Duolingo Replaces Human Contract Workers with AI: A Game-Changer in Language Learning and Workforce Efficiency
Duolingo has established itself as one of the most popular language-learning platforms in the world, offering a unique, gamified experience for users eager to master new languages. Known for its accessibility, affordability, and diverse selection of courses, the platform has gained millions of active users globally. Over the years, Duolingo has continuously innovated its approach to language learning, integrating cutting-edge technology to enhance the user experience. One such technological advancement gaining traction within the company is Artificial Intelligence (AI), a force that is reshaping not just Duolingo’s product offerings, but its internal operations as well.
In an effort to streamline its operations and reduce costs, Duolingo has announced plans to replace human contract workers with AI. This shift represents a significant pivot in the company’s workforce strategy, moving from reliance on human contributors for various roles to fully automated systems powered by AI. The decision is emblematic of a broader trend in the tech industry, where companies are increasingly turning to AI-driven solutions to replace or augment human labor. While the allure of AI lies in its potential for increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness, this move also raises important questions about the future of work, the ethics of AI replacing human workers, and the long-term impact on Duolingo’s culture and business model.
The purpose of this blog post is to explore the factors behind Duolingo’s decision to replace human contract workers with AI, examine the potential benefits and drawbacks of this transition, and analyze the implications for both the company’s employees and its users. By the end of this post, readers will gain a deeper understanding of how Duolingo’s AI-driven future could shape the landscape of language education and workforce dynamics in the tech sector.
The Role of Human Contract Workers at Duolingo
Human contract workers have long played an integral role in Duolingo’s operations. Initially, the platform’s success was largely attributed to its innovative use of technology, particularly its gamified approach to language learning. However, behind the scenes, a significant portion of Duolingo’s functionality was supported by human workers who provided essential contributions in various capacities. These contract workers were key to maintaining the high standards of the platform’s content, user experience, and customer support.
One of the primary functions of human contract workers at Duolingo involved content moderation and quality assurance. Given the wide range of languages offered on the platform, maintaining the accuracy and appropriateness of language content was crucial. Human workers were tasked with reviewing user-generated content, such as translations and sentences submitted by learners. This ensured that the content adhered to the platform’s standards and provided a high-quality learning experience. Human reviewers were particularly valuable in dealing with nuanced language issues, such as idiomatic expressions, regional dialects, and culturally sensitive topics. The limitations of AI in understanding these subtleties meant that human oversight was essential to avoid errors and misinterpretations.
Another area where contract workers contributed significantly was in the realm of customer support. Duolingo has always prided itself on offering responsive customer service to its millions of users, and human agents were responsible for addressing issues related to account management, billing, technical support, and user feedback. While the company has automated many aspects of its customer service with AI-driven chatbots and FAQs, the complexity of certain user inquiries required human intervention. Contract workers were relied upon to handle more intricate issues that AI systems could not resolve, ensuring a smooth and personalized experience for Duolingo’s customers.
Additionally, human contract workers supported the company’s expansion into new languages and markets. Duolingo’s mission is to make education accessible to everyone, regardless of location or socioeconomic background, and to achieve this goal, the platform has continually added new languages. Human workers, particularly linguists and translators, were hired on a contract basis to develop new language courses, review translations, and refine the learning experience for speakers of various languages. This human expertise ensured that Duolingo’s offerings were not only linguistically accurate but also culturally relevant.
Despite their crucial role, human contract workers were not permanent employees of Duolingo. Instead, they were hired on a temporary, project-based basis, which allowed the company to remain agile and cost-effective. These workers were typically brought in for specific tasks or periods of high demand, such as when new languages were launched or when there was a surge in user engagement. The reliance on contract workers allowed Duolingo to access a diverse pool of talent without the financial commitment of permanent staffing. However, this model also came with its own set of challenges. Contract workers often faced uncertainty in terms of job stability, as their roles were limited in scope and duration. Furthermore, the lack of long-term employment benefits such as healthcare or retirement plans highlighted the precarious nature of these positions.
The decision to replace human contract workers with AI is a significant shift for Duolingo, as it marks the end of an era where human expertise was central to the company’s operations. While the move may result in cost savings and operational efficiencies, it also raises concerns about the loss of valuable human insight, particularly in areas requiring nuanced judgment and cultural sensitivity. The following sections will delve into the reasons behind this transition and its potential impact on both the company’s workforce and the broader language learning ecosystem.
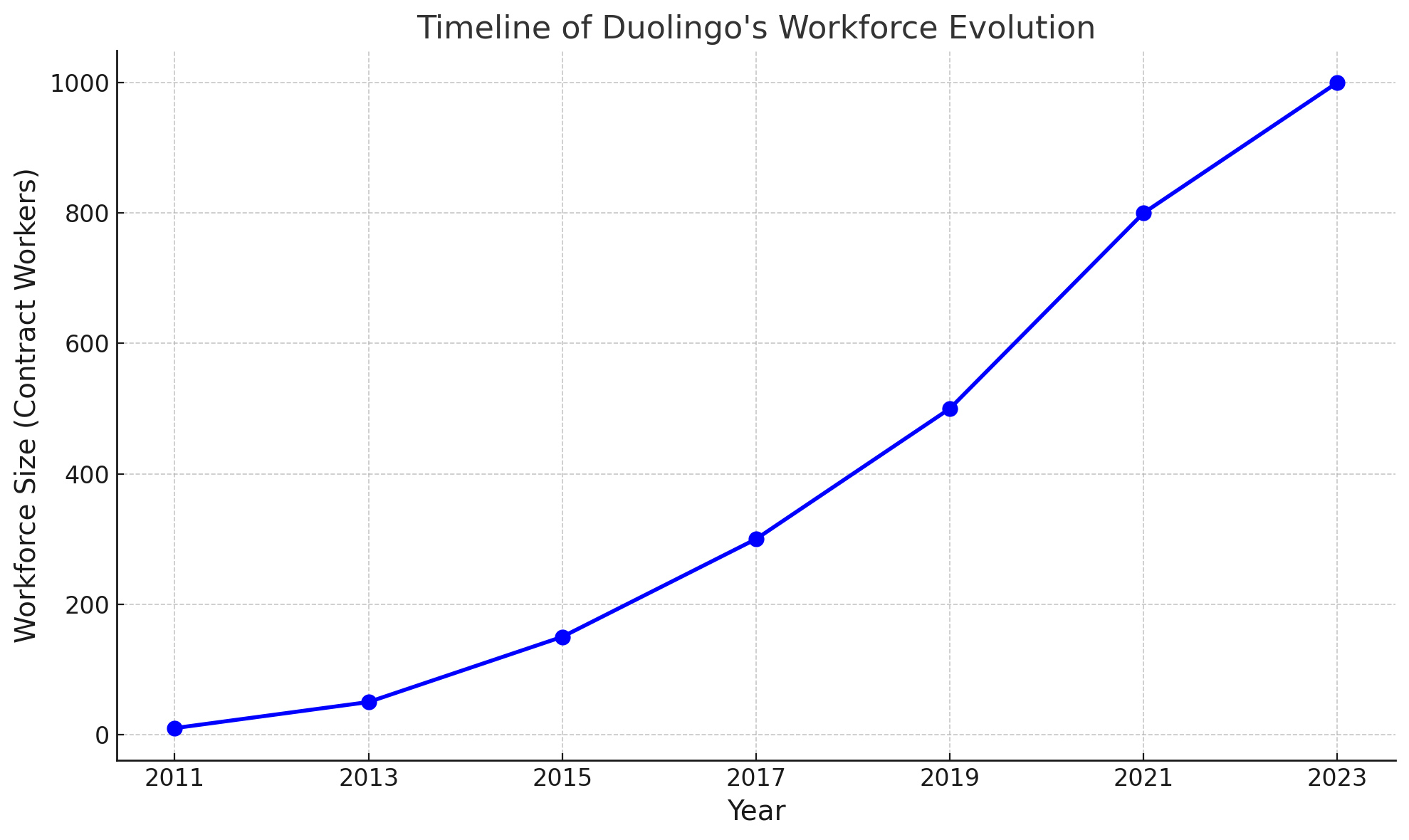
To better understand the evolution of Duolingo's workforce, it is important to consider the growth of human contract workers over the years. Initially, the company relied heavily on human contributors to maintain content quality, provide customer support, and develop new language courses. As Duolingo expanded its user base and increased its offerings, the number of contract workers steadily grew. Chart 1 illustrates the timeline of this workforce expansion, offering a visual representation of how Duolingo's reliance on human labor evolved before the shift toward automation. This chart serves as a backdrop for understanding the company's move to integrate AI technologies, highlighting the growth that preceded the transition.
The Shift Toward AI: Why and How Duolingo is Making the Change
The decision to replace human contract workers with Artificial Intelligence (AI) marks a pivotal moment in Duolingo’s evolution as a company. As the world increasingly turns to automation and AI to optimize operations, Duolingo is no exception. The move reflects the broader trend in the tech industry where AI-driven solutions are replacing traditional human labor in an effort to achieve greater efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. While this shift may be seen as a strategic business decision, it also signifies a transformative step toward the future of language education, as Duolingo seeks to leverage cutting-edge technology to improve the user experience and streamline internal operations.
Why Duolingo is Turning to AI
There are several key factors driving Duolingo’s decision to integrate AI into its workforce, replacing human contract workers in the process. Foremost among these is the desire to reduce operational costs. The reliance on human contract workers, while valuable, can be expensive, especially for a global platform like Duolingo. Contract workers are hired on a temporary basis, often with varying rates depending on the scope of their work. Moreover, managing a large, diverse workforce of contractors requires significant administrative resources. By shifting to AI, Duolingo stands to eliminate many of these costs, automating processes that would otherwise require human oversight and management.
AI offers several advantages in terms of operational efficiency. Tasks such as content moderation, user support, and even language translation can be automated using sophisticated algorithms, machine learning models, and natural language processing (NLP) techniques. This can significantly reduce the need for manual labor, enabling Duolingo to handle a higher volume of tasks more quickly and with fewer resources. AI systems can also operate 24/7, ensuring that the platform remains responsive to users’ needs around the clock, without the need to schedule or manage human labor in different time zones.
Furthermore, AI technology allows Duolingo to scale its operations more effectively. As the platform expands into new languages and markets, the volume of content that needs to be generated, reviewed, and moderated increases. AI-powered systems can handle this surge in demand much more effectively than a human workforce, enabling Duolingo to maintain the high-quality standards it is known for, even as it grows. Moreover, AI systems can continuously learn and adapt, improving over time through reinforcement learning and data-driven feedback loops. This capacity for self-improvement makes AI a highly attractive option for Duolingo as it looks to stay ahead in a competitive market.
How Duolingo is Implementing AI
Duolingo’s strategy for replacing human contract workers with AI is based on the application of advanced technologies in natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and automated systems. These technologies are integral to the platform’s language-learning model, as they allow for more precise and personalized interactions with users.
One of the key AI technologies being deployed is NLP, which enables the platform to better understand and process the vast amount of linguistic data that users generate. NLP algorithms are being used to automate the moderation of user-generated content, ensuring that the translations, sentences, and exercises within the app meet Duolingo’s quality standards. These systems are capable of analyzing the context of sentences, detecting errors in grammar or structure, and offering suggestions for improvement. Over time, as these models are trained on larger datasets, their accuracy and ability to handle more complex linguistic challenges will continue to improve.
Another area where AI is making a significant impact is in customer support. Duolingo has already integrated AI-powered chatbots into its platform, allowing users to get quick answers to their questions without the need for human intervention. These chatbots are capable of handling a wide range of inquiries, from account management to technical troubleshooting. The AI models are continually refined to recognize and respond to more nuanced user issues, and they can direct users to human agents only when necessary. This not only streamlines the support process but also ensures that users receive timely responses, even during peak hours.
Furthermore, Duolingo is using AI to improve its language instruction capabilities. Through machine learning algorithms, the platform can now provide more personalized learning experiences for its users. By analyzing a learner’s progress, behavior, and areas of struggle, the system can tailor lessons and recommendations to meet the individual’s needs. This adaptive learning approach is more efficient than relying on human instructors to provide one-on-one guidance, especially for a platform with millions of users.
Duolingo is also exploring the potential of AI to help with the creation of new language courses. Traditionally, new courses have required extensive input from human linguists and translators. However, with AI’s ability to process vast amounts of linguistic data, Duolingo can now expedite the creation of courses by using AI to analyze existing language materials and generate course content. This process not only speeds up course development but also allows Duolingo to expand its offerings to even more languages, including rare and less commonly taught ones.
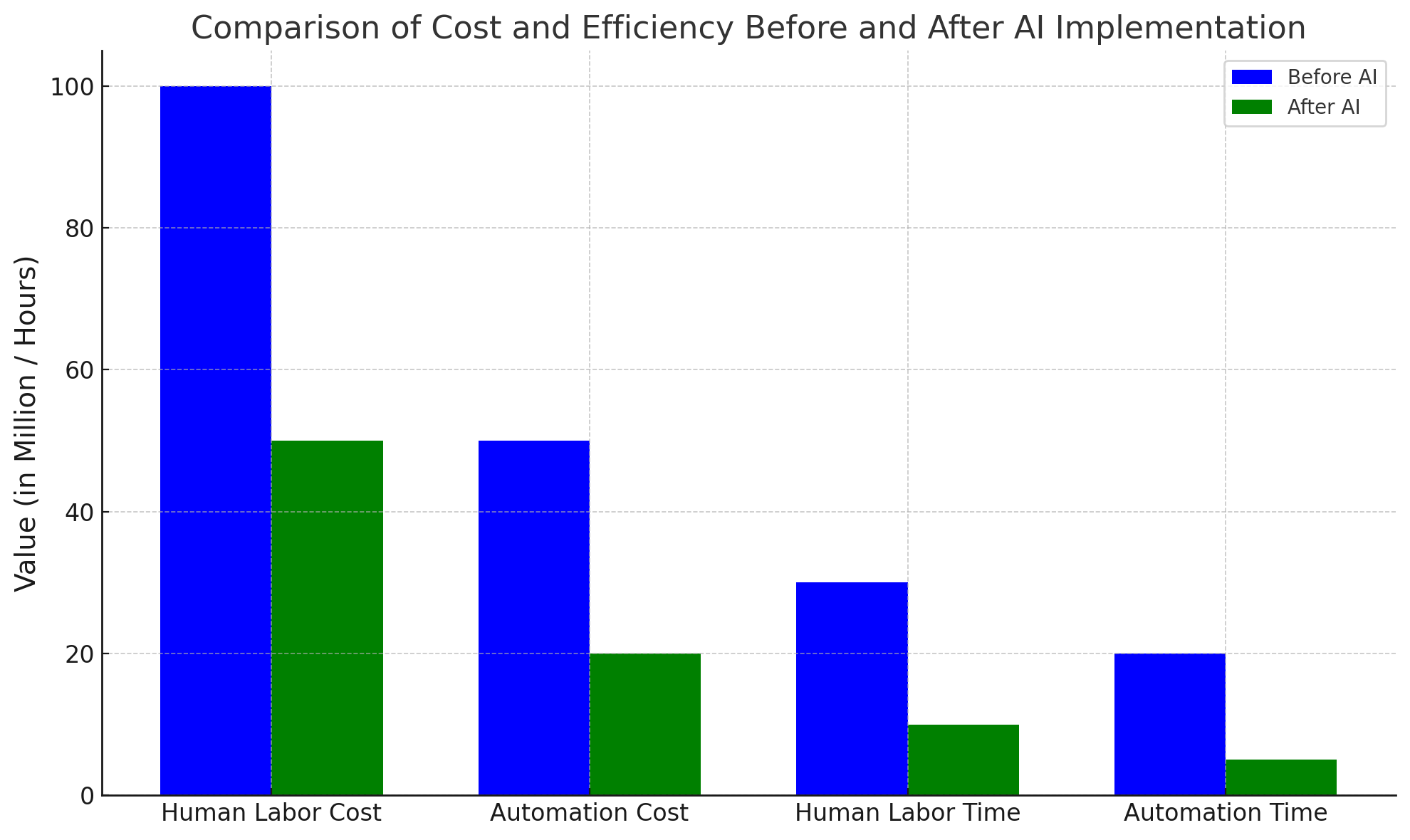
As Duolingo moves towards a more AI-driven model, the impact on cost and efficiency becomes increasingly apparent. With the introduction of AI, many tasks previously handled by human contract workers can now be automated, reducing both operational costs and time spent on manual labor. Chart 2 provides a clear comparison of the costs and efficiency levels before and after the AI implementation, illustrating how the company can achieve significant savings and increased productivity by replacing human labor with AI-driven solutions. This comparison not only underscores the financial and operational benefits of AI but also sets the stage for understanding the broader implications of automation at Duolingo.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the many advantages that AI offers, Duolingo must carefully manage the transition to ensure that the shift from human workers to AI is both ethical and effective. The implementation of AI raises several concerns, particularly regarding the potential for job displacement. While the company may be reducing costs, it must also consider the impact on the workers whose jobs are being replaced. The loss of human jobs, particularly in areas where AI has yet to fully match human judgment, could lead to resistance from employees and the public. Duolingo will need to navigate these challenges by offering support to affected workers, such as providing retraining opportunities or assisting in job placement.
Additionally, while AI is capable of automating many tasks, there are still areas where human judgment is invaluable. Language, for example, is filled with nuance, cultural context, and subtleties that are difficult for AI to fully comprehend. As Duolingo integrates AI, it will need to ensure that it does not sacrifice the quality of the user experience by over-relying on technology. Balancing the strengths of AI with the insights of human workers will be crucial for maintaining the platform’s reputation and user satisfaction.
Conclusion
Duolingo’s shift towards AI represents a strategic move to optimize its operations and stay competitive in the rapidly evolving edtech landscape. By leveraging AI technologies such as natural language processing, machine learning, and automated systems, the company can improve its efficiency, scalability, and user experience. However, the move to replace human contract workers with AI also raises important questions about the future of work, job displacement, and the ethical implications of relying on technology to perform tasks traditionally handled by humans.
Impact on Employees and Users
The decision to replace human contract workers with AI at Duolingo, while seemingly a progressive step in terms of technological adoption, has far-reaching implications for both employees and users. As the company shifts toward a more automated workforce, the effects on its employees—particularly contract workers—are likely to be significant. Similarly, users of the platform will also experience both the advantages and potential challenges associated with this transition. In this section, we will explore the impact on Duolingo’s workforce, the company’s efforts to address potential concerns, and how users are likely to benefit from AI integration.
Impact on Employees: Job Displacement and Reskilling
One of the most immediate and pressing consequences of Duolingo’s decision to replace human contract workers with AI is the displacement of jobs. As the platform moves toward automation, contract workers who have been responsible for content moderation, customer support, and language course development are likely to lose their roles. While Duolingo’s AI solutions can handle many of the tasks previously performed by humans, they cannot replicate the breadth of human insight and judgment that is often required in areas such as cultural sensitivity, regional dialects, and complex customer service interactions. This raises a fundamental question: how can Duolingo balance the efficiency of AI with the irreplaceable value of human employees?
Job displacement in the tech sector, particularly in positions traditionally filled by contractors, is a growing concern across industries. The rise of AI-driven automation has led to increasing anxiety about job security among workers, particularly those whose roles are most susceptible to automation. In the case of Duolingo, contract workers who relied on the company for temporary employment may face challenges finding new positions, particularly if they lack the technical skills required for roles in AI development or data science. While the company’s decision may result in cost savings, it is crucial that Duolingo takes steps to mitigate the negative impact on its workforce. This could involve offering retraining programs, helping displaced workers transition into new roles, or providing severance packages and career support services.
Furthermore, as Duolingo embraces AI, the skills required for employment within the company will evolve. Employees who were once focused on manual tasks such as reviewing user-generated content and answering customer service inquiries may need to pivot toward more technical roles, such as AI oversight, machine learning model training, or data analysis. Duolingo could help facilitate this transition by investing in reskilling initiatives, providing its workforce with access to courses and certifications in AI and data science. By doing so, the company could help future-proof its workforce, allowing employees to remain relevant and competitive in an increasingly automated world.
Impact on Users: Enhanced Efficiency and Personalization
For Duolingo’s users, the shift to AI-driven operations promises a number of potential benefits. Perhaps the most significant of these is enhanced efficiency. AI systems, unlike human workers, can operate continuously without the need for breaks or sleep, offering a level of consistency that human employees simply cannot match. By integrating AI into content moderation, customer support, and language instruction, Duolingo can offer faster response times and improve the overall user experience. This will likely lead to a more seamless and uninterrupted learning journey, as users can expect quicker resolutions to technical issues or content-related queries.
One of the standout features of AI-powered language learning systems is their ability to provide highly personalized experiences for individual learners. Through machine learning algorithms, Duolingo’s platform can analyze a user’s behavior, learning patterns, and progress over time to tailor lessons and suggestions accordingly. This personalized approach enables the platform to better meet the specific needs of each user, enhancing the effectiveness of the learning process. For example, if a learner struggles with a particular language concept or word group, the AI can identify this weakness and provide additional practice in those areas, helping to accelerate the learner’s mastery of the language.
Moreover, AI can enable Duolingo to introduce more advanced language features that were previously out of reach due to the limitations of human resources. For example, Duolingo could use AI to offer more dynamic conversation practice, allowing users to engage in realistic dialogues with AI-driven characters. These dialogues could simulate real-world scenarios, helping learners practice their language skills in a more interactive and engaging way. The integration of AI also means that Duolingo can expand its offerings to include a wider variety of languages, including rare or endangered languages that would otherwise require specialized human translators.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the many potential benefits of AI integration, there are several challenges and ethical considerations that Duolingo must navigate as it moves toward automation. The most significant of these is the question of fairness and the potential for bias in AI systems. While AI models are designed to learn from vast amounts of data, these datasets can often reflect existing biases, including those related to language, culture, or gender. If Duolingo’s AI systems are trained on biased data, they may inadvertently perpetuate these biases in their interactions with users. For instance, AI-generated translations or responses could favor certain dialects or cultural norms while neglecting others. As a result, Duolingo must ensure that its AI systems are developed with inclusivity in mind, using diverse datasets and regularly auditing models for fairness.
Another consideration is the potential loss of the human touch in customer service. While AI chatbots and virtual assistants can provide quick and efficient responses to user inquiries, they often lack the empathy and understanding that human agents bring to complex or emotionally charged situations. For example, a user struggling with a language barrier or a technical issue may feel frustrated by an automated response that fails to address their specific concerns. While AI can certainly enhance the efficiency of customer support, Duolingo must be careful not to sacrifice the personal connection that many users value in their interactions with the company.
Lastly, there are concerns about the long-term implications of relying on AI to replace human workers across industries. While AI is undoubtedly capable of performing many tasks with efficiency and precision, there remains a risk that an over-reliance on automation could erode the human elements that make services like Duolingo unique. The role of human expertise in education, customer service, and content creation is difficult to replicate, and as Duolingo shifts to AI, it must ensure that it does not lose sight of the value that human workers bring to the table.
Conclusion
The shift toward AI at Duolingo will undoubtedly bring significant benefits in terms of operational efficiency and user experience, particularly in areas such as personalized learning and customer support. However, the move also raises complex questions about job displacement, ethical considerations, and the potential loss of the human element that has been integral to the company’s success. As Duolingo continues to embrace AI, it must balance the advantages of automation with the need for fairness, inclusivity, and human oversight. For employees, the company must consider offering reskilling opportunities to ensure that the transition to AI does not leave workers behind. For users, the challenge will be to ensure that the human touch is not lost in the pursuit of efficiency and scalability. Ultimately, Duolingo’s success in navigating these challenges will determine how AI can be integrated into education in a way that benefits both the workforce and the end user.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Duolingo’s decision to replace human contract workers with Artificial Intelligence (AI) marks a significant turning point in the company’s strategy and reflects broader trends in the tech industry towards automation and the use of AI to optimize operations. While the transition promises several advantages—chiefly in terms of operational efficiency, cost reduction, and scalability—it also raises important questions about the ethical implications of AI replacing human labor, the potential loss of the human touch in service delivery, and the future of work in an increasingly automated world.
In the short term, Duolingo stands to benefit from reduced operational costs and increased efficiency. AI can handle tasks such as content moderation, customer support, and language course development at a scale and speed that human workers cannot match. The shift to AI also allows Duolingo to provide users with a more personalized and dynamic learning experience, as machine learning models can adapt lessons and feedback based on individual performance. Furthermore, AI systems can operate continuously, offering a seamless, always-available user experience, something that is particularly important for a global platform like Duolingo, which operates across various time zones and markets.
However, the transition comes with a set of challenges, especially in terms of employee displacement. Contract workers who have contributed to Duolingo’s success may face job losses or the need to pivot their skills to more technical roles. While AI can handle many routine tasks, it is still far from capable of replacing the nuanced judgment, cultural sensitivity, and creativity that human workers bring to the table. The loss of these skills could negatively impact the platform’s ability to handle complex user issues, maintain cultural relevance, and preserve the quality of content. As such, Duolingo must carefully manage this transition, offering retraining programs or other forms of support to its displaced workers and ensuring that it retains the human insight necessary for delivering a high-quality learning experience.
Looking ahead, Duolingo’s integration of AI is likely to play a critical role in shaping the future of language learning and the broader education technology landscape. The potential for AI to expand the reach of language education is enormous, as the technology can rapidly scale and provide personalized instruction to millions of users worldwide. Moreover, AI’s ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data could pave the way for more sophisticated and effective learning tools, from adaptive language models to advanced conversational practice. As Duolingo continues to refine its AI systems, the platform will likely see even more advanced features, such as the ability to offer real-time translations or simulate lifelike conversations in various languages. These advancements could make Duolingo an even more invaluable tool for language learners, further solidifying its position as a leader in the edtech sector.
However, Duolingo’s future success will depend on its ability to strike a balance between AI’s efficiency and the indispensable value of human expertise. As the platform evolves, it will need to ensure that its use of AI does not compromise the quality of the learning experience or alienate its user base. Ethical considerations, particularly regarding the fairness of AI systems and their potential biases, must be at the forefront of the company’s development efforts. Regular audits and a commitment to inclusivity will be essential to ensure that the AI models reflect diverse linguistic and cultural perspectives.
In addition, Duolingo must be transparent with its users about the role of AI in its operations, ensuring that they are aware of both the benefits and limitations of the technology. Clear communication about the ways in which AI will enhance their learning experience, as well as its current limitations, will help build trust and ensure that users feel comfortable with the changes. It will also be important for Duolingo to maintain human oversight in areas where AI is not yet capable of providing the level of empathy, cultural awareness, or creativity needed, particularly in customer service and content moderation.
The role of AI in education is likely to continue expanding in the coming years, and Duolingo’s decision to replace human workers with AI will serve as a case study for other edtech companies considering similar transitions. As AI becomes more embedded in educational tools, it could have profound implications not only for language learning but for the broader landscape of online education. Duolingo’s success—or failure—in integrating AI will offer valuable lessons on the ethical use of automation, the balance between human and machine contributions, and the importance of preserving the human elements that define educational experiences.
Looking forward, the future of Duolingo will likely be shaped by its ability to adapt and evolve in response to both technological advancements and societal expectations. The company must continue to refine its AI systems, address potential ethical concerns, and find innovative ways to leverage AI while maintaining the unique elements that have made Duolingo such a successful and beloved platform. At the same time, Duolingo must prioritize the welfare of its workers, both current and future, ensuring that its transition to AI-driven operations does not come at the expense of the people who have helped build the company into what it is today.
In conclusion, Duolingo’s move towards AI represents a bold step forward in the quest to create more scalable, efficient, and personalized language learning experiences. While the transition to AI-powered systems offers significant benefits, it also brings with it challenges related to job displacement, ethical considerations, and the potential loss of the human element that has been integral to the company’s success. As Duolingo navigates this shift, it must remain committed to maintaining a balance between technology and humanity, ensuring that the future of language learning is both innovative and inclusive. By doing so, Duolingo can continue to lead the charge in reshaping how people around the world learn languages, while also setting a precedent for how AI can be integrated into education in a responsible and sustainable manner.
References
- How AI is Changing the Future of Education – https://www.edtechmagazine.com
- The Rise of AI in the Workforce – https://www.forbes.com
- Duolingo's Shift to AI: Why It Matters – https://www.theverge.com
- The Impact of AI on Job Displacement – https://www.bbc.com
- AI-Powered Education: A New Era – https://www.educationtechnology.com
- How Automation is Shaping the Future of Work – https://www.cnbc.com
- AI in EdTech: How Artificial Intelligence is Revolutionizing Learning – https://www.techcrunch.com
- Understanding AI and Its Role in Modern Education – https://www.edutopia.org
- AI and Automation: The Future of Human Work – https://www.washingtonpost.com
- The Ethical Implications of AI Replacing Human Workers – https://www.hbr.org
