Ericsson and Supermicro Drive Industrial AI Revolution with 5G-Powered Edge Computing

In an era defined by intelligent automation and hyper-connectivity, the convergence of 5G and artificial intelligence (AI) stands as a transformative force reshaping industries worldwide. A newly announced partnership between Ericsson—a global leader in telecommunications infrastructure—and Supermicro—a renowned provider of high-performance computing and storage solutions—aims to accelerate this convergence by delivering 5G-powered AI capabilities to factories, retail environments, and hospitals. This strategic collaboration addresses a growing market demand for real-time data processing and ultra-low latency applications at the network edge, where decision-making and automation increasingly occur.
Ericsson’s robust portfolio of private 5G networks enables enterprises to deploy dedicated, secure, and high-performance wireless infrastructures tailored to their operational needs. These private networks are designed to support mission-critical applications, seamlessly integrating with Supermicro’s edge server platforms to run advanced AI workloads on-site. Together, the two companies are creating an end-to-end solution that promises to unlock new efficiencies, elevate customer and patient experiences, and drive innovation across a broad spectrum of industry verticals.
The rationale behind this partnership is grounded in a global digital transformation trend that is reshaping how data is generated, transmitted, and utilized. Industry 4.0 initiatives in manufacturing are pushing for greater automation, predictive maintenance, and quality control through AI and connected sensors. Retailers are exploring ways to deliver hyper-personalized customer experiences and optimize operations in real time. Healthcare providers, meanwhile, are adopting AI-enhanced diagnostics and smart monitoring systems to improve patient care outcomes while ensuring operational resilience.
At the heart of these advancements lies the critical need for reliable, low-latency connectivity and local compute power. While cloud computing remains essential for large-scale data storage and processing, many enterprise applications increasingly require real-time decision-making at the network edge. This is where private 5G networks and AI-capable edge servers play a pivotal role. By bringing computing closer to the point of data generation, enterprises can reduce latency, enhance security, and ensure compliance with data sovereignty regulations.
The significance of this partnership extends beyond technical synergies. It also reflects a broader industry shift toward integrated solutions ecosystems. Enterprises no longer seek isolated technologies but demand cohesive platforms that enable rapid innovation and deployment. Ericsson and Supermicro’s joint offering aligns with this expectation by combining expertise in connectivity and compute infrastructure, ensuring seamless orchestration of AI-driven applications across distributed environments.
Moreover, the partnership is timely. According to recent market research, the global market for 5G edge AI solutions is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 35% over the next five years. This growth is fueled by escalating demand for use cases ranging from autonomous robotics in manufacturing to smart surveillance in retail and AI-assisted patient monitoring in healthcare. Enterprises that can harness the combined power of 5G and AI will gain a competitive edge by enabling faster, more intelligent operations.
In this context, the Ericsson–Supermicro partnership is poised to become a key enabler of next-generation enterprise digital transformation. It will empower factories to become smarter and more agile, retail environments to become more responsive and personalized, and hospitals to deliver higher-quality patient care through AI-enhanced insights.
This blog will explore the key dimensions of this groundbreaking collaboration. We will begin by examining the underlying technology stack, exploring how Ericsson’s private 5G networks and Supermicro’s edge servers create a powerful foundation for AI-driven innovation. We will then analyze the impact of this partnership across manufacturing, retail, and healthcare sectors, showcasing how these industries are already evolving through 5G-powered AI. Following this, we will assess market strategy and competitive positioning, providing insights into how this partnership fits within the broader landscape of 5G and edge computing solutions. Finally, we will consider the challenges, policy implications, and future outlook, offering a holistic view of the opportunities and risks that lie ahead.
As enterprises worldwide seek to navigate an increasingly complex and fast-evolving digital landscape, partnerships like the one between Ericsson and Supermicro illuminate the path forward. Through intelligent connectivity and localized compute power, the future of industry is not only connected—it is also profoundly intelligent.
The Technology Stack: Integrating 5G, AI, and Edge Infrastructure
At the core of the Ericsson and Supermicro partnership lies a sophisticated technology stack purpose-built to address the evolving computational, networking, and operational demands of enterprises embracing digital transformation. This integration of 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and edge computing infrastructure represents not just a convergence of technologies but a fundamental shift in how data is processed, transmitted, and acted upon in real time.
Ericsson’s Private 5G Networks: Low-Latency, High-Reliability Connectivity
Ericsson’s contribution to the partnership centers on its private 5G network infrastructure, a solution tailored to the needs of enterprises operating in mission-critical environments. Unlike public 5G networks, which serve a broad user base, private 5G networks are isolated, customizable, and optimized for specific operational scenarios such as manufacturing floors, retail environments, and hospital campuses.
These networks offer ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC)—a crucial enabler for real-time AI inference and machine control. With latency often reduced to below 10 milliseconds, enterprises can confidently deploy AI models that require immediate feedback loops, such as robotic vision systems or patient monitoring analytics. Moreover, private 5G ensures secure data transmission, a key consideration in sectors such as healthcare and retail, where data privacy and regulatory compliance are paramount.
A critical component of Ericsson’s network stack is its support for network slicing. This capability allows the physical 5G infrastructure to be partitioned into multiple virtual networks, each tailored for specific use cases with unique performance requirements. For instance, one slice can prioritize machine-to-machine communication for factory automation, while another handles high-definition video streams from hospital monitoring devices. This granular control enhances the efficiency, safety, and responsiveness of enterprise operations.
Supermicro’s Edge Servers: High-Performance AI Workload Processing
Supermicro complements Ericsson’s connectivity layer with its modular, high-performance edge computing platforms. These servers are engineered to operate in rugged, space-constrained environments, making them ideal for deployment on manufacturing floors, in retail outlets, or within hospital IT closets. Their support for AI accelerators—such as NVIDIA GPUs, Intel AI processors, and custom ASICs—enables the execution of complex deep learning models at the edge, significantly reducing dependency on centralized cloud resources.
The edge compute layer is essential for running AI workloads with real-time constraints, such as computer vision for defect detection in manufacturing or real-time footfall analytics in retail. Supermicro’s edge systems also support containerized workloads through platforms like Kubernetes, allowing for seamless deployment, orchestration, and scalability of AI applications. This is particularly valuable in dynamic environments where applications need to be frequently updated or scaled based on demand.
Furthermore, Supermicro’s architecture is optimized for energy efficiency and thermal management, both critical for continuous operation in environments without dedicated data center infrastructure. With remote management capabilities and built-in security modules, these edge platforms reduce operational overhead while ensuring robust cybersecurity protections.
AI Integration: Enabling Intelligent, Context-Aware Applications
The AI layer is the unifying force that brings actionable intelligence to enterprise workflows. Leveraging Ericsson’s low-latency 5G infrastructure and Supermicro’s compute power, AI applications can ingest data from sensors, cameras, and IoT devices in real time, perform inference on-site, and deliver immediate insights.
Examples of AI use cases enabled by this architecture include:
- Factories: Predictive maintenance algorithms analyzing sensor data to forecast equipment failures and reduce unplanned downtime.
- Retail: Computer vision systems identifying shelf stockouts and customer traffic patterns to optimize merchandising.
- Hospitals: AI models processing patient vitals in ICUs to detect early signs of deterioration and alert medical staff.
These use cases benefit significantly from edge AI inference, where models are deployed close to data sources, minimizing the time and bandwidth required for round-trip communication with the cloud. Additionally, this approach enhances data privacy and sovereignty, particularly in healthcare scenarios where regulatory frameworks like HIPAA or GDPR demand strict data handling practices.
System Architecture and Orchestration
The interoperability between Ericsson’s 5G core and Supermicro’s edge infrastructure is enabled through a cloud-native architecture, built on open standards and APIs. This design facilitates flexible integration with enterprise software platforms and third-party AI solutions, allowing organizations to build customized workflows that suit their specific operational contexts.
To orchestrate this system, containerization tools such as Docker and Kubernetes are used to manage and scale AI microservices across distributed edge nodes. Additionally, AI model lifecycle management is streamlined through MLOps frameworks that support continuous training, testing, and deployment, ensuring models remain accurate and responsive as operating conditions evolve.
For enterprises with hybrid infrastructure strategies, the architecture supports edge-cloud synergy. Certain non-time-sensitive tasks, such as AI model training or archival storage, can be offloaded to centralized or cloud data centers, while latency-sensitive inference remains at the edge.
Cybersecurity and Resilience
Given the mission-critical nature of the targeted sectors, cybersecurity is a foundational pillar of this technology stack. Ericsson’s networks incorporate end-to-end encryption, secure boot, and identity management, while Supermicro’s servers feature TPM modules, intrusion detection, and firmware-level hardening. These safeguards are complemented by AI-driven security analytics that monitor for anomalies, intrusions, and potential breaches.
Operational resilience is further enhanced through redundancy and failover mechanisms built into both the network and compute layers. This ensures continuity of service in the event of hardware failures, cyberattacks, or network outages—an indispensable feature in healthcare and industrial environments.
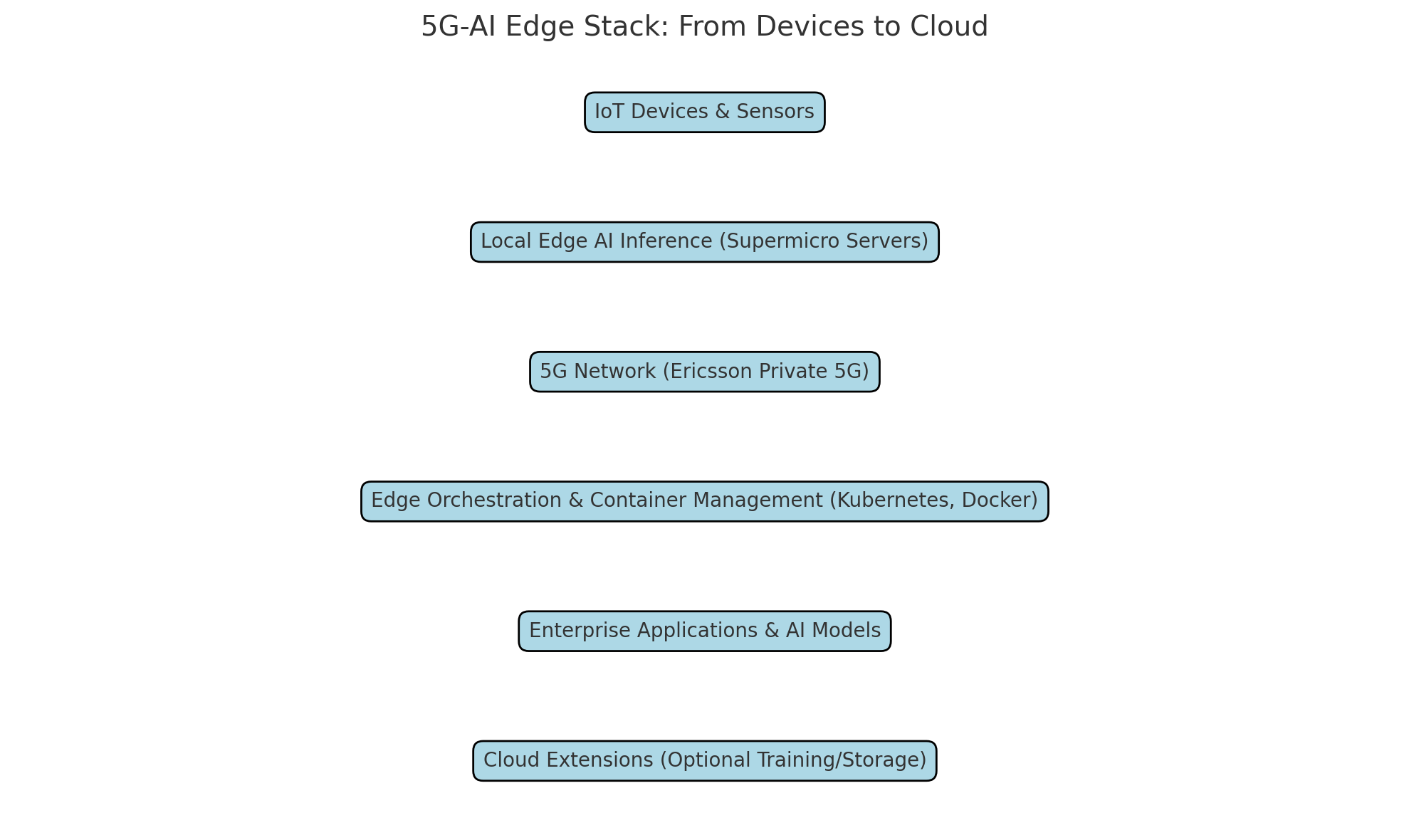
In summary, the Ericsson and Supermicro partnership delivers a synergistic technology stack that empowers enterprises to deploy AI-powered solutions at the edge with unmatched speed, reliability, and intelligence. By combining high-speed 5G connectivity with advanced edge compute capabilities and a flexible, secure orchestration framework, this integrated platform sets a new standard for real-time, AI-driven operations across industries.
Sectoral Impact: Factories, Retail, and Hospitals Transformed
The integration of 5G-powered AI solutions through the Ericsson and Supermicro partnership marks a pivotal advancement in the application of digital technologies across key industry sectors. By delivering ultra-low latency connectivity and high-performance edge computing, this combined solution enables real-time data processing and intelligent automation in environments where milliseconds matter. Three sectors poised to reap transformative benefits are factories, retail, and healthcare—each characterized by unique operational challenges and opportunities that are now being addressed through the synergistic capabilities of private 5G and AI.
Factories: Enabling Industry 4.0 through Intelligent Automation
Manufacturing, long a vanguard of industrial innovation, is undergoing a profound transformation under the banner of Industry 4.0. Central to this evolution is the deployment of connected sensors, autonomous systems, and AI-driven analytics that enhance efficiency, quality, and flexibility on the factory floor.
AI-Driven Robotics and Automation
Modern factories increasingly rely on robotic arms and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to perform repetitive, precision-driven tasks. These systems require instantaneous communication and decision-making, which traditional Wi-Fi or wired networks struggle to support at scale. Ericsson’s private 5G networks provide the necessary low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity, enabling real-time control of robotic systems. When combined with Supermicro’s edge servers running advanced AI models, these robots can adapt their behaviors dynamically based on live sensor inputs and visual data.
Predictive Maintenance
One of the most significant cost-saving applications is predictive maintenance. AI models continuously analyze data streams from industrial equipment—such as temperature, vibration, and acoustic signals—to detect anomalies and predict potential failures. By processing this data locally on Supermicro’s edge servers and transmitting alerts via Ericsson’s 5G network, manufacturers can preempt unplanned downtime, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend equipment lifespan.
Visual Defect Detection
Quality assurance, traditionally reliant on manual inspection, is now enhanced through AI-powered computer vision systems. High-resolution cameras capture images of products at various stages of production, while AI models analyze these images in real time to detect defects with a level of accuracy surpassing human capabilities. By processing these workloads at the edge, factories can ensure that defective products are identified and addressed immediately, minimizing waste and ensuring consistent product quality.
Operational Efficiency
By integrating AI insights with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and digital twin models, manufacturers gain holistic visibility into their operations. This enables smarter scheduling, inventory management, and production optimization, resulting in higher throughput, lower costs, and improved agility in responding to market demands.
Retail: Elevating Customer Experience and Operational Intelligence
The retail sector, faced with the dual imperatives of enhancing customer experience and optimizing operational efficiency, stands to benefit immensely from 5G-powered AI. The combined solution from Ericsson and Supermicro provides the technological backbone for delivering personalized, responsive, and data-driven retail environments.
Smart Shelves and Inventory Automation
Retailers are deploying smart shelf systems equipped with weight sensors and cameras to monitor inventory levels in real time. AI models running on edge servers process this data to detect stockouts and optimize replenishment schedules. This ensures that products are always available to customers while reducing excess inventory and minimizing operational costs.
Customer Behavior Analytics
Understanding customer behavior is critical to optimizing store layouts, marketing strategies, and product offerings. Through computer vision systems integrated with Ericsson’s 5G networks and Supermicro’s edge servers, retailers can analyze foot traffic patterns, dwell times, and demographic information in real time. This data empowers retailers to make data-driven decisions about product placement, promotions, and staffing.
Personalized In-Store Experiences
AI-driven recommendation engines, powered by data collected at the edge, enable retailers to offer personalized promotions to customers in-store. For instance, digital signage can display targeted advertisements based on customer profiles and real-time shopping behavior, enhancing engagement and conversion rates.
Contactless Checkout
The rise of frictionless checkout systems—such as AI-enabled self-checkout kiosks and smart carts—relies heavily on low-latency networks and robust edge computing. By processing transaction data and validating product selections in real time, retailers can deliver a seamless and secure checkout experience that enhances customer satisfaction.
Hospitals: Advancing Patient Care through Intelligent Health Systems
Healthcare represents one of the most impactful domains for the application of 5G-powered AI. The Ericsson and Supermicro solution empowers hospitals to deploy smart healthcare systems that enhance patient outcomes, streamline clinical workflows, and improve operational resilience.
AI-Assisted Diagnostics
Medical imaging and diagnostic processes are being revolutionized through AI. Supermicro’s edge servers enable the local processing of large imaging datasets—such as MRI and CT scans—using deep learning models that assist radiologists in identifying anomalies with greater accuracy and speed. By leveraging Ericsson’s low-latency 5G networks, these insights can be shared rapidly across clinical teams, facilitating faster decision-making and improving patient outcomes.
Smart ICU Monitoring
In intensive care units (ICUs), continuous monitoring of patient vitals is critical. AI models deployed at the edge analyze data from monitors and sensors in real time, detecting early signs of deterioration or critical events. This enables proactive interventions, reducing the risk of adverse outcomes. The use of private 5G ensures that this data is transmitted securely and reliably within the hospital environment.
Operational Efficiency and Asset Tracking
Hospitals can optimize operations through real-time tracking of medical equipment and supplies. AI-powered asset tracking systems, supported by 5G connectivity, enable staff to locate critical equipment quickly, reducing delays and improving patient care efficiency. Additionally, predictive analytics can help manage inventory of medical supplies, ensuring availability while minimizing waste.
Enhanced Telemedicine
The combination of 5G and AI also enhances telemedicine capabilities. High-definition video consultations, augmented by AI-driven diagnostic tools, provide patients with more accurate and comprehensive remote care experiences. Low-latency 5G networks ensure that these consultations are smooth and responsive, even in bandwidth-constrained environments.
Quantitative Benefits Across Sectors
Across factories, retail environments, and hospitals, the application of 5G-powered AI delivers measurable benefits:
- Efficiency gains of up to 30-50% in manufacturing through predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Revenue uplifts of 10-15% in retail through personalized experiences and smarter inventory management.
- Reduction in ICU mortality rates and shorter hospital stays through AI-enhanced monitoring and diagnostics.
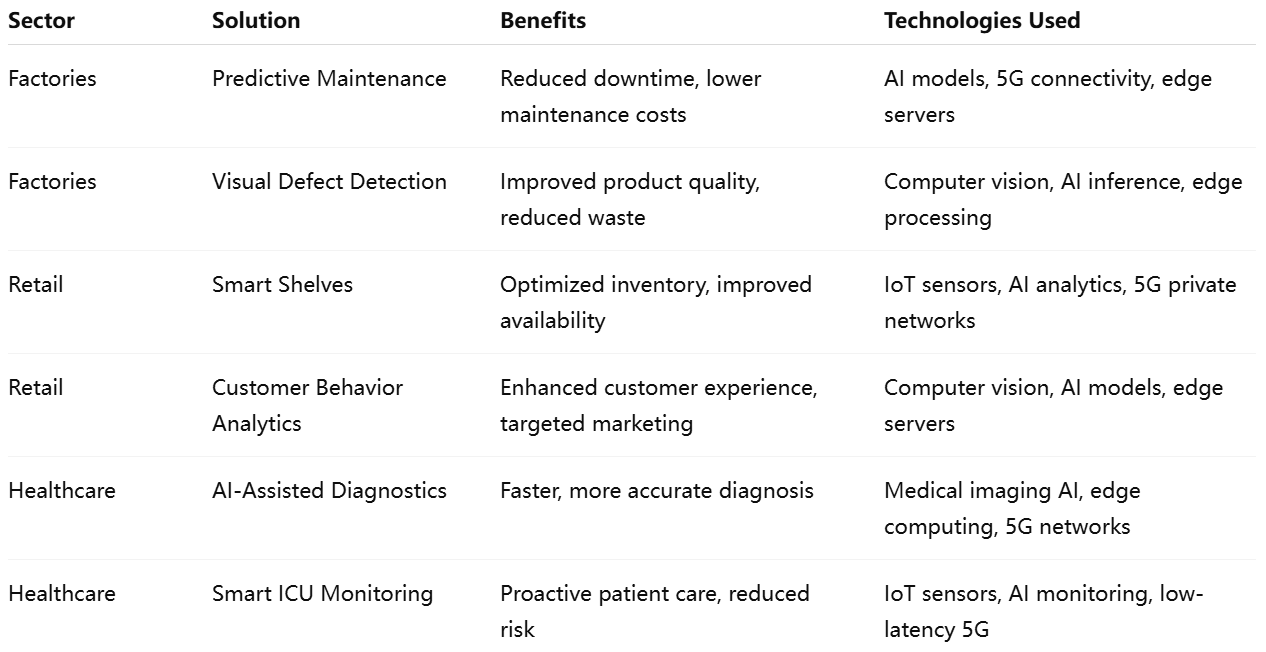
In summary, the Ericsson and Supermicro partnership is catalyzing sector-specific innovations that elevate operational performance and transform user experiences. From intelligent factories and smart retail stores to AI-enhanced hospitals, this integrated 5G-AI platform empowers enterprises to harness the full potential of real-time intelligence. As adoption accelerates, these advancements are poised to redefine industry benchmarks for efficiency, quality, and responsiveness, ushering in a new era of digitally enabled transformation.
Market Strategy and Competitive Positioning
The partnership between Ericsson and Supermicro represents a strategic alignment that goes beyond a simple collaboration of technologies. It is a carefully constructed response to a rapidly evolving market where 5G-enabled AI edge solutions are becoming critical to enterprise digital transformation. In this section, we examine the market strategy driving this partnership, its positioning relative to key competitors, and the broader industry dynamics shaping this emerging space.
Strategic Motivations: Combining Connectivity and Compute at the Edge
At the heart of this partnership lies a clear recognition of market demand for integrated, real-time AI capabilities that operate close to data sources. Enterprises across verticals increasingly require solutions that combine ultra-reliable low-latency connectivity with high-performance local compute to support latency-sensitive AI applications.
Ericsson brings to this equation its expertise in 5G private network infrastructure, having already established a strong presence in industrial deployments worldwide. The company’s ability to deliver secure, dedicated, and high-performance wireless connectivity is a key enabler for intelligent edge applications. Meanwhile, Supermicro contributes modular, AI-optimized edge servers that support a wide array of AI frameworks and hardware accelerators.
By offering an end-to-end stack—from 5G radio access networks (RAN) and core systems to edge compute nodes and AI orchestration tools—this partnership positions itself as a one-stop solution provider for enterprises seeking to deploy intelligent, connected applications. This is a notable differentiator in a market where many competing solutions still rely on fragmented architectures requiring complex system integration.
Furthermore, the partnership is strategically aligned with broader trends in enterprise IT investment:
- Increasing preference for private 5G networks over Wi-Fi in mission-critical environments.
- Growing demand for AI-powered automation and real-time decision-making.
- Rising need for data sovereignty and edge processing due to regulatory requirements.
- Expanding focus on hybrid edge-cloud architectures to balance latency, bandwidth, and cost considerations.
Competitive Landscape
The 5G edge AI market is rapidly attracting major technology players, each bringing distinct strengths and strategies. The Ericsson-Supermicro alliance faces competition from both established incumbents and innovative challengers.
Dell Technologies and VMware
Dell has aggressively entered the edge computing space, leveraging its Edge Gateway platforms and VMware’s telco cloud solutions to support edge AI deployments. Its ecosystem is attractive to enterprises already invested in Dell infrastructure, but it tends to rely on multi-vendor integration rather than a tightly coupled 5G + edge solution.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
HPE’s Edgeline series and its Aruba 5G partnerships offer compelling solutions for edge AI workloads. HPE emphasizes hybrid cloud integration and as-a-service consumption models, positioning itself as a flexible option for enterprises with cloud-first strategies.
Nokia
Nokia’s MX Industrial Edge platform integrates private 5G with edge computing and has seen success in manufacturing verticals. Like Ericsson, Nokia leverages its telecom heritage, but its edge compute partnerships are more nascent compared to Supermicro’s mature server offerings.
Huawei
Huawei’s 5G and AI portfolios are technologically advanced but face regulatory headwinds and geopolitical barriers in Western markets. While strong in China and parts of Asia, Huawei’s global competitiveness is constrained by supply chain restrictions and limited access to advanced AI chips.
Emerging Cloud-Edge Players
Hyperscalers such as AWS (AWS Wavelength), Microsoft (Azure Private MEC), and Google Cloud (Anthos for Telecom) are also entering the 5G edge AI space. They offer cloud-native edge platforms integrated with telecom partner networks. However, many enterprises—especially those in healthcare and manufacturing—remain wary of cloud lock-in and favor on-premises edge compute for latency, control, and data privacy reasons. Here, the Ericsson-Supermicro stack provides an attractive alternative.
Differentiators of the Ericsson-Supermicro Offering
The Ericsson-Supermicro partnership brings several competitive advantages that resonate with enterprise customers:
- Tightly Integrated Stack
A fully integrated solution from 5G RAN to edge compute, optimized for AI workloads, reduces deployment complexity and time-to-value. - AI-Optimized Edge Infrastructure
Supermicro’s wide range of AI servers—supporting GPUs, FPGAs, and specialized AI accelerators—enables flexible deployment of advanced AI models. - Private 5G Expertise
Ericsson’s leadership in private 5G deployments, combined with proven interoperability with industrial and healthcare systems, enhances trust and reliability. - Open, Cloud-Native Architecture
Compatibility with Kubernetes, Docker, and leading AI frameworks ensures that enterprises can adopt best-of-breed AI applications without vendor lock-in. - Focus on Data Sovereignty and Compliance
Edge-first architecture ensures that sensitive data—such as patient records or proprietary manufacturing data—can be processed locally in compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations.
Global and Local Deployment Considerations
The partnership’s market strategy is also attuned to regional market dynamics. In Europe, where data privacy is paramount and regulatory frameworks are stringent, the ability to deploy localized AI processing with private 5G connectivity is highly attractive. In North America, industrial and healthcare verticals are prioritizing low-latency, high-reliability networks that can support AI-powered automation.
In Asia-Pacific, where manufacturing dominates and Industry 4.0 adoption is accelerating, there is robust demand for AI-enhanced robotics and predictive maintenance solutions that can operate autonomously on the factory floor.
Ericsson and Supermicro’s combined global reach and localized deployment capabilities position them well to address these diverse market needs. Additionally, the alliance is likely to benefit from the growing interest among governments and industry bodies in fostering domestic edge computing ecosystems, particularly in sectors deemed critical infrastructure.
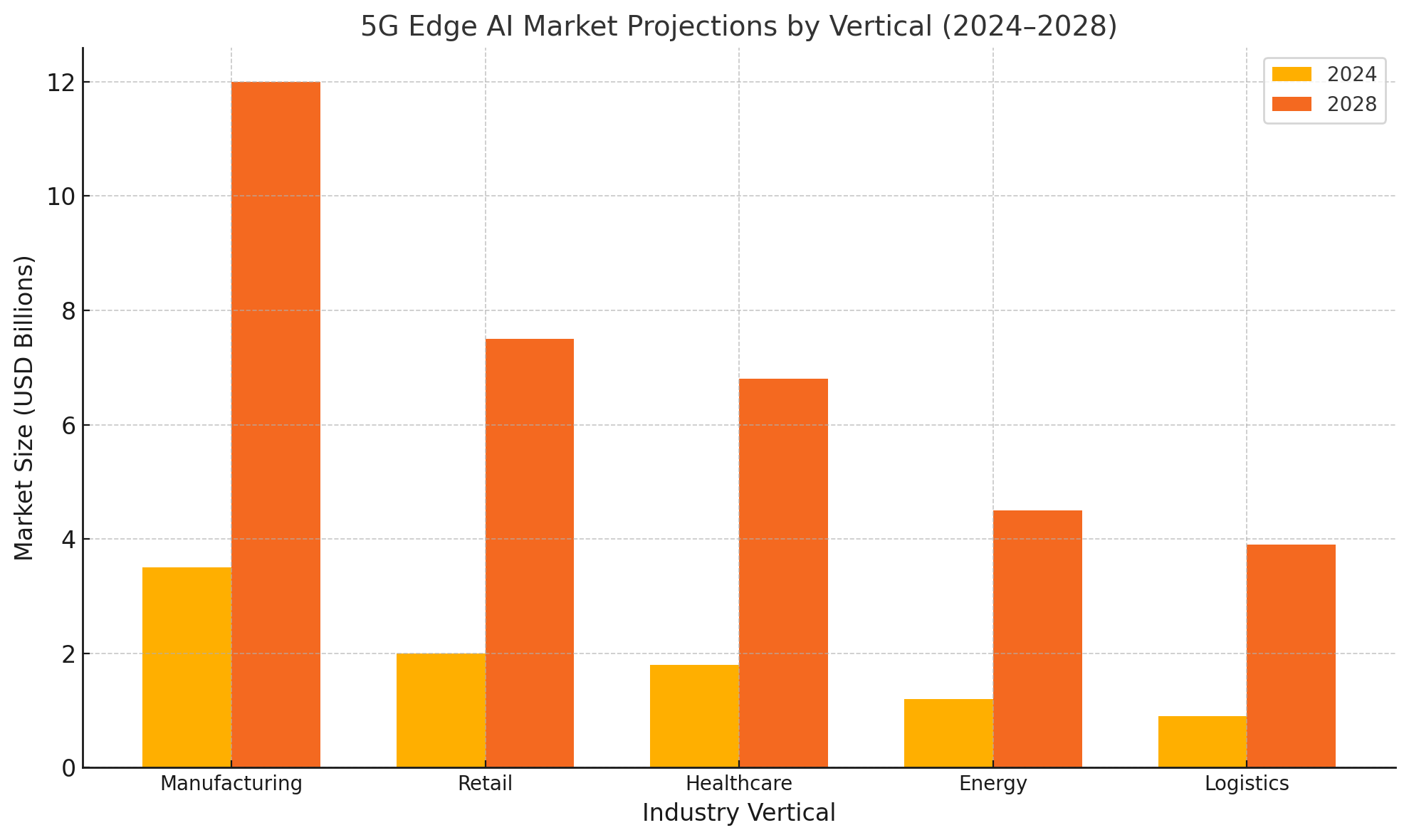
Future Partner Ecosystem Expansion
Looking ahead, Ericsson and Supermicro are expected to cultivate a broader ecosystem of partners to further differentiate their offering. Potential avenues include:
- AI software vendors specializing in computer vision, predictive maintenance, and healthcare analytics.
- Cloud providers offering hybrid edge-cloud orchestration tools.
- Systems integrators capable of customizing deployments for complex enterprise environments.
- Cybersecurity firms to enhance end-to-end security across the stack.
By fostering such an ecosystem, the partnership can deliver industry-specific solutions that are ready for rapid deployment and scale—an increasingly critical buying criterion for enterprises navigating accelerated digital transformation timelines.
Conclusion
In summary, the Ericsson-Supermicro partnership is strategically positioned to become a leading enabler of intelligent, 5G-powered edge solutions for enterprises across key verticals. Its integrated, open architecture offers a compelling value proposition amid a competitive landscape populated by fragmented, cloud-first, or telecom-centric alternatives.
As enterprise demand for real-time AI processing at the edge continues to grow, the success of this partnership will hinge on its ability to maintain technological leadership, expand ecosystem partnerships, and deliver scalable, secure, and cost-effective solutions across global markets. By combining connectivity expertise with AI-optimized compute infrastructure, Ericsson and Supermicro are well-equipped to drive the next wave of digital transformation across industries.
Challenges, Policy Implications, and Future Outlook
While the collaboration between Ericsson and Supermicro offers a compelling vision of AI-enabled, 5G-powered digital transformation, it also brings forth a range of technical, regulatory, and strategic challenges that must be addressed to ensure long-term scalability and success. These challenges intersect with broader policy considerations, especially around data governance, cybersecurity, infrastructure resilience, and environmental sustainability. This section outlines the primary risks and barriers confronting the deployment of 5G-AI edge infrastructure and explores what lies ahead for this fast-evolving domain.
Technical Challenges: Orchestration, Interoperability, and Latency Constraints
Despite the architectural promise of integrating 5G and AI at the edge, significant technical complexities persist. One of the foremost challenges is orchestrating distributed AI workloads across a hybrid edge-cloud environment. While Kubernetes and other container orchestration platforms provide foundational tools, the real-world management of large-scale, latency-sensitive, and context-aware AI services remains an open problem. Issues such as resource contention, network jitter, and data inconsistency across nodes can affect model accuracy and operational reliability.
Interoperability is another challenge. Enterprises typically operate heterogeneous IT environments with legacy systems, multiple software vendors, and diverse hardware configurations. Ensuring that Ericsson and Supermicro’s integrated solution can seamlessly interface with third-party platforms—from industrial control systems to hospital information management tools—requires adherence to open standards, robust APIs, and comprehensive system integration services.
Moreover, while 5G offers ultra-low latency under ideal conditions, performance can degrade in environments with signal interference, physical obstructions, or high device densities. For mission-critical applications such as robotic surgery or autonomous manufacturing lines, maintaining consistent sub-10ms latency is non-negotiable. Achieving this requires meticulous radio planning, dedicated spectrum allocations, and real-time network monitoring—all of which introduce operational complexity and cost.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
The convergence of AI, edge computing, and 5G expands the threat surface for cyberattacks. Edge nodes deployed in physically accessible locations—such as factory floors or retail stores—are particularly vulnerable to tampering, theft, or physical sabotage. Additionally, AI inference pipelines can be exploited through adversarial attacks, where malicious inputs are used to manipulate model outcomes.
To mitigate these risks, the Ericsson-Supermicro platform must implement multi-layered security architectures. This includes secure boot mechanisms, encrypted communication channels, hardware-based authentication, runtime anomaly detection, and AI model hardening techniques. Furthermore, zero-trust network principles should be enforced, wherein every device and data packet is continuously verified regardless of its origin or presumed trustworthiness.
Data privacy is especially critical in sectors like healthcare and retail. The use of edge AI to analyze biometric data, patient vitals, or shopping behavior requires strict compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA. Enterprises must establish clear data governance policies that define who can access what data, how it is stored, and under what conditions it may be transmitted to the cloud. Any breaches in this chain of trust can result in legal liabilities, reputational damage, and financial penalties.
Regulatory and Policy Implications
As AI and 5G become deeply embedded in critical infrastructure, regulatory oversight will intensify. Governments and standardization bodies are already exploring policies related to AI accountability, network neutrality, spectrum allocation, and cross-border data flows. For instance, the deployment of private 5G networks in certain jurisdictions requires licensing, adherence to electromagnetic safety standards, and environmental impact assessments.
AI regulation is evolving in parallel. The EU Artificial Intelligence Act, for example, classifies AI systems based on risk categories and mandates documentation, auditing, and transparency for high-risk applications such as medical diagnostics or biometric identification. Solutions deployed through the Ericsson-Supermicro platform will need to embed explainability, fairness, and auditability features into their AI models to meet these emerging requirements.
There is also increasing interest in data localization mandates, where sensitive data must remain within national borders. This trend reinforces the value proposition of edge AI but also imposes constraints on cloud interoperability and cross-jurisdictional data processing. Policymakers will play a central role in defining how enterprises navigate these trade-offs while preserving innovation.
Supply Chain and Geopolitical Risks
The physical components powering 5G and AI infrastructure—semiconductors, networking chips, servers, and sensors—are embedded in global supply chains that remain vulnerable to geopolitical tensions, export restrictions, and logistics disruptions. The recent semiconductor shortages and U.S.–China technology trade conflicts highlight how dependent the ecosystem remains on a few critical chokepoints.
Ericsson and Supermicro must proactively manage supplier diversification, inventory strategies, and geographical manufacturing risks to ensure continuity of service delivery. This may include sourcing from trusted vendors, increasing investment in onshore production capacity, and fostering open-source hardware ecosystems to reduce reliance on proprietary or restricted technologies.
Additionally, national security considerations may limit the use of certain foreign-sourced components in public sector or critical infrastructure deployments. As edge AI becomes increasingly integrated into domains such as defense, healthcare, and transportation, navigating these regulatory constraints will become an integral aspect of market strategy.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
The combined deployment of 5G infrastructure and AI-enabled edge computing raises concerns about energy consumption and environmental impact. While edge processing can reduce the carbon footprint associated with centralized cloud data centers and long-distance data transfers, running powerful AI workloads on distributed edge nodes still consumes significant energy.
To address this, Ericsson and Supermicro must prioritize energy-efficient hardware design, dynamic workload scheduling, and renewable energy sourcing for edge deployments. Advances in low-power AI chips, liquid cooling systems, and server virtualization can also help mitigate the environmental footprint of intelligent edge systems. Furthermore, providing enterprises with carbon impact dashboards and green AI metrics could enhance transparency and support sustainability goals.
Future Outlook: Scaling the Intelligent Edge
Despite these challenges, the future trajectory for 5G-powered AI at the edge is overwhelmingly positive. As AI models become more specialized, compute-efficient, and context-aware, their suitability for edge deployment will only increase. Simultaneously, 5G networks will continue to evolve, with Release 18 and beyond promising even lower latencies, enhanced reliability, and improved support for massive IoT deployments.
We can expect a significant expansion of applications across new verticals, including:
- Logistics: Real-time fleet management, automated inventory scanning, and AI-driven route optimization.
- Energy: Predictive maintenance for turbines, grid optimization, and anomaly detection in transmission lines.
- Education: Smart classrooms, immersive AR/VR learning environments, and AI-enhanced content delivery.
- Public Safety: AI surveillance, emergency response coordination, and real-time hazard detection.
Furthermore, the integration of generative AI models at the edge—capable of creating text, images, and simulations in real time—may unlock new frontiers in human-computer interaction and collaborative robotics.
As AI development continues to mature, we are likely to see an increase in federated learning models, where edge devices collaborate to train global AI systems without sharing raw data. This approach offers a powerful means of balancing data privacy, model performance, and regulatory compliance, especially in sensitive domains like healthcare.
Conclusion
The Ericsson–Supermicro partnership has the potential to redefine the architecture of enterprise intelligence, enabling organizations to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, agility, and insight through localized AI and high-speed connectivity. However, realizing this vision requires careful navigation of technical hurdles, regulatory landscapes, and environmental concerns.
As the 5G edge AI market matures, success will hinge not only on technological innovation but also on trust, governance, and resilience. Enterprises and regulators alike must work collaboratively to establish frameworks that support safe, ethical, and sustainable deployment of these transformative technologies.
Ultimately, the intelligent edge is not just a technological evolution—it is a strategic imperative. By embracing it now, industries can position themselves at the forefront of a smarter, faster, and more adaptive future.
References
- https://www.ericsson.com/en/5g
- https://www.supermicro.com/en/products/edge-computing
- https://www.ericsson.com/en/industries/private-networks
- https://www.supermicro.com/en/solutions/artificial-intelligence
- https://aws.amazon.com/wavelength/
- https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/azure-private-mec/
- https://cloud.google.com/anthos/telecom
- https://www.hpe.com/us/en/solutions/edge-computing.html
- https://www.dell.com/en-us/dt/solutions/edge-computing/index.htm
- https://nokia.com/networks/solutions/private-wireless/
