Duolingo’s AI Revolution: From Language Learning to a Global EdTech Powerhouse
In the dynamic landscape of educational technology, Duolingo has long stood as a pioneering force in democratizing access to language learning through its gamified mobile platform. Founded in 2011, the Pittsburgh-based company has amassed hundreds of millions of users globally, cultivating a loyal base through its intuitive user interface, playful animations, and bite-sized lesson format. However, recent strategic signals from the company’s executive leadership point to a broader ambition: to transform Duolingo from a language-focused application into a more expansive AI-powered education platform.
This shift was underscored in a recent earnings call and subsequent media engagement where Duolingo’s Chief Financial Officer, Matthew Skaruppa, emphasized that artificial intelligence is not merely an enhancement tool but a fundamental driver for the company’s next phase of evolution. According to Skaruppa, AI holds the key to expanding Duolingo’s product suite, entering new markets, and building scalable educational tools that transcend traditional subject boundaries. The CFO’s remarks are timely, arriving at a critical juncture when generative AI is reshaping the global education industry, promising hyper-personalized learning, intelligent feedback mechanisms, and content scalability on an unprecedented level.
Duolingo’s pivot toward AI-driven educational expansion is not entirely surprising. The company has been incrementally introducing artificial intelligence into its core language learning app over the past few years. Notable features such as “Roleplay,” powered by generative models akin to GPT, allow users to practice conversational scenarios with virtual characters. Other AI-enhanced features like “Explain My Answer” use machine learning to provide contextualized feedback in real time. These innovations have not only improved user retention but have also streamlined internal content creation workflows, reducing the need for human reviewers and curriculum developers. From a financial standpoint, these efficiencies have contributed to Duolingo’s ability to scale with relatively lean operating costs—a point Skaruppa highlighted as a core strategic advantage.
Yet, the most intriguing element of Duolingo’s new vision lies beyond its existing success in language education. The company is actively developing and investing in parallel learning applications, including Duolingo ABC, a literacy-focused app aimed at young children, and Duolingo Math, which introduces elementary and middle-school level math skills through the same gamified learning experience. These products are still in the early stages of growth but represent significant proof points in Duolingo’s thesis that its brand, distribution network, and AI capabilities can be applied to a wide array of learning domains. The implications of this shift are profound. If successful, Duolingo may evolve from a niche language app into a full-spectrum edtech ecosystem, competing not only with traditional publishers and online education providers, but also with emerging AI-native learning platforms.
At the core of this transition is a philosophical commitment to accessibility and personalization, which has long underpinned Duolingo’s product strategy. Skaruppa’s remarks emphasized that the integration of artificial intelligence enables a level of adaptive learning previously impossible through conventional means. By leveraging large language models and predictive algorithms, Duolingo can now create content that adjusts in real time to a user’s proficiency, learning style, and engagement pattern. This has significant implications not just for user satisfaction and retention, but also for educational outcomes. As AI continues to evolve, so too will the platform’s ability to support students at vastly different levels—be it a beginner attempting their first English sentence or an advanced learner preparing for the TOEFL.
What makes Duolingo’s approach particularly noteworthy in the broader AI conversation is its dual commitment to pedagogical integrity and technological innovation. Unlike some edtech firms that merely plug AI into existing systems, Duolingo has reengineered its product stack to be AI-native. This means that AI is not an afterthought—it is baked into the very foundation of how content is created, how user interaction is assessed, and how new features are conceptualized and deployed. In doing so, Duolingo is setting a precedent for what next-generation educational apps could look like: adaptive, autonomous, and algorithmically optimized for impact.
However, this rapid evolution is not without its challenges. As Duolingo expands into new subject areas and adopts more sophisticated AI models, it must also navigate the complexities of educational ethics, algorithmic bias, and data privacy. Furthermore, the company’s ambitious plans place it on a collision course with legacy educational institutions and tech giants who are similarly racing to dominate the future of learning. This raises important questions about the scalability of AI in education, the boundaries of automation in teaching, and the role of human educators in a world increasingly shaped by machine intelligence.
In this blog post, we will explore the strategic, financial, and technological dimensions of Duolingo’s AI-led expansion beyond language learning. We begin by taking a closer look at the company’s financial underpinnings and how its investment in AI aligns with its business model. From there, we delve into the AI infrastructure powering Duolingo’s product evolution, followed by an examination of its competitive positioning in the global edtech market. We then assess the challenges and risks that lie ahead, particularly in scaling AI responsibly. Finally, we conclude by reflecting on what Duolingo’s transformation means for the broader trajectory of educational technology.
Through this comprehensive analysis, it becomes clear that Duolingo’s ambition is more than a mere rebranding—it is a strategic reinvention grounded in the belief that AI can democratize high-quality education across geographies, demographics, and disciplines. If the company succeeds, it will not only redefine its own future but may also catalyze a paradigm shift in how the world learns.
Financial Backbone and Strategic Positioning
Duolingo’s strategic emphasis on artificial intelligence is not occurring in a vacuum; it is intimately tied to the company's robust financial positioning and its long-term goal of sustainable, AI-driven expansion. As highlighted by Chief Financial Officer Matthew Skaruppa, the integration of AI technologies across Duolingo’s operations is not simply about innovation for its own sake—it is a calculated move designed to generate operating leverage, improve profitability, and enable scalable content delivery without proportional increases in cost. In this section, we examine the financial underpinnings that make this transformation possible and analyze how AI investment aligns with Duolingo’s broader business objectives.
Since its IPO in 2021, Duolingo has consistently demonstrated strong revenue growth across its key business segments. The company’s three primary revenue sources—subscription income, advertising revenue, and Duolingo English Test (DET) fees—have each played a critical role in fueling its product development and market expansion. Among these, subscription services constitute the lion’s share, driven by the popularity of Duolingo Plus (now Super Duolingo), a premium offering that removes ads and introduces additional learning features. This subscription base has grown substantially year-over-year, providing the company with a reliable stream of recurring income.
From a financial strategy perspective, Duolingo’s recurring revenue model is highly conducive to experimentation with frontier technologies like AI. According to recent earnings disclosures, the company has allocated a growing portion of its operational budget to AI research and development, including partnerships with foundational model providers and the scaling of internal machine learning teams. This investment has resulted in a meaningful increase in platform efficiency. As Skaruppa noted, Duolingo has been able to deliver more lessons, features, and personalized feedback to a growing user base without a commensurate rise in human capital expenses. In effect, AI is serving as a multiplier of productivity—an asset class that amplifies existing capabilities rather than replacing them outright.
To illustrate the relationship between Duolingo’s revenue growth and AI investment, consider the following chart:
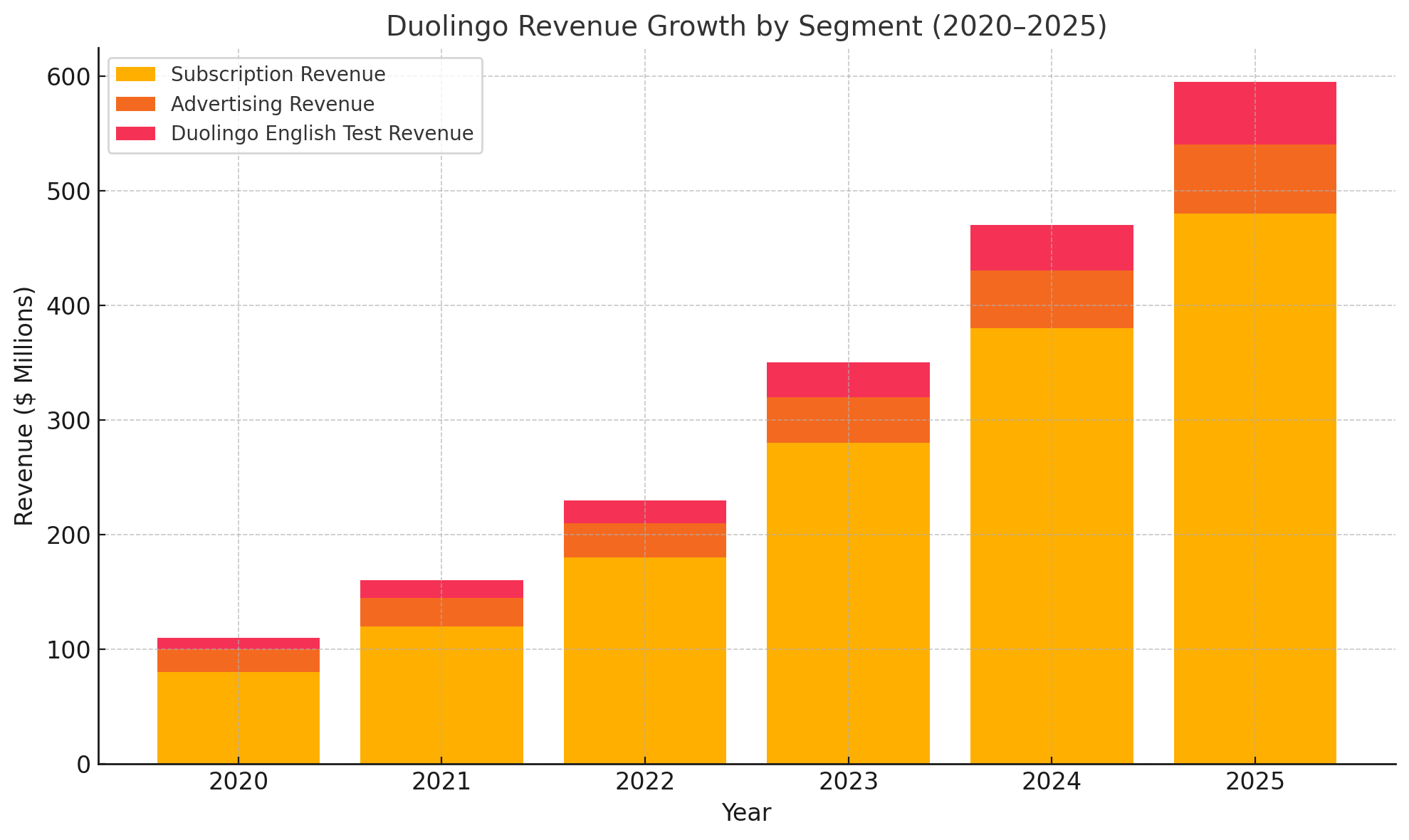
This visual representation underscores the increasingly dominant role of subscriptions in Duolingo’s revenue portfolio, alongside steady contributions from advertising and the English Test. AI-driven product improvements—such as smarter lesson personalization, automated explanations, and GPT-based interactive roleplays—have contributed directly to higher engagement and retention, thereby boosting lifetime customer value (LTV) and reducing churn rates.
Equally critical to understanding Duolingo’s financial strategy is the Duolingo English Test (DET). Initially launched as a response to the pandemic-era disruption of traditional English language testing, the DET has since gained wide acceptance from hundreds of universities worldwide. This product line is uniquely positioned to benefit from AI enhancements, particularly in the areas of automated proctoring, adaptive testing algorithms, and real-time fraud detection. As international student mobility rebounds post-COVID, Duolingo is well-placed to capitalize on a high-margin, scalable product that serves a global market in need of low-cost, accessible certification options.
The CFO’s emphasis on AI as a mechanism for financial scalability also reflects in Duolingo’s efforts to lower the cost per learner while maintaining high educational standards. A key example of this efficiency play is the use of generative AI to create course content in new languages. Traditionally, course development was labor-intensive, requiring a combination of language experts, curriculum designers, and beta testers. With AI, Duolingo has managed to reduce development cycles by generating early drafts of lessons and explanations, which are then fine-tuned by human editors. This hybrid model has significantly compressed time-to-market for new language courses and could potentially be applied to math and literacy products as well.
A breakdown of relevant financial metrics supports this narrative of AI-enabled growth and efficiency:
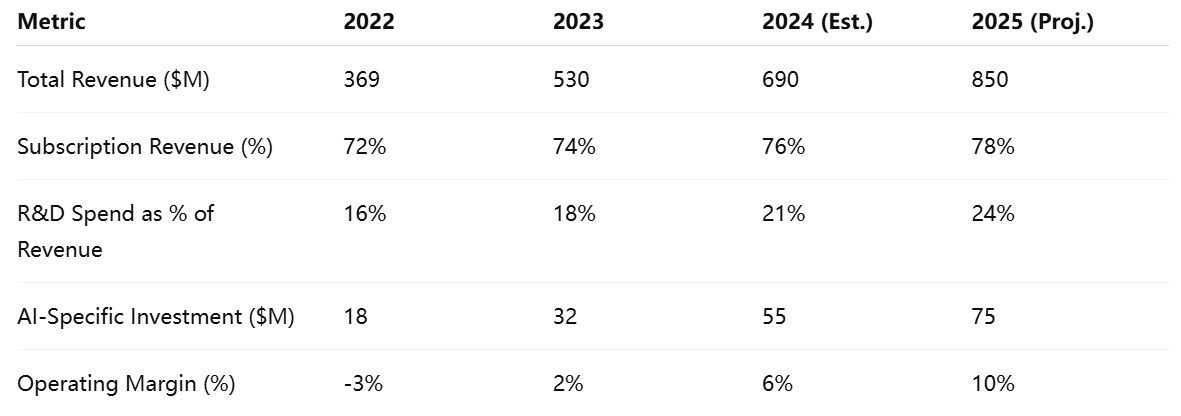
These figures highlight a steady upward trajectory in revenue and profitability, supported by rising investment in AI and product development. Of particular note is the jump in AI-specific spending, which has more than quadrupled between 2022 and 2025. This reflects Duolingo’s belief that AI is not an auxiliary tool, but a core strategic pillar of its future.
Moreover, Duolingo’s asset-light business model—anchored in software and digital content—allows it to scale globally without the capital expenditures typically associated with physical infrastructure. This lean operational structure is further enhanced by AI, which automates routine workflows and unlocks new levels of user engagement. The CFO’s comments made it clear that the company is leveraging these advantages to expand its addressable market beyond language learning and into general education, without compromising profitability.
From an investor relations perspective, Duolingo’s strategic alignment of financial discipline and technological innovation is a compelling narrative. The company has managed to achieve both top-line growth and bottom-line improvement while aggressively investing in next-generation AI. This balance is rare in the edtech sector, where many firms struggle with high content costs and user acquisition expenses. In contrast, Duolingo’s brand strength, network effects, and in-app virality provide a strong moat, allowing AI to serve as an accelerant rather than a risky bet.
In conclusion, the financial rationale behind Duolingo’s AI-first strategy is grounded in its proven ability to grow revenue efficiently, improve margins, and scale content delivery through technology. The CFO’s vision, as articulated in public disclosures, reveals a company that is not only adapting to the AI era but actively shaping its own trajectory through calculated investment, product innovation, and operational excellence. With AI as a central pillar of both growth and efficiency, Duolingo is well-positioned to redefine its role in the global education landscape—not just as a language app, but as a scalable, intelligent, and financially sound learning platform.
The AI Engine Behind Duolingo’s Transformation
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a peripheral enhancement within Duolingo’s product ecosystem; it is now the foundational engine driving the company’s transition into a diversified educational technology platform. At the core of Duolingo’s transformation is a deliberate re-architecture of its learning model—one that leverages AI to personalize content, scale product development, automate feedback, and unlock entirely new verticals in education. This section explores how Duolingo is embedding AI across its product lines, the models and infrastructures supporting this shift, and the broader implications for user experience and business scalability.
Duolingo’s first meaningful application of AI came in the form of personalized learning paths, which replaced the company’s earlier linear progression model. By using machine learning algorithms trained on user behavior and learning performance data, Duolingo restructured its content delivery system to prioritize mastery over memorization. Rather than pushing users through rigid lesson structures, the AI system adapts dynamically—reviewing weak areas, adjusting difficulty levels, and offering tailored exercises to improve retention. This transition marked a crucial philosophical shift: away from one-size-fits-all education toward a more adaptive, learner-centric model.
Perhaps the most groundbreaking application of AI within Duolingo’s flagship language product is the integration of generative models to simulate interactive learning environments. A standout example is "Roleplay," a feature that uses a GPT-based conversational AI to engage users in contextual dialogues with fictional characters. For instance, a user learning French might practice ordering food in a Parisian café or checking into a hotel—scenarios constructed by the model based on user level, past mistakes, and curriculum goals. These conversations are not hard-coded but generated on the fly, creating virtually limitless possibilities for practice and feedback. According to Duolingo, this feature has significantly improved user engagement and language fluency, especially in developing conversational confidence.
Complementing this is the "Explain My Answer" tool, another AI-powered feature that provides real-time, individualized feedback on why a user’s answer is correct or incorrect. Leveraging natural language understanding (NLU) models, this tool enhances metacognition by offering context-aware explanations that go beyond binary right-or-wrong signals. In doing so, Duolingo bridges a critical gap in digital education—replicating, to some extent, the nuanced feedback traditionally provided by human instructors.
These features are made possible through a combination of proprietary machine learning models, third-party foundational models such as OpenAI’s GPT, and an increasingly AI-native infrastructure built in-house. Duolingo has established a hybrid AI stack that allows for experimentation at scale. Lightweight models are often deployed on-device to ensure fast response times, while more complex tasks like dialogue generation or adaptive lesson sequencing are handled server-side. This flexible architecture enables Duolingo to innovate quickly, optimize cost-efficiency, and localize learning experiences across a diverse global user base.
One of the lesser-known but equally impactful applications of AI at Duolingo is in content generation and curriculum development. Traditionally, the creation of new courses and lessons involved a time-intensive process of expert drafting, peer review, and user testing. With generative AI, much of this can be accelerated. Models are now used to generate initial drafts of lesson text, sample questions, pronunciation guides, and even audio files using text-to-speech engines. Human linguists still play a role in quality control, but the overall time-to-market for launching a new language or skill has decreased significantly. This has allowed Duolingo to expand its course offerings more rapidly than would have been feasible with a purely manual process.
The company’s AI capabilities are also being extended to its adjacent educational products, such as Duolingo ABC (focused on literacy) and Duolingo Math. In ABC, AI is used to adjust the pacing of phonics instruction for early learners based on individual progress. For Duolingo Math, AI algorithms adapt the difficulty of questions in real-time, ensuring that students neither plateau nor become frustrated due to steep difficulty curves. Although these products are still gaining traction, they serve as important testbeds for AI applications beyond language, validating Duolingo’s thesis that its learning methodology and AI stack are transferable across domains.
To better understand user adoption trends and the growing impact of AI-driven features, the following chart illustrates the uptake of AI tools across Duolingo’s products:
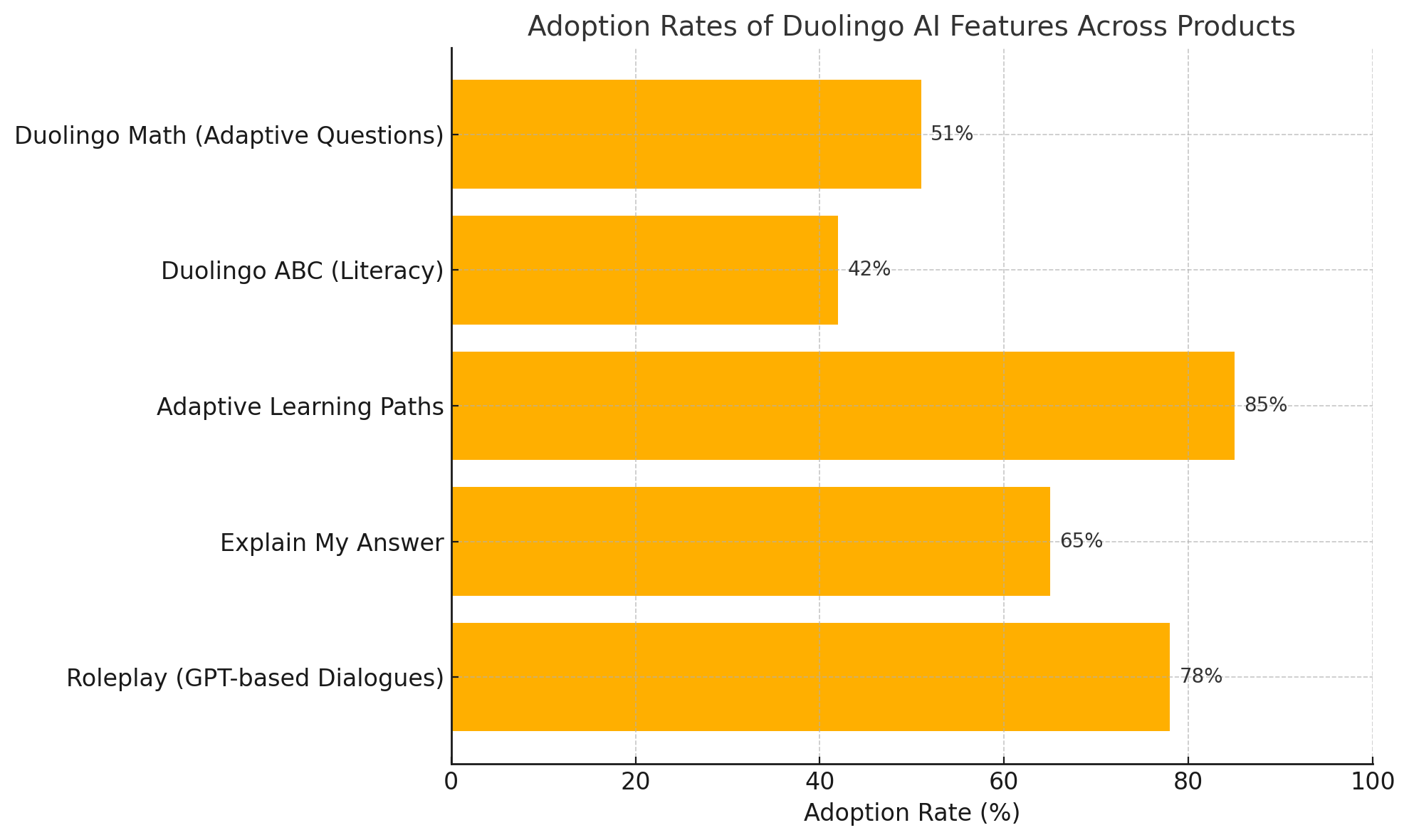
The chart highlights strong adoption of GPT-powered Roleplay in Duolingo’s language app, followed by the growing use of Explain My Answer and adaptive math challenges. These trends indicate not just user interest, but a growing dependence on AI to deliver personalized, immersive, and efficient learning experiences. The data also reveal that AI features are particularly popular among paying subscribers—a correlation that underscores their monetization potential.
Behind the scenes, Duolingo has built a formidable AI research function that includes partnerships with top-tier AI labs and the development of proprietary tooling. The company has increasingly focused on reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to fine-tune AI behavior, ensuring that outputs align with educational best practices and user expectations. Duolingo’s AI teams work closely with curriculum designers and UX researchers to integrate AI into the product in a way that enhances, rather than disrupts, the core learning experience.
A particularly innovative direction is Duolingo’s exploration of voice-enabled learning, where AI-driven speech recognition and synthesis technologies are being used to assess pronunciation and speaking fluency. This feature is being rolled out incrementally and holds promise for language learners who lack access to live speaking partners. Using deep learning models trained on multilingual speech datasets, Duolingo can now detect pronunciation errors with high precision and provide corrective feedback—all within a gamified, non-intimidating interface.
However, with great innovation comes great responsibility. Duolingo has taken a cautious approach to deploying AI in sensitive contexts, particularly when it comes to younger learners and high-stakes testing. Safeguards are in place to monitor for bias, hallucination, and privacy violations, especially in AI-generated dialogues and explanations. The company’s internal review processes involve human oversight, adversarial testing, and red-teaming strategies to catch potential issues before they reach end-users.
Looking ahead, Duolingo envisions AI playing an even larger role in future product verticals, potentially including science education, test preparation, and even soft skills training. The company's leadership has expressed interest in building AI tutors capable of delivering long-form educational narratives, conducting assessments, and simulating real-world challenges. Such capabilities, if realized, could position Duolingo at the forefront of a new era in personalized learning—one where AI is not just a tool, but an intelligent co-instructor.
In summary, the AI engine behind Duolingo’s transformation is multifaceted, encompassing personalized learning, generative feedback, content acceleration, and cross-domain adaptability. By embedding AI into its core infrastructure, Duolingo is not only enhancing its existing products but also laying the groundwork for future innovations that may fundamentally redefine how education is delivered at scale. The company’s commitment to ethical, pedagogically sound AI deployment reinforces its credibility in the edtech space and sets a high bar for its competitors.
Competitive Landscape and Market Expansion Strategy
As Duolingo transitions from a language-learning app to a broader AI-powered education platform, it must navigate an increasingly complex and competitive landscape. The edtech sector is witnessing a rapid influx of players—from AI-native startups to global technology giants—all vying for dominance in the next generation of digital learning. Duolingo’s response to this competition has been strategic, leveraging its brand strength, scalable AI infrastructure, and data-driven approach to both defend its core market and expand into adjacent verticals. In this section, we analyze Duolingo’s competitive positioning, its differentiation strategy, and the avenues through which it is pursuing international growth and subject diversification.
Navigating a Crowded EdTech Ecosystem
The current edtech environment is more competitive than ever. Longstanding educational platforms such as Khan Academy, Quizlet, and Coursera have integrated AI features into their ecosystems, offering personalized learning, intelligent tutoring systems, and adaptive content delivery. Meanwhile, newer entrants like Socratic by Google and Byju’s Future School are attempting to capture market share by embedding generative AI from the outset. Even general-purpose AI platforms, such as ChatGPT and Claude, are being repurposed by educators and students for real-time question answering, test preparation, and explanation-based learning.
In this context, Duolingo’s primary advantage lies in its tightly integrated product design. Unlike competitors that bolt AI features onto existing infrastructure, Duolingo has architected its platform with AI at the core. This deep integration allows for seamless user experiences, consistent performance, and effective feedback loops across its suite of products. Furthermore, the company's commitment to pedagogical integrity ensures that AI enhancements are not only innovative but also instructional. This focus on educational efficacy differentiates Duolingo from tools that emphasize AI novelty without clear learning outcomes.
Another key differentiator is Duolingo’s gamification model, which has consistently driven higher engagement and retention rates compared to traditional learning systems. The strategic use of behavioral economics—through streaks, XP points, badges, and leaderboards—complements the AI-driven personalization to create a compelling, habit-forming experience. While competitors like Memrise and Babbel also employ gamified techniques, Duolingo’s scale, brand recognition, and community features provide it with a unique moat in this domain.
Global Reach and Localized Learning
Duolingo’s expansion strategy is rooted in its ability to localize learning content efficiently, a capability that has been greatly enhanced by AI. By using machine translation models and neural network-based pronunciation engines, the company can tailor lessons for different linguistic and cultural contexts without the need for extensive manual intervention. This localization is critical for expanding in high-growth emerging markets such as India, Brazil, Indonesia, and Nigeria—regions where mobile-first learning is not just a convenience but a necessity.
To further support this global strategy, Duolingo has invested in refining its speech recognition and synthesis tools for non-English accents and dialects. AI models trained on region-specific linguistic data enable better evaluation of user pronunciation and provide culturally appropriate corrections. This has been particularly important in countries where English is taught as a second language but is spoken with significant local variation. As a result, Duolingo has been able to deliver more inclusive and effective language learning experiences that accommodate a wide array of user backgrounds.
In parallel, Duolingo’s Duolingo English Test (DET) has emerged as a powerful vehicle for international expansion. Unlike traditional standardized tests such as TOEFL or IELTS, the DET can be taken online at a lower cost, with AI-based proctoring and scoring systems ensuring test integrity. This makes it especially appealing to students in under-resourced regions who need English certification for immigration or academic purposes. With a growing list of academic institutions recognizing the DET, Duolingo has positioned itself as a credible player in the high-stakes testing arena—a sector long dominated by a few legacy incumbents.
Subject Diversification as a Market Entry Strategy
Beyond geographic expansion, Duolingo’s move into new subjects—particularly literacy and math—reflects a calculated approach to increasing its total addressable market (TAM). Products such as Duolingo ABC and Duolingo Math allow the company to reach different age groups and educational stages, thereby expanding beyond its traditional user base of adult language learners.
Duolingo ABC targets early childhood literacy and is designed to teach foundational reading skills through phonics-based lessons and storybooks. The app uses AI to assess comprehension in real time and adjusts story difficulty accordingly. Meanwhile, Duolingo Math incorporates spaced repetition, adaptive questioning, and visual problem-solving to make numeracy more engaging for K–8 students. Although these products are still in their growth phase, early adoption data and user reviews suggest they hold strong potential, especially in the U.S. and other digitally mature markets.
Importantly, these subject areas are not isolated experiments but are being integrated into Duolingo’s larger ecosystem. User accounts are unified across products, allowing for shared gamification elements, user profiles, and AI-driven personalization. This ecosystem approach enables Duolingo to cross-sell and retain users across multiple educational journeys, thereby improving lifetime value and reducing acquisition costs.
Partnerships and Ecosystem Leverage
Duolingo’s expansion strategy is further bolstered by a selective partnership approach. While the company has historically maintained a proprietary tech stack, it has partnered with AI model providers like OpenAI for specific generative capabilities, such as conversational AI and intelligent explanations. These partnerships allow Duolingo to stay at the cutting edge of AI innovation without diverting excessive internal resources toward foundational model development.
Additionally, Duolingo’s presence in app stores and educational institutions gives it considerable ecosystem leverage. The app regularly ranks at the top of the Education category in both iOS and Android marketplaces, providing organic visibility and trust. Integration with education platforms like Google Classroom and Apple Schoolwork could further extend its utility in formal education settings, though Duolingo remains primarily consumer-focused.
Finally, Duolingo’s pricing strategy—offering robust free tiers with optional subscriptions—has allowed it to scale globally while maintaining accessibility. This freemium model, underpinned by AI efficiency, ensures that user acquisition and engagement remain high even in price-sensitive markets. The addition of premium features powered by AI (e.g., Roleplay, Explain My Answer) provides a clear value proposition for conversion without alienating free users.
Maintaining Strategic Agility in a Rapidly Evolving Market
The education market is subject to constant shifts in technology, pedagogy, and user expectations. Duolingo’s competitive strategy hinges on its ability to remain agile—to continuously iterate on AI models, respond to feedback, and pivot as needed. The company’s agile development cycles, data-driven culture, and direct-to-consumer feedback channels provide a strategic edge in adapting to market changes.
That said, Duolingo must also contend with macro-level risks, including geopolitical changes affecting app availability, shifting regulations on AI in education, and evolving user privacy standards. Competitors with deeper enterprise ties or government relationships may have advantages in certain institutional markets. To remain competitive, Duolingo will need to further deepen its AI competencies while maintaining regulatory compliance and user trust.
In summary, Duolingo’s approach to competition and market expansion is defined by its AI-first infrastructure, strategic subject diversification, and data-optimized global outreach. By reinforcing its competitive moat through innovation, user engagement, and inclusive design, Duolingo is positioning itself as a formidable force not only in language learning but in the broader edtech universe. The next phase of its journey will depend on how effectively it scales its innovations and adapts to the evolving competitive landscape.
Challenges, Risks, and the Road Ahead
As Duolingo embraces artificial intelligence to power its transformation into a full-spectrum education platform, it faces a number of significant challenges that extend beyond technical execution. While AI opens doors to personalization, efficiency, and subject expansion, it also brings forth complex risks related to pedagogy, ethics, security, and long-term sustainability. In this final core section, we explore the multifaceted risks Duolingo must navigate and outline the strategic considerations that will shape the company’s journey forward.
Balancing Automation with Pedagogical Integrity
At the heart of Duolingo’s mission is its commitment to delivering high-quality, research-backed educational content. The increasing reliance on AI—particularly generative and adaptive models—poses a real risk to this mission if not carefully governed. While artificial intelligence can generate explanations, simulate conversations, and personalize lesson plans, it can also introduce inconsistencies, hallucinated content, and pedagogically unsound logic if left unchecked.
For example, the Roleplay feature, powered by generative language models, must walk a fine line between engaging dialogue and educational relevance. Unlike human instructors, AI may occasionally generate responses that are grammatically correct but linguistically unnatural or culturally inappropriate. This could result in learners internalizing flawed language patterns. Similarly, Explain My Answer must provide explanations that are not only accurate but age-appropriate and aligned with pedagogical standards. Any misalignment between AI outputs and instructional objectives could degrade user trust and learning outcomes.
To mitigate these risks, Duolingo has implemented rigorous human-in-the-loop systems. These include content moderation pipelines, expert validation processes, and adversarial testing to detect harmful outputs before features are released. However, as the company scales its AI applications across more subjects and languages, maintaining this level of oversight will become increasingly complex. The challenge lies in ensuring that AI remains a tool that enhances human judgment, rather than replacing it prematurely or uncritically.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
Duolingo’s global reach and AI-driven architecture place it under the scrutiny of emerging regulations around algorithmic transparency, data privacy, and child safety. In markets like the European Union, the AI Act mandates strict compliance for educational technologies that employ automated decision-making. Likewise, jurisdictions such as California and India have introduced or proposed frameworks that demand greater disclosure around data usage, consent, and bias mitigation in AI systems.
Given that Duolingo serves millions of underage users through products like Duolingo ABC and Duolingo Math, the stakes are even higher. AI features in these apps must comply with child protection regulations such as COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act) in the United States and GDPR-K in the EU. This requires extensive infrastructure to ensure that children’s data is not exploited, shared inappropriately, or used to train commercial models without consent.
In addition, AI models—particularly those trained on large and diverse datasets—can inadvertently reflect or amplify cultural biases. In a language learning context, this may manifest in gendered assumptions, regional stereotyping, or exclusionary language. Duolingo must continue to invest in bias auditing frameworks, multicultural review boards, and inclusive design protocols to ensure that its AI tools reflect the diversity of its global user base.
Operational and Technical Risks
From an operational standpoint, scaling AI across a platform as vast as Duolingo presents logistical challenges. These include latency management, model retraining, content caching, and real-time inference across different geographies. As Duolingo adds more AI-driven features and expands into more languages, the computational load increases exponentially. Ensuring that the platform remains responsive and lightweight for mobile-first users—especially in bandwidth-constrained regions—is a non-trivial engineering feat.
Moreover, as Duolingo partners with external AI providers such as OpenAI for certain generative tasks, it becomes exposed to third-party dependency risks. Changes in API pricing, service availability, or licensing terms could disrupt product continuity or increase costs. This reinforces the need for Duolingo to strike a balance between building in-house capabilities and strategically outsourcing specific AI functions.
Security is another key concern. AI models—especially those involving user-generated content—can be exploited through prompt injection, data poisoning, or adversarial attacks. As Duolingo becomes more reliant on AI to manage dialogue, assessment, and feedback, it must bolster its AI security architecture, including input sanitization, anomaly detection, and usage monitoring systems.
The Role of Human Educators and Hybrid Learning Models
One of the most pressing philosophical questions surrounding Duolingo’s evolution is the role of human educators in an increasingly AI-automated system. While Duolingo has never aimed to replace formal schooling, its product design inherently disintermediates traditional teacher-led instruction. As the platform moves into subjects like math, literacy, and potentially science, it enters domains where live instruction, emotional support, and peer interaction are critical components of learning.
To maintain its educational credibility, Duolingo must clarify its position in the broader learning ecosystem. This could involve partnerships with schools, integrations with classroom tools, or the development of educator dashboards that allow teachers to monitor and complement Duolingo-led learning. In doing so, the company can position AI not as a substitute for teachers, but as an augmentative tool that enhances access, personalization, and consistency.
Moreover, Duolingo may explore hybrid learning models, where AI guides the majority of self-paced learning, while human tutors or mentors step in for higher-order tasks such as project-based assessments or emotional encouragement. Such models are already gaining traction in corporate training and higher education and could represent the future of comprehensive, scalable education.
Strategic Outlook and Future Vision
Looking ahead, Duolingo’s ability to lead the next wave of edtech innovation will depend on its strategic clarity, ethical stewardship, and technical resilience. The company has already articulated a vision of becoming a “world-class AI learning company,” and its investments in infrastructure, research, and product development reflect that ambition.
Key areas of future exploration include:
- Multimodal learning: Integrating video, voice, and AR/VR for immersive education.
- Agent-based learning companions: Persistent AI tutors that evolve with the learner over time.
- Workforce training: Expanding into job-oriented learning modules, certifications, and upskilling content.
- Open-access research: Contributing datasets and findings to the broader AI and education research communities.
These initiatives, however, will only be impactful if they are executed with a clear understanding of the social contract that educational platforms hold. As Duolingo’s AI becomes more powerful, so too does its responsibility to ensure that learners are empowered, not manipulated; guided, not merely gamified.
In conclusion, Duolingo’s transformation into an AI-first education platform is both a remarkable achievement and an ongoing responsibility. The company’s strategic focus, engineering excellence, and product innovation have positioned it as a leader in the next era of learning. Yet the path forward is fraught with challenges—pedagogical, ethical, technical, and societal. By acknowledging these risks and proactively addressing them, Duolingo has the opportunity not only to expand beyond language learning, but to redefine what accessible, personalized, and impactful education can look like in the age of artificial intelligence.
References
- Duolingo Investor Relations – Quarterly Reports
https://investors.duolingo.com/financials - The Verge – Duolingo uses GPT-4 to power new AI features
https://www.theverge.com/2023/3/21/duolingo-gpt4-ai-language-learning - TechCrunch – Duolingo’s roadmap includes expanding beyond language learning
https://techcrunch.com/duolingo-expansion-ai - Duolingo Blog – Inside Duolingo: How AI Shapes Our Learning Experience
https://blog.duolingo.com/ai-language-learning/ - OpenAI – Case Study: Duolingo Uses GPT-4
https://openai.com/customer-stories/duolingo - EdSurge – The Rise of AI in Education Platforms
https://www.edsurge.com/news/ai-in-edtech-platforms - CNBC – Duolingo’s growth strategy tied to AI-powered products
https://www.cnbc.com/duolingo-ai-growth-strategy - Harvard Business Review – Designing AI Systems for Education
https://hbr.org/designing-ai-systems-education - World Economic Forum – AI and the Future of Personalized Learning
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/ai-future-of-learning - Fast Company – Duolingo Math and Literacy Apps Signal AI Ambitions
https://www.fastcompany.com/duolingo-math-literacy-apps-ai
