot is carving a niche in regulated and productivity-centric industries.
Perplexity AI: A Rising Disruptor
Among the most intriguing challengers in the AI-powered search domain is Perplexity AI. Positioned as an "answer engine" rather than a search engine, Perplexity combines real-time retrieval with LLM-generated answers, offering a lightweight, citation-rich alternative to traditional query engines.
Perplexity’s strength lies in transparency and source fidelity. Every sentence it generates is backed by clearly labeled links, allowing users to verify claims instantly. This stands in contrast to both Google AI Mode and ChatGPT, which, while incorporating citations, do not always provide sentence-level sourcing.
The platform also emphasizes low-friction UX—there is no need for accounts, plugins, or subscriptions to access core functionality. For power users and researchers, this simplicity paired with high traceability has driven organic adoption, particularly among academic and tech-savvy audiences.
Yet, Perplexity remains a niche product relative to Google's global footprint. It lacks the scale, infrastructure, and default positioning that Google enjoys through its browser (Chrome), mobile OS (Android), and app ecosystem.
Comparative Assessment: Google’s Strategic Advantages
In the face of these competitors, Google’s AI Mode possesses several unique strengths that position it for dominance in the AI-powered search future:
Data Ecosystem Ownership
Google controls the largest index of public web content, the most-used browser, the top email service, the leading mobile OS, and one of the largest video platforms. This ecosystem enables AI Mode to leverage first-party data, user history, and cross-application context to generate deeply personalized and contextually aware responses—without relying on third-party aggregators.
Built-In Distribution
AI Mode is being rolled out natively within Google Search, which handles over 8.5 billion queries per day. This gives Google a massive testing ground and adoption base, allowing it to collect feedback and iterate faster than rivals dependent on opt-in platforms.
Brand Trust and Familiarity
While trust in generative AI remains a challenge across the board, Google’s longstanding presence as the internet’s front page gives it an edge in mainstream acceptance. Users are more likely to trust an AI answer generated within Google’s search interface than in a new or unbranded environment, even if the underlying model performance is similar.
Hybrid Human-AI Interaction Design
Google's design philosophy for AI Mode emphasizes user agency, presenting AI summaries alongside traditional links, interactive buttons, and structured data cards. This hybrid model allows users to cross-reference, verify, and engage at their preferred depth, bridging the gap between AI fluency and traditional browsing.
Risks, Controversies, and Regulatory Outlook
As the competitive landscape intensifies, so too does scrutiny from regulators, publishers, and the public. Google, by integrating AI-generated content directly into Search, assumes responsibility not only for accuracy but for fairness and neutrality. Critics warn that this consolidation of editorial control may marginalize independent voices and concentrate power over public knowledge.
There are also concerns around antitrust enforcement, especially as Google’s AI Mode may displace traffic from third-party publishers whose content is being synthesized without direct compensation. In contrast, initiatives like OpenAI’s licensing deals with news outlets, and Perplexity’s overt source listing, have been seen as more transparent and equitable.
Ultimately, success in this space will require not just technical excellence, but ethical leadership, transparency, and engagement with content creators and policymakers.
In conclusion, Google’s AI Mode enters a competitive landscape where generative AI has become the new battleground. While OpenAI, Microsoft, and Perplexity offer compelling alternatives, Google’s scale, data ownership, and user base provide it with formidable advantages. The true test, however, will lie in how well Google balances innovation with responsibility—and whether it can sustain user trust while navigating the increasingly complex web of information, advertising, and accountability.
Conclusion
Google’s introduction of AI Mode signifies a watershed moment in the evolution of search—a technological and philosophical shift from passive information retrieval to dynamic knowledge generation. No longer content with merely indexing the web, Google now positions itself as a reasoning companion, capable of understanding, synthesizing, and proactively responding to user intent through generative artificial intelligence.
This transformation is rooted in the integration of Gemini 1.5, a large language model with advanced multimodal and long-context capabilities, seamlessly embedded within the familiar framework of Google Search. With AI Mode, users can now engage in natural, contextual conversations; upload images or speak prompts; and receive concise, citation-backed insights that span a wide spectrum of tasks. From researching travel plans to comparing products or exploring complex topics, the experience of “searching” has been fundamentally redefined.
However, the implications of AI Mode extend far beyond convenience. For SEO practitioners, publishers, and advertisers, this evolution mandates a reevaluation of long-standing digital strategies. The decline in visibility for traditional links, the rise of machine-selected summaries, and the emergence of conversational engagement demand new models of optimization and monetization. Structured content, semantic clarity, and technical fidelity are becoming more crucial than ever—not merely to rank well, but to be selected as source material for AI-generated overviews.
At the same time, Google must navigate a series of delicate trade-offs. The platform’s dual role as both gatekeeper and generator of knowledge introduces challenges around fairness, editorial transparency, and content attribution. The tension between efficiency and diversity of perspective is increasingly evident, raising ethical questions that will require continued engagement with regulators, publishers, and civil society.
In a broader context, the competitive landscape underscores the rapid pace of innovation in the generative search domain. OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Microsoft’s Copilot, and Perplexity AI each represent distinct approaches—some more open, others more integrated—but all converging on the idea that the future of search lies in understanding, not indexing. Google’s advantage lies in its scale, data depth, and infrastructure maturity, but maintaining leadership will depend on its ability to balance innovation with responsibility.
Ultimately, the advent of AI Mode is not just a technological advancement—it is a redefinition of the user-agent relationship. Search, as we knew it, was about finding pages. Search, as it is becoming, is about finding answers, perspectives, and even actions. As AI becomes the mediator between user and web, the responsibility to ensure accuracy, inclusivity, and transparency grows in parallel.
For users, this means an era of unprecedented access to curated knowledge. For businesses and creators, it necessitates adaptation, agility, and renewed creativity. And for Google, it represents both its greatest opportunity and its most consequential test in the age of generative intelligence.
As AI Mode rolls out and matures, its success will not be measured solely in speed or user retention—but in whether it can sustain the openness, reliability, and diversity that made the original web search indispensable to billions.
References
- Google Blog – AI Overviews in Search
https://blog.google/products/search/generative-ai-overviews - The Verge – Google’s AI-Powered Search Explained
https://www.theverge.com/2024/ai-google-search-ai-overviews - OpenAI – ChatGPT with Web Browsing
https://openai.com/chatgpt/browsing - Perplexity AI – Answer Engine Overview
https://www.perplexity.ai - Microsoft – Copilot in Bing and Edge
https://blogs.microsoft.com/blog/microsoft-copilot - TechCrunch – Google Launches AI Mode in Search
https://techcrunch.com/google-ai-mode-search - Wired – How Generative AI Is Reshaping the Web
https://www.wired.com/story/generative-ai-in-search - Search Engine Journal – AI and the Future of SEO
https://www.searchenginejournal.com/ai-future-seo - CNBC – Google Introduces New AI Search Experience
https://www.cnbc.com/google-ai-search-overviews - Reuters – Google’s AI Strategy in Search
https://www.reuters.com/technology/google-reimagines-search-ai
